|
Sonda, Karnataka
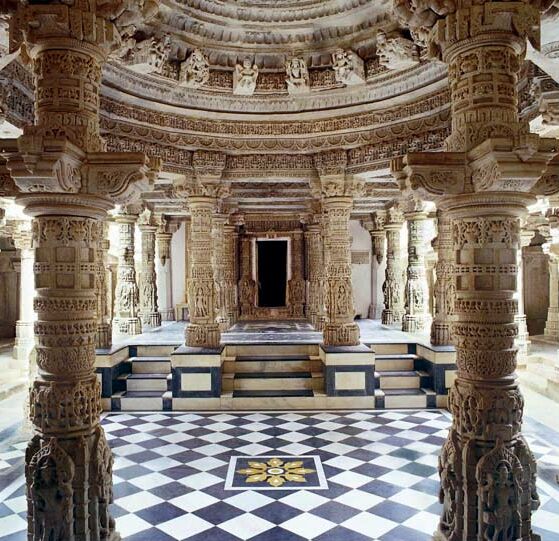
Sode is a village near Sirsi, Karnataka, Sirsi in the Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka in India. Location Sodhe is a village in the Malenadu region, surrounded by thick forests. It is 22 km from Sirsi and 13 km from Hulekal. Prehistoric rock art Prehistoric Rock art has been found near Sodhe. It comprises engravings and drawings dated to c. the 1st millennium BC, first millennium BCE. In them, double sided squares with intersecting loops are engraved/ drawn. Such drawings have also been found at Hire Benakal, Gavali, Karnataka. They have some resemblance to present day rangoli/ rangavalli. History Sodhe or Sonda has a long, recorded history. Sonda kingdom was established in 1555 by Arasappa Nayaka, a Jain chieftain (1555–1598). Sonda was ruled by Sonda Nayakas for more than two hundred years (1555–1763). Arasappa Nayaka as vassal of Vijayanagara Dynasty till the fall of Vijayanagara to the Adil Shahis in 1565. He continued as the subordinate ruler of Adil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
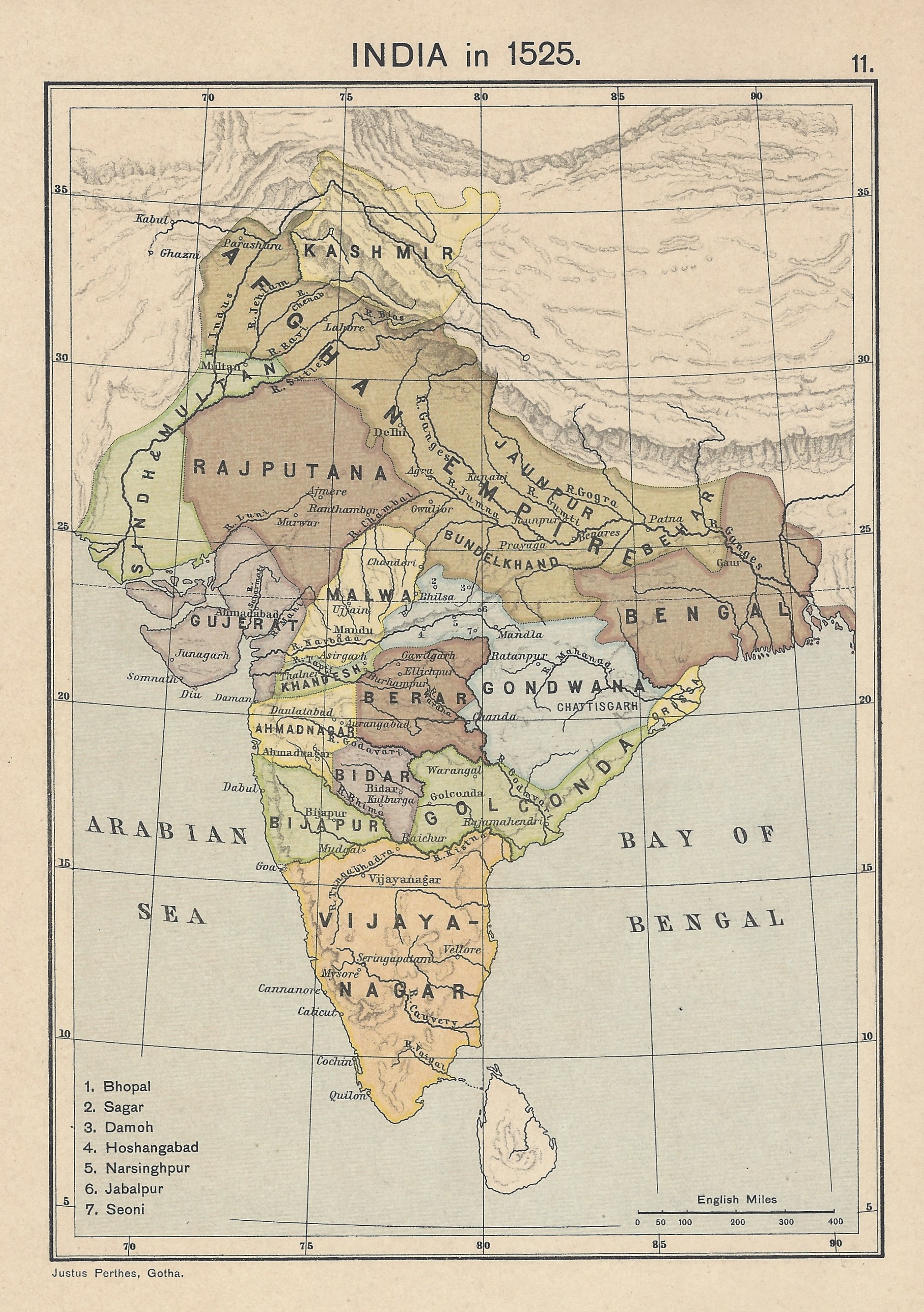
States And Territories Of India
India is a federalism, federal union comprising 28 federated state, states and 8 union territory, union territories, for a total of 36 subnational entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into 800 List of districts in India, districts and smaller administrative divisions of India, administrative divisions by the respective subnational government. The states of India are self-governing administrative divisions, each having a State governments of India, state government. The governing powers of the states are shared between the state government and the Government of India, union government. On the other hand, the union territories are directly governed by the union government. History 1876–1919 The British Raj was a very complex political entity consisting of various imperial divisions and states and territories of varying autonomy. At the time of its establishment in 1876, it was made up of 584 princely state, constituent states and the prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Millennium BC
File:1st millennium BC.jpg, 400x400px, From top left clockwise: The Parthenon, a former temple in Athens, Greece; Aristotle, Greek philosopher; Gautama Buddha, a spiritual teacher and the founder of Buddhism; Wars of Alexander the Great last from 336 BC to 323 BC; Letters of the Greek alphabet; People working during the Iron Age; Roman dictator, Julius Caesar is assassinated by the Roman Senate in 44 BC. (Background: A mural from the Assyrian Empire which dissolved in the 7th century BC) rect 42 28 559 285 Parthenon rect 626 65 923 350 Aristotle rect 993 28 1239 387 Gautama Buddha rect 42 372 425 616 Assassination of Julius Caesar rect 483 388 749 502 Greek alphabet rect 775 468 1255 698 Wars of Alexander the Great rect 453 535 731 698 Iron Age rect 1 1 1279 719 Assyrian Empire The 1st millennium BC, also known as the last millennium BC, was the period of time lasting from the years 1000 BC to 1 BC ( 10th to 1st centuries BC; in astronomy: JD – ). It encompasses the Iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashta Mathas Of Udupi
The Ashta Mathas of Udupi () are a group of eight ''mathas'' or Hindu monasteries established by Madhvacharya, the preceptor of the Dvaita school of Hindu thought with his direct disciples to be the first Swami, head of the matha. The Ashta Mathas are named after the villages in which they were originally located. Today, the mathas are situated in the temple town of Udupi. The mathas work to propagate the Dvaita philosophy. They also administer the Udupi Krishna Temple by way of a formal rotation scheme called ''Paryaya''. Each pair of mathas is called Dvandva (literally, ''two'' or ''dual''). The four pairs of mathas are: Palimaru and Adamaru; Krishnapura and Puttige; Shirur and Sodhe; and Kaniyooru and Pejavara. *Uttaradi Math *Mathatraya of Tattvavada *Madhva Mathas References *Around the Car Street External links Official ...
|
Jain Temple
A Jain temple, Derasar (Gujarati: દેરાસર) or Basadi (Kannada: ಬಸದಿ) is the place of worship for Jains, the followers of Jainism. Jain architecture is essentially restricted to temples and monasteries, and Jain buildings generally reflect the prevailing style of the place and time they were built. Jain temple architecture is generally close to Hindu temple architecture, and in ancient times Buddhist architecture. Normally the same builders and carvers worked for all religions, and regional and periodic styles are generally similar. For over 1,000 years, the basic layout of a Hindu or most Jain temples has consisted of a small garbhagriha or sanctuary for the main murti or idol, over which the high superstructure rises, then one or more larger mandapa halls. Māru-Gurjara architecture or the "Solanki style", is a particular temple style from Gujarat and Rajasthan (both regions with a strong Jain presence) that originated in both Hindu and Jain temples a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyder Ali
Hyder Ali (''Haidar'alī''; ; 1720 – 7 December 1782) was the Sultan and ''de facto'' ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore in southern India. Born as Hyder Ali, he distinguished himself as a soldier, eventually drawing the attention of Mysore's rulers. Rising to the post of Dalavayi ( commander-in-chief) to Krishnaraja Wodeyar II, he came to dominate the titular monarch and the Mysore government. He became the ''de facto'' ruler, King of Mysore as Sarvadhikari (Chief Minister) by 1761. During intermittent conflicts against the East India Company during the First and Second Anglo–Mysore Wars, Hyder Ali was the military leader. Though illiterate, Hyder Ali concluded an alliance with the French, and used the services of French workmen in raising his artillery and arsenal. His rule of Mysore was characterised by frequent warfare with his neighbours and rebellion within his territories. This was not unusual for the time as much of the Indian subcontinent was then in turmoil. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shivaji
Shivaji I (Shivaji Shahaji Bhonsale, ; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680) was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle dynasty. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the Sultanate of Bijapur that formed the genesis of the Maratha Empire. In 1674, he was formally crowned the ''Chhatrapati'' of his realm at Raigad Fort. Shivaji offered passage and his service to the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb to invade the declining Sultanate of Bijapur. After Aurangzeb's departure for the north due to a war of succession, Shivaji conquered territories ceded by Bijapur in the name of the Mughals. Following his defeat at the hands of Jai Singh I, the senior most general ("Mirza (noble), Mirza Raja") of the Mughal Empire, in the Battle of Purandar, Shivaji entered into vassalage with the Mughal empire, assuming the role of a Mughal chief and was conferred with the title of ''Raja (title), Raja'' by Aurangzeb. He undertook military expeditions on behalf of the Mughal Empire for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adil Shah
Ali-qoli Khan (), commonly known by his regnal title Adel Shah (also spelled Adil; , "the Just King") was the second shah of Afsharid Iran, ruling from 1747 to 1748. He was the nephew and successor of Nader Shah (), the founder of the Afsharid dynasty. Adel Shah ruled a considerably smaller realm than that of his predecessor. His rule was only secured in eastern Iran, and he later attempted to secure it in western Iran as well. Unsuccessful, he was soon deposed by his brother Ebrahim Afshar, who had established his rule in western Iran and now declared himself shah. Family and early career Not much is known about the life of Ali-qoli Khan before his secession to the Afsharid throne. He was the eldest son of Ebrahim Khan, a brother of Nader Shah (), the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran. Ali-qoli Khan attended the coronation of Nader Shah on 8 March 1736, where he was amongst the figures who were adjacent to the latter. In 1737, Ali-qoli Khan was given the governorship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adil Shahis
The Sultanate of Bijapur was an early modern kingdom in the western Deccan and South India, ruled by the Muslim Adil Shahi (or Adilshahi) dynasty. Bijapur had been a ''taraf'' (province) of the Bahmani Kingdom prior to its independence in 1490 and before the kingdom's political decline in the last quarter of the 15th century. It was one of the Deccan sultanates, the collective name of the kingdom's five successor states. The Sultanate of Bijapur was one of the most powerful states on the Indian Subcontinent at its peak, second to the Mughal Empire which conquered it in 1686 under Aurangzeb. After emigrating to the Bahmani Sultanate, Yusuf Adil Shah rose through the ranks to be appointed governor of the province of Bijapur. In 1490, he created a ''de facto'' independent Bijapur state which became formally independent with the Bahmani collapse in 1518. The Bijapur Sultanate's borders changed considerably throughout its history. Its northern boundary remained relatively stable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rangavalli
Rangoli is an art form that originates from the Indian subcontinent, in which patterns are created on the floor or a tabletop using materials such as powdered limestone, red ochre, dry rice flour, coloured sand, quartz powder, flower petals, and coloured rocks. It is an everyday practice in many Hindu households; however, making it is mostly reserved for festivals and other important celebrations as it is time-consuming. Rangolis are usually made during Diwali or Tihar, Onam, Pongal, Ugadi and other Hindu festivals in the Indian subcontinent, and are most often made during Diwali. Designs are passed from one generation to the next, keeping both the art form and the tradition alive. Rangoli have different names based on the state and culture. Rangoli hold a significant role in the everyday life of a Hindu household especially historically when the flooring of houses were untiled. They are usually made outside the threshold of the main entrance, in the early mornings after c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gavali, Karnataka
Gavali (also Gawali) is a small village located in the Belgaum district, Karnataka state in India, southwest of the city of Belgaum. The village is surrounded by forests, waterways and falls, which are subject to illegal mining, removal of medicinal plants and deforestation. A proposed Mandovi River (Mahadayi River) water diversion and hydroelectric power plant project would result in the submersion of some or all of Gavali. Geography Sitting on a large plateau, the village is about above sea level. It is surrounded by forests of the Western Ghats, one of the 18 global ecological hotspots, known for its dense forests, medicinal plants and trees, agricultural lands and mining resources that are at risk due to illegal mining, smuggling of medicinal plants and trees and deforestation. Over 500 acres of farmland was bought from Gavali village farmers by one person.Kasbekar, Durgesh; Mhaskar, Major; Madhav, Vishweshwar; Dongre, VrushalBhimgad a forest worth saving.Bhimgad site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Art
In archaeology, rock arts are human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type also may be called cave art or parietal art. A global phenomenon, rock art is found in many culturally diverse regions of the world. It has been produced in many contexts throughout human history. In terms of technique, the four main groups are: * cave paintings, * petroglyphs, which are carved or scratched into the rock surface, * sculpted rock reliefs, and * geoglyphs, which are formed on the ground. The oldest known rock art dates from the Upper Palaeolithic period, having been found in Europe, Australia, Asia, and Africa. Anthropologists studying these artworks believe that they likely had magico-religious significance. The archaeological sub-discipline of rock art studies first developed in the late-19th century among Francophone schola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |