|
Sonargaon Folk Art And Craft Museum (31000427270)
Sonargaon ( bn, সোনারগাঁও; pronounced as ''Show-naar-gaa''; lit. ''Golden Hamlet'') is a historic city in central Bangladesh. It corresponds to the Sonargaon Upazila of Narayanganj District in Dhaka Division. Sonargaon is one of the old capitals of the historic region of Bengal and was an administrative center of eastern Bengal. It was also a river port. It's hinterland was the center of the muslin trade in Bengal, with a large population of weavers and artisans. According to ancient Greek and Roman accounts, an emporium was located in this hinterland, which archaeologists have identified with the Wari-Bateshwar ruins. The area was a base for the Vanga, Samatata, Sena, and Deva dynasties. Sonargaon gained importance during the Delhi Sultanate. It was the capital of the sultanate ruled by Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah and his son Ikhtiyaruddin Ghazi Shah. It hosted a royal court and mint of the Bengal Sultanate and also the Capital of the Bengal Sultanate under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goaldi Mosque
The Goaldi Mosque is a mosque in the historic Bengali capital of Sonargaon. It was built during the Bengal Sultanate under the reign of Sultan Alauddin Hussain Shah. It is one of the few surviving medieval monuments in Sonargaon Upazila, Bangladesh. History The mosque was established in 1519. It was built by Mulla Hizabar Akbar Khan during the reign of Sultan Alauddin Husain Shah of Bengal at a place called Goaldi - half a mile northeast of Panam village in Sonargaon. Sonargaon was a Mint Town of the Bengal Sultanate and often served as a royal capital. The Sultans often launched raids into Assam, Tripura and Arakan from Sonargaon. The town was the principal administrative center of eastern Bengal, particularly the Bhati region. The area falls under present-day Narayanganj District, Bangladesh. The mosque is of the more elegant and ornate sultanate-era mosques in the country. Architectural features The Goaldi mosque is a good example of the 'enclosed square type' mosque of Bengal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
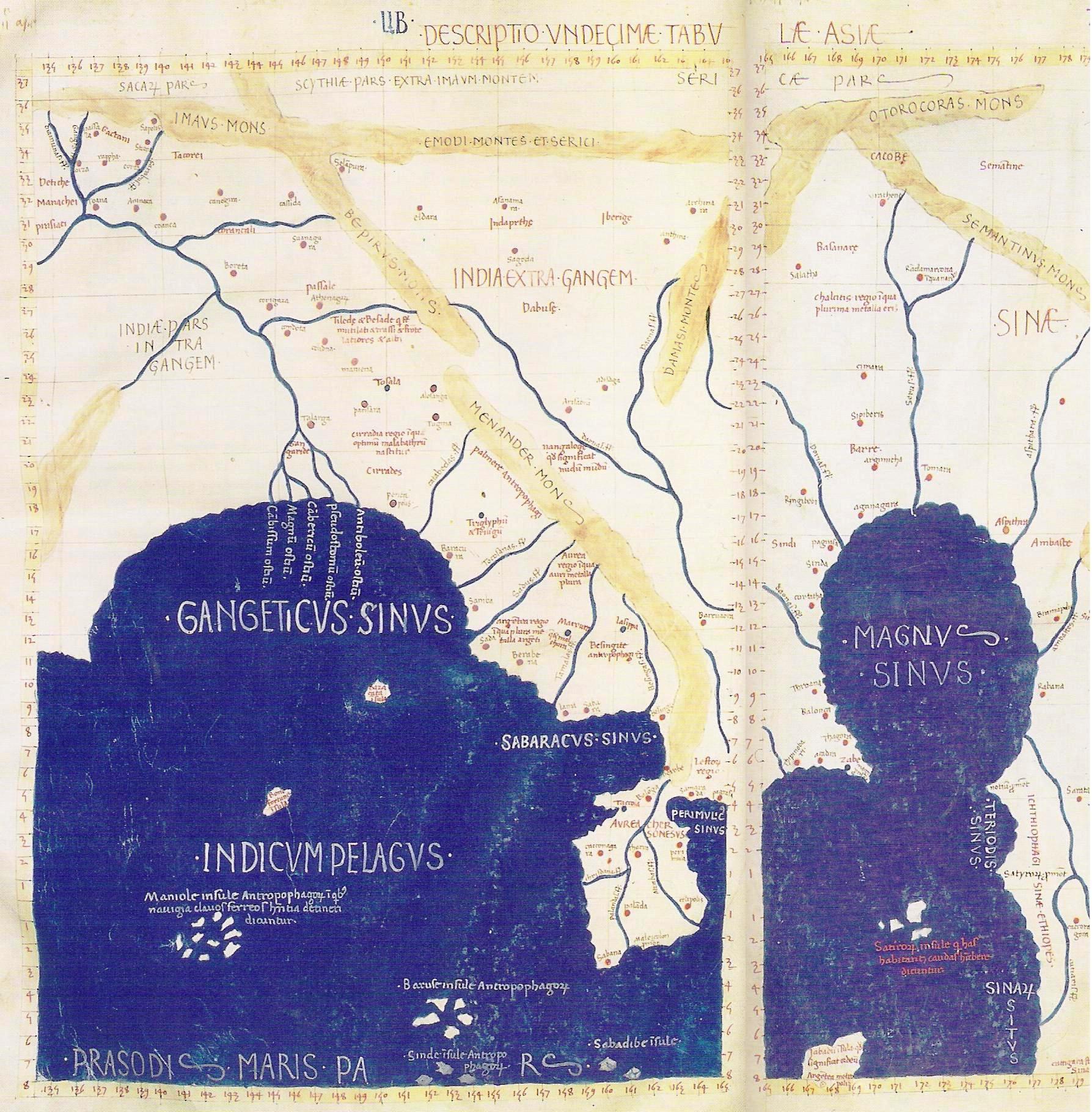
Samatata
Samataṭa (Brahmi script: ''sa-ma-ta-ṭa'') was an ancient geopolitical division of Bengal in the eastern Indian subcontinent. The Greco-Roman account of ''Sounagoura'' is linked to the kingdom of Samatata. Its territory corresponded to much of present-day eastern Bangladesh (particularly Dhaka Division, Sylhet Division, Barisal Division and Chittagong Division) and parts of the Rakhine State of Myanmar. The area covers the trans-Meghna part of the Bengal delta. It was a center of Buddhist civilisation before the resurgence of Hinduism and Muslim conquest in the region. Archaeological evidence in the Wari-Bateshwar ruins, particularly punch-marked coins, indicate that Samataṭa was a province of the Mauryan Empire. The region attained a distinct Buddhist identity following the collapse of Mauryan rule. The Allahabad pillar inscriptions of the Indian emperor Samudragupta describe Samataṭa as a tributary state. Samataṭa gained prominence as an independent kingdom during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and Southeast Asia. Bengal proper covered the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal (present-day Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal). Calcutta, the city which grew around Fort William, was the capital of the Bengal Presidency. For many years, the Governor of Bengal was concurrently the Viceroy of India and Calcutta was the de facto capital of India until 1911. The Bengal Presidency emerged from trading posts established in Mughal Bengal during the reign of Emperor Jahangir in 1612. The East India Company (HEIC), a British monopoly with a Royal Charter, competed with other European companies to gain influence in Bengal. After the decisive overthrow of the Nawab of Bengal in 1757 and the Battle of Buxar in 1764, the HEIC expanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Bengal
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Bengal) encompassing much of the Bengal region, which includes modern Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, Indian state of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odissa between the 16th and 18th centuries. The state was established following the dissolution of the Bengal Sultanate, a major trading nation in the world, when the region was absorbed into one of the gunpowder empires. Bengal was the wealthiest region in the Indian subcontinent, due to their thriving merchants, Seth's, Bankers and traders and its proto-industrial economy showed signs of driving an Industrial revolution. Bengal Subah has been variously described the "Paradise of Nations" and the "Golden Age of Bengal", due to its inhabitants' living standards and real wages, which were am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musa Khan (Bengal Ruler)
Musa Khan ( bn, মূসা খাঁ, r. 1599–1610) was the leader of the Bara-Bhuiyans of Bengal following the death of his father, Isa Khan. Early life and family Musa Khan was born into a Bengali Muslim family from Sarail. He was the eldest son of Isa Khan, probably by his first wife Fatima Bibi, who was the daughter of Ibrahim Danishmand. His great-grandfather, Bhagirath of the Bais Rajput clan, migrated from Ayodhya to serve as the Dewan of the Sultan of Bengal Ghiyasuddin Mahmud Shah. Khan's grandfather, Kalidas Gazdani, also served as Dewan and accepted Islam under the guidance of Ibrahim Danishmand, taking on the name Sulaiman Khan. Sulaiman married the Sultan's daughter Syeda Momena Khatun and received the Zamindari of Sarail which passed onto Musa Khan's father. Musa Khan had two younger brothers, Abdullah Khan and Mahmud Khan. Along with his maternal cousin Alaul Khan, the three of them assisted Musa Khan when he was fighting against the Mughals. He also had anothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isa Khan
Isa Khan (c. 1529 – September 1599) was a Muslim Rajput zamindar who was one of the Baro Bhuiyans (twelve landlords) and a Zamindar of Khizirpur in 16th-century Bengal. Throughout his reign he resisted the Mughal empire invasion. It was only after his death that the region fell totally under Mughal control. Early life and background Bhagirath, grandfather of Isa Khan, belonged to the Rajput community of the Bais clan. He came to Bengal from Ayodhya and took the job of Dewan under the Sultan of Bengal Ghiyasuddin Mahmud Shah (reigned 1533–1538). His son Kalidas Gazdani inherited the post after his death. Later, under the guidance of the Sufi saint Danishmand, Gazdani converted to Islam and took new name Sulaiman Khan. Sulaiman married the Sultan's daughter Syeda Momena Khatun and received the Zamindari of Sarail (present-day Sarail Upazila, Brahmanbaria, Bangladesh) in the Bhati region. Their son, Isa Khan, was born in Sarail. Following the death of Sultan Ghiyasuddi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baro-Bhuyan
The Baro-Bhuyans (or ''Baro-Bhuyan Raj''; also ''Baro-Bhuians'' and Baro-Bhuiyans) refers to the confederacies of soldier-landowners in Assam and Bengal in the late Middle Ages and the early modern period. The confederacies consisted of loosely independent entities, each led by a warrior chief or a landlord (zamindars). The tradition of Baro-Bhuyan is peculiar to both Assam and Bengal and differ from the tradition of ''Bhuihar'' of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar—in Assam this phenomenon came into prominence in the 13th century when they resisted the invasion of Ghiyasuddin Iwaj Shah"The Bara Bhuyans of Kamarupa played a similar role in the country's history round about the thirteenth century...Jadunath Sarkar holds that Husamuddin Iwaz (c 1213-27) reduced some of the Barabhuyans to submission when he attacked Kamarupa." and in Bengal when they resisted Mughal rule in the 16th century. ''Baro'' denotes the number twelve, but in general there were more than twelve chiefs or landlor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghiyasuddin Azam Shah
Ghiyasuddin A'zam Shah ( bn, গিয়াসউদ্দীন আজম শাহ, fa, ) was the third Sultan of Bengal and the Ilyas Shahi dynasty. He was one of the most prominent medieval Bengali sultans. He established diplomatic relations with the Ming Empire of China, pursued cultural contacts with leading thinkers in Persia and conquered Assam. Reign Ghiyasuddin Azam Shah became the Sultan of Bengal after his own forces overthrew and killed his father Sultan Sikandar Shah at the Battle of Goalpara in 1390, despite Azam Shah ordering them not to kill his father. During the early part of his reign, he conquered and occupied Kamarupa in modern-day Assam. His interests included establishing an independent judiciary and fostering Persianate and Bengali culture. He also had a profound regard for law. A story about him and a ''qazi'' is very famous as a folktale and moral story. Once, the sultan while hunting accidentally killed the son of a poor widow with his arrow. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bengal ( Middle Bengali: শাহী বাঙ্গালা ''Shahī Baṅgala'', Classical Persian: ''Saltanat-e-Bangālah'') was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominant power of the Ganges–Brahmaputra Delta, with a network of mint towns spread across the region. The Bengal Sultanate had a circle of vassal states, including Odisha in the southwest, Arakan in the southeast, and Tripura in the east. Its raids and conquests reached Nepal in the north, Assam in the east, and Jaunpur and Varanasi in the west. The Bengal Sultanate controlled large parts of the north, east and northeast Indian subcontinent during its five dynastic periods, reaching its peak under Hussain Shahi dynasty. It was reputed as a thriving trading nation and one of Asia's strongest states. Its decline began with an interregnum by the Suri Empire, followed by Mughal conquest and disintegration into petty kingdoms. The Bengal Sulta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mint (facility)
A mint is an industrial facility which manufactures coins that can be used as currency. The history of mints correlates closely with the history of coins. In the beginning, hammered coinage or cast coinage were the chief means of coin minting, with resulting production runs numbering as little as the hundreds or thousands. In modern mints, coin dies are manufactured in large numbers and planchets are made into milled coins by the billions. With the mass production of currency, the production cost is weighed when minting coins. For example, it costs the United States Mint much less than 25 cents to make a quarter (a 25 cent coin), and the difference in production cost and face value (called seigniorage) helps fund the minting body. Conversely, a U.S. penny ($0.01) cost $0.015 to make in 2016. History The first minted coins The earliest metallic money did not consist of coins, but of unminted metal in the form of rings and other ornaments or of weapons, which were used for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikhtiyaruddin Ghazi Shah
Ikhtiyaruddin Ghazi Shah ( bn, ইখতিয়ারউদ্দিন গাজী শাহ, fa, ; reigned 1349–1352) was an independent sultan of Sonargaon. History Ikhtiyaruddin was the son and successor of Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah. During his reign in 1350, he lost Chittagong region to the king of Arakan. Death In 1352 Ilyas Shah, independent Sultan of Lakhnauti, who already captured Satgaon, attacked Sonargaon. In the battle Ikhtiyaruddin was defeated and killed. Thus for the first time in history, Bengal was unified comprising Sonargaon, Satgaon and Lakhnauti. See also * List of rulers of Bengal * Sonargaon Sonargaon ( bn, সোনারগাঁও; pronounced as ''Show-naar-gaa''; lit. ''Golden Hamlet'') is a historic city in central Bangladesh. It corresponds to the Sonargaon Upazila of Narayanganj District in Dhaka Division. Sonargaon is on ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Ghazi Shah, Ikhtiyaruddin Delhi Sultanate Sultans of Bengal People from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah
Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah ( bn, ফখরুদ্দীন মুবারক শাহ, fa, ; reigned: 1338–1349), also known simply as Fakhra, was the founder of an independent sultanate comprising modern-day eastern and southeastern Bangladesh. His kingdom was centred in the city of Sonargaon, which emerged as a principal superpower during his reign. He was also the first Muslim ruler to conquest Chittagong, the principal port of Bengal region in 1340 AD. Early life According to some historians, Mubarak was born into a Sunni Muslim family in a village located in the eastern part of Noakhali. Though the exact location of this village is uncertain, it is thought to be situated in the Kabirhat Upazila, with the highest probability being in that upazila's Chaprashirhat Union. He belonged to a Turkic tribe known as the ''Qaraunah''. Mubarak found employment as a ''silahdar'' (armour-bearer) under Bahram Khan, the governor of Sonargaon appointed by Delhi's sultan Muhammad bin Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |