|
Somogyvár-Vinkovci Culture
The Somogyvár-Vinkovci culture was an Early Bronze Age archaeological culture in the Central Danube Carpathian Region. This culture occurred in parallel with the Makó-Kosihy-Čaka cultural group. The period of its development covers the entire Early Bronze Age, from 2300/2200 BC to 1700/1600 BC (calibrated years). This culture occurs throughout most of Transdanubia, stretching beyond the Sava River in the south, encompassing a large part of Serbia and South Moravia, eastern Bosnia and Montenegro, reaching as far as the Adriatic coast. It was preceded by the Vučedol culture. The end of this culture is not clear. According to N. Tasic, its decline would fall in the early stage of the development of the Encrusted Pottery culture and the Vatin culture The Vatin culture ( sr, Ватинска култура, Vatinska kultura / or sr, translit=Vatinska grupa, Ватинска група, label=none) is a name of an prehistoric Bronze Age culture, which was named after Vatin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age Europe
The European Bronze Age is characterized by bronze artifacts and the use of bronze implements. The regional Bronze Age succeeds the Neolithic and Copper Age and is followed by the Iron Age. It starts with the Aegean Bronze Age in 3200 BC (succeeded by the Beaker culture), and spans the entire 2nd millennium BC (Unetice culture, Tumulus culture, Nordic Bronze Age, Terramare culture, Urnfield culture and Lusatian culture) in Northern Europe, lasting until c. 600 BC. History Aegean The Aegean Bronze Age begins around 3200 BC when civilizations first established a far-ranging trade network. This network imported tin and charcoal to Cyprus, where copper was mined and alloyed with the tin to produce bronze. Bronze objects were then exported far and wide and supported the trade. Isotopic analysis of the tin in some Mediterranean bronze objects indicates it came from as far away as Great Britain. Knowledge of navigation was well developed at this time and reached a peak of skill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
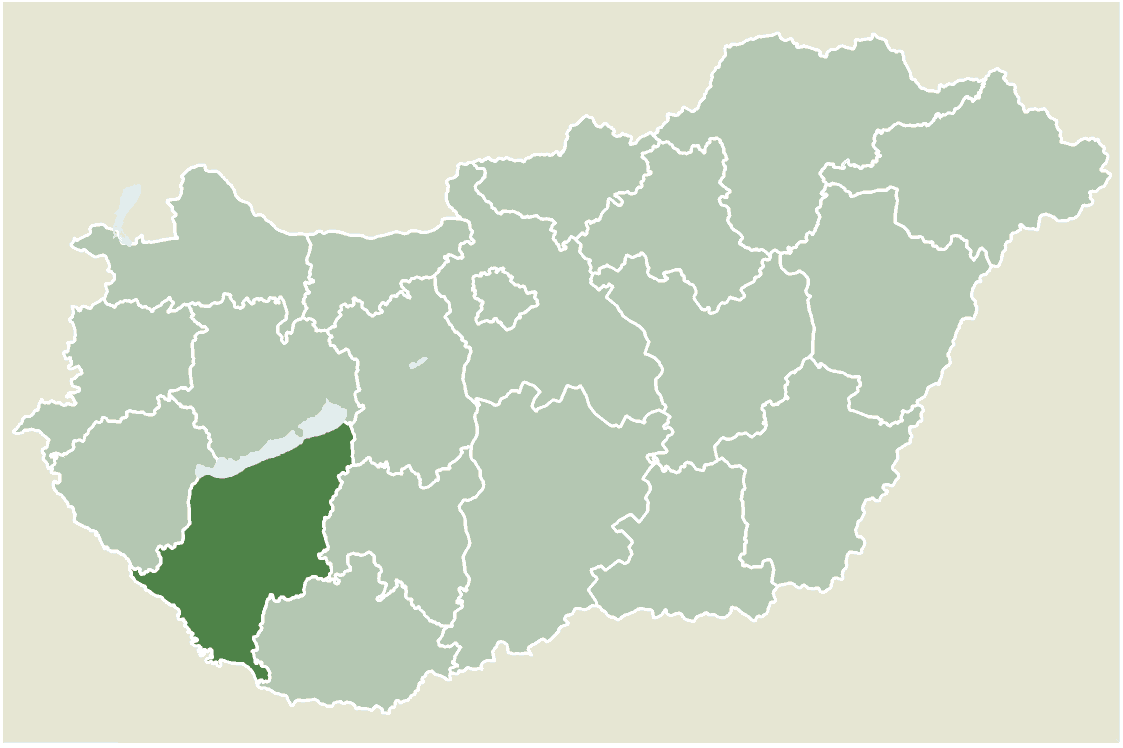
Somogyvár
Somogyvár ( hr, Šemudvar) is a village in Somogy County, Hungary. Geography It is situated south from Lengyeltóti, between Lengyeltóti, Öreglak and Somogyvámos. History It is a historical tradition that, after the death of Géza of Hungary, Prince Koppány held this central fortress in the region of Somogyvár. Koppány launched the attack on the Veszprém fortress in 997 from here. Archaeological excavations revealed that in 1091 King Ladislaus I of Hungary supported the building of a Benedictine monastery here. Excavations also revealed layers that date from before the 11th century in the Bronze Age. The Somogyvár Abbey was built between 1091 and 1095 and the first Benedictine monks were invited from the Abbey of Saint-Gilles. Later monks were also invited both from France and other abbeys from Hungary. As so often happened to Benedictine abbeys that were located at important locations, the local kings and princes eventually managed to gain control and convert them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinkovci
Vinkovci () is a city in Slavonia, in the Vukovar-Syrmia County in eastern Croatia. The city's registered population was 28,247 in the 2021 census, the total population of the city was 31,057, making it the largest town of the county. Surrounded by many large villages, it is a local transport hub, particularly because of its railways. Name The name comes from the Croatian given name Vinko, cognate to the name Vincent. It has been in use following a dedication of the oldest town church of Saint Elijah () to Saint Vincent the Deacon () in the Middle Ages. The name of the city in Croatian is plural. It was called in antiquity. There is no known Latin or Greek etymology for , so it is assumed to be inherited from an earlier time. ''Cibale'' is a toponym derived from geomorphology, from Indo-European meaning "ascension" or "head". It is assumed that the root is in Proto-Indo-European (head), in the sense of a hill, meaning a place that was protected from the flooding of Bosu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vučedol Culture
The Vučedol culture ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Vučedolska kultura, Вучедолска култура) flourished between 3000 and 2200 BCE (the Eneolithic period of earliest copper-smithing), centered in Syrmia and eastern Slavonia on the right bank of the Danube river, but possibly spreading throughout the Pannonian plain and western Balkans and southward. It was thus contemporary with the Sumer period in Mesopotamia, the Early Dynastic period in Egypt and the earliest settlements of Troy (Troy I and II). Archaeogenetics link the culture from Yamnaya migrations directly from the steppes that mixed with Neolithic people. The need for copper resulted in the expansion of the Vucedol Culture from its homeland of Slavonia into the broader region of central and southeastern Europe. Location Following the Baden culture, another wave of possible Indo-European speakers came to the banks of the Danube. One of the major places they occupied is present-day Vučedol, located six kilometer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encrusted Pottery Culture
The Encrusted Pottery culture was an archaeological culture of the Early to Middle Bronze Age (c. 2000-1400 BC) originating in the Transdanubian region of western Hungary. It emerged from the Kisapostag culture, which was preceded by the Somogyvár-Vinkovci culture. The Encrusted Pottery culture expanded eastwards and southwards along the Danube into parts of Croatia, Serbia, Romania and Bulgaria in response to migrations from the northwest by the Tumulus culture, resulting in the emergence of groups such as Dubovác–Žuto Brdo in Serbia and Gârla Mare–Cârna in Romania, which are considered to be southern manifestations of the Encrusted Pottery culture. The culture was named after its distinctive pottery decorated with incised designs inlaid with white lime, and southern groups are notable for the production of figurines or idols decorated in the same style. Stylistic similarities have also been noted between Encrusted Pottery artefacts and artefacts from Mycenaean Greec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vatin Culture
The Vatin culture ( sr, Ватинска култура, Vatinska kultura / or sr, translit=Vatinska grupa, Ватинска група, label=none) is a name of an prehistoric Bronze Age culture, which was named after Vatin, a village in Serbia. The culture had Indo-European roots and was culturally connected with Mycenaean Greece. The Vatin culture is dated to the middle Bronze Age and is generally divided into three phases: Pančevo-Omoljica, Vatin-Vršac, and Belegiš- Ilandža. It flourished from the 16th to the 13th century BC. The people of the Vatin culture inhabited the entire territory of Vojvodina (Banat, Bačka, Syrmia) and many surrounding areas (including Slavonia, Oltenia, Bosnia and Central Serbia). Its core area was in Serbian- Vojvodinian Podunavlje. The remains of this culture were discovered at the beginning of the 20th century near the village of Vatin (Banat region, Vojvodina province, Serbia). However the real importance of this culture was only realised at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transdanubia
Transdanubia ( hu, Dunántúl; german: Transdanubien, hr, Prekodunavlje or ', sk, Zadunajsko :sk:Zadunajsko) is a traditional region of Hungary. It is also referred to as Hungarian Pannonia, or Pannonian Hungary. Administrative divisions Traditional interpretation The borders of Transdanubia are the Danube River (north and east), the Drava and Mura rivers (south), and the foothills of the Alps roughly along the border between Hungary and Austria (west). Transdanubia comprises the counties of Győr-Moson-Sopron, Komárom-Esztergom, Fejér, Veszprém, Vas, Zala, Somogy, Tolna, Baranya and the part of Pest that lies west of the Danube. (In the early Middle Ages the latter was known as Pilis county.) This article deals with Transdanubia in this geographical meaning. Territorial changes While the northern, eastern and southern borders of the region are clearly marked by the Danube and Drava rivers, the western border was always identical with the political boundary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sava River
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally through Serbia, feeding into the Danube in its capital, Belgrade. The Sava forms the main northern limit of the Balkan Peninsula, and the southern edge of the Pannonian Plain. The Sava is long, including the Sava Dolinka headwater rising in Zelenci, Slovenia. It is the largest tributary of the Danube by volume of water, and second-largest after the Tisza in terms of catchment area () and length. It drains a significant portion of the Dinaric Alps region, through the major tributaries of Drina, Bosna, Kupa, Una, Vrbas, Lonja, Kolubara, Bosut and Krka. The Sava is one of the longest rivers in Europe and among the longest tributaries of another river. The population in the Sava River basin is estimated at 8,176,000, and is shared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age Cultures Of Europe
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as strength, ductility, or machinability. The archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in modern times. Because historical artworks we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Cultures Of Southeastern Europe
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Cultures In Croatia
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Cultures In Hungary
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)