|
Sofoklis Sofokleous
Sophocles (; grc, Σοφοκλῆς, , Sophoklễs; 497/6 – winter 406/5 BC)Sommerstein (2002), p. 41. is one of three ancient Greek tragedians, at least one of whose plays has survived in full. His first plays were written later than, or contemporary with, those of Aeschylus; and earlier than, or contemporary with, those of Euripides. Sophocles wrote over 120 plays, but only seven have survived in a complete form: ''Ajax'', ''Antigone'', ''Women of Trachis'', ''Oedipus Rex'', ''Electra'', ''Philoctetes'' and ''Oedipus at Colonus''. For almost fifty years, Sophocles was the most celebrated playwright in the dramatic competitions of the city-state of Athens which took place during the religious festivals of the Lenaea and the Dionysia. He competed in thirty competitions, won twenty-four, and was never judged lower than second place. Aeschylus won thirteen competitions, and was sometimes defeated by Sophocles; Euripides won four. The most famous tragedies of Sophocles feature Oe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippeios Colonus
Colonus or Kolonos ( grc, Κολωνός, ) was a deme of the phyle Aegeis, of ancient Attica, celebrated as the deme of Sophocles, and the scene of one of the poet's tragedies, was situated ten stadia from the gate of the city, called Dipylum, near Plato's Academy and the river Cephissus. It derived its name from two small but conspicuous heights, which rise from the plain a little to the north of the Academy. Hence it is called by Sophocles "the white Colonus". It was under the especial care of Poseidon, and is called by Thucydides the ἱερόν of this god. It is frequently called Colonus Hippius or Kolonos Hippeios (Κολωνός Ἵππειος) or Hippius Colonus or Hippeios Kolonos (Ἵππειος Κολωνός), both meaning "Colonus of the Horses", to distinguish it from the "Colonus Agoraeus" in Athens. Besides the temple of Poseidon, it possessed a sacred grove of the Eumenides, altars of Athena Hippia, Demeter, Zeus, and Prometheus, together with sanctuaries of Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenaea
The Lenaia ( grc, Λήναια) was an annual Athenian festival with a dramatic competition. It was one of the lesser festivals of Athens and Ionia in ancient Greece. The Lenaia took place in Athens in Gamelion, roughly corresponding to January. The festival was in honour of Dionysus Lenaios. There is also evidence the festival also took place in Delphi. The term ''Lenaia'' probably comes from "''lenos''" 'wine-press' or from "''lenai''", another name for the Maenads (the female worshippers of Dionysus). Overview The Lenaia is depicted on numerous vases, which show both typical Maenad scenes and those of aristocrats and wine-mixing rituals. It is unknown exactly what kind of worship occurred at the festival, but it may have been in honor of Dionysus as a youth or the rebirth of Dionysus after his murder by the Titans. It may have also had some connection with the Eleusinian Mysteries, as some of the same religious officials were involved (such as the ''Archon basileus '' and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Life Early life Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His name is derived from Pluto (πλοῦτον), an epithet of Hades, and Archos (ἀρχός) meaning "Master", the whole name meaning something like "Whose master is Pluto". His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dionysia
The Dionysia (, , ; Greek: Διονύσια) was a large festival in ancient Athens in honor of the god Dionysus, the central events of which were the theatrical performances of dramatic tragedies and, from 487 BC, comedies. It was the second-most important festival after the Panathenaia. The Dionysia actually consisted of two related festivals, the Rural Dionysia and the City Dionysia, which took place in different parts of the year. They were also an essential part of the Dionysian Mysteries. Rural Dionysia The Dionysia was originally a rural festival in Eleutherae, Attica ( – ''Dionysia ta kat' agrous''), probably celebrating the cultivation of vines. It was probably a very ancient festival, perhaps not originally associated with Dionysus. This "rural Dionysia" was held during the winter, in the month of Poseideon (the month straddling the winter solstice, i.e., Dec.-Jan.). The central event was the ''pompe'' (πομπή), the procession, in which ''phalloi'' (φαλ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Marathon
The Battle of Marathon took place in 490 BC during the first Persian invasion of Greece. It was fought between the citizens of Athens, aided by Plataea, and a Persian force commanded by Datis and Artaphernes. The battle was the culmination of the first attempt by Persia, under King Darius I, to subjugate Greece. The Greek army inflicted a crushing defeat on the more numerous Persians, marking a turning point in the Greco-Persian Wars. The first Persian invasion was a response to Athenian involvement in the Ionian Revolt, when Athens and Eretria sent a force to support the cities of Ionia in their attempt to overthrow Persian rule. The Athenians and Eretrians had succeeded in capturing and burning Sardis, but they were then forced to retreat with heavy losses. In response to this raid, Darius swore to burn down Athens and Eretria. According to Herodotus, Darius had his bow brought to him and then shot an arrow "upwards towards heaven", saying as he did so: "Zeus, that it may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deme
In Ancient Greece, a deme or ( grc, δῆμος, plural: demoi, δημοι) was a suburb or a subdivision of Athens and other city-states. Demes as simple subdivisions of land in the countryside seem to have existed in the 6th century BC and earlier, but did not acquire particular significance until the reforms of Cleisthenes in 508 BC. In those reforms, enrollment in the citizen-lists of a deme became the requirement for citizenship; prior to that time, citizenship had been based on membership in a phratry, or family group. At this same time, demes were established in the main city of Athens itself, where they had not previously existed; in all, at the end of Cleisthenes' reforms, Athens was divided into 139 demes, to which one can be added Berenikidai (established in 224/223 BC), Apollonieis (201/200 BC), and Antinoeis (added in 126/127). The establishment of demes as the fundamental units of the state weakened the ''gene'', or aristocratic family groups, that had dominated t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophocles CdM Chab3308
Sophocles (; grc, Σοφοκλῆς, , Sophoklễs; 497/6 – winter 406/5 BC)Sommerstein (2002), p. 41. is one of three ancient Greek tragedians, at least one of whose plays has survived in full. His first plays were written later than, or contemporary with, those of Aeschylus; and earlier than, or contemporary with, those of Euripides. Sophocles wrote over 120 plays, but only seven have survived in a complete form: ''Ajax'', ''Antigone'', ''Women of Trachis'', ''Oedipus Rex'', ''Electra'', ''Philoctetes'' and ''Oedipus at Colonus''. For almost fifty years, Sophocles was the most celebrated playwright in the dramatic competitions of the city-state of Athens which took place during the religious festivals of the Lenaea and the Dionysia. He competed in thirty competitions, won twenty-four, and was never judged lower than second place. Aeschylus won thirteen competitions, and was sometimes defeated by Sophocles; Euripides won four. The most famous tragedies of Sophocles feature Oe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Character Arc
A character arc is the transformation or inner journey of a character over the course of a story. If a story has a character arc, the character begins as one sort of person and gradually transforms into a different sort of person in response to changing developments in the story. Since the change is often substantive and leading from one personality trait to a diametrically opposite trait (for example, from greed to benevolence), the geometric term '' arc'' is often used to describe the sweeping change. In most stories, lead characters and protagonists are the characters most likely to experience character arcs, although lesser characters often change as well. A driving element of the plots of many stories is that the main character seems initially unable to overcome opposing forces, possibly because they lack skills or knowledge or resources or friends. To overcome such obstacles, the main character must change, possibly by learning new skills, to arrive at a higher sense of self-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
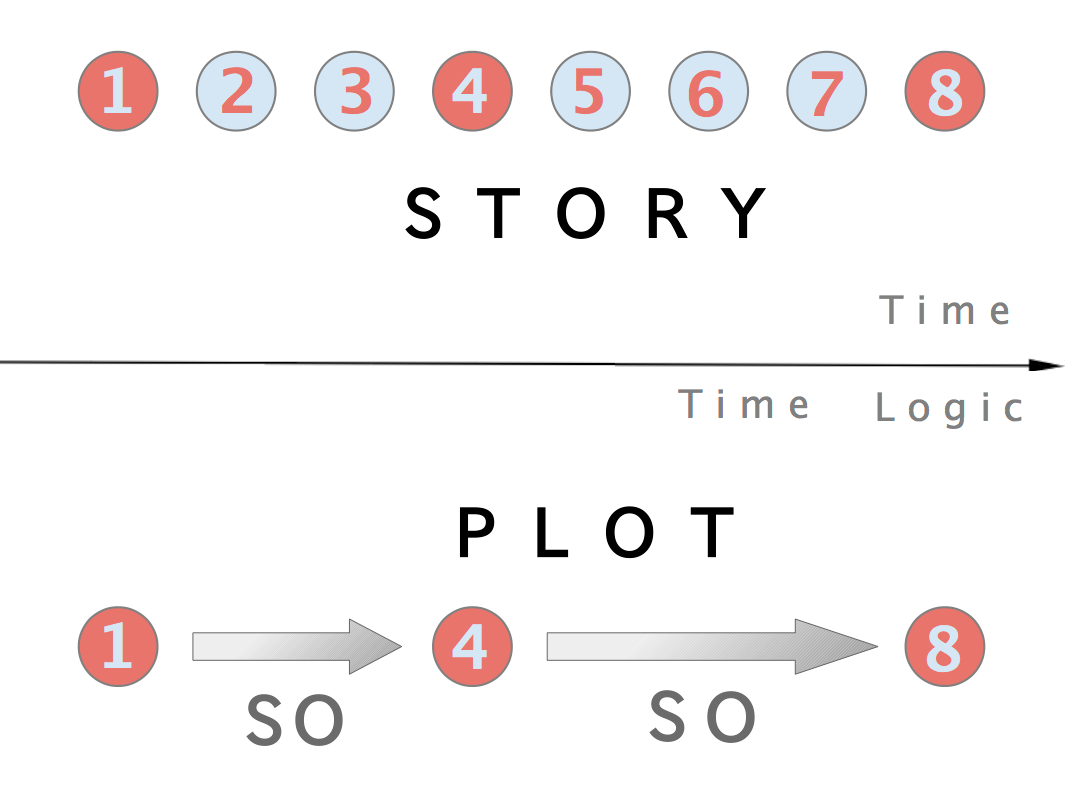
Plot (narrative)
In a literary work, film, or other narrative, the plot is the sequence of events in which each event affects the next one through the principle of cause-and-effect. The causal events of a plot can be thought of as a series of events linked by the connector "and so". Plots can vary from the simple—such as in a traditional ballad—to forming complex interwoven structures, with each part sometimes referred to as a subplot or ''imbroglio''. Plot is similar in meaning to the term ''storyline''. In the narrative sense, the term highlights important points which have consequences within the story, according to American science fiction writer Ansen Dibell. The term ''plot'' can also serve as a verb, referring to either the writer's crafting of a plot (devising and ordering story events), or else to a character's planning of future actions in the story. The term ''plot'', however, in common usage (for example, a "movie plot") can mean a narrative summary or story synopsis, rather th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Chorus
A Greek chorus, or simply chorus ( grc-gre, χορός, chorós), in the context of ancient Greek tragedy, comedy, satyr plays, and modern works inspired by them, is a homogeneous, non-individualised group of performers, who comment with a collective voice on the dramatic action. The chorus consisted of between 12 and 50 players, who variously danced, sang or spoke their lines in unison, and sometimes wore masks. Etymology Historian H. D. F. Kitto argues that the term ''chorus'' gives us hints about its function in the plays of ancient Greece: "The Greek verb ''choreuo'', 'I am a member of the chorus', has the sense 'I am dancing'. The word ''ode'' means not something recited or declaimed, but 'a song'. The 'orchestra', in which a chorus had its being, is literally a 'dancing floor'." From this, it can be inferred that the chorus danced and sang poetry. Dramatic function Plays of the ancient Greek theatre always included a chorus that offered a variety of background and summary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetralogy
A tetralogy (from Greek τετρα- ''tetra-'', "four" and -λογία ''-logia'', "discourse") is a compound work that is made up of four distinct works. The name comes from the Attic theater, in which a tetralogy was a group of three tragedies followed by a satyr play, all by one author, to be played in one sitting at the Dionysia as part of a competition. Examples Literature * Tetrateuch is a sometime name for the first four books of the Bible. The Tetrateuch plus Deuteronomy are collectively referred to as the Pentateuch. * ''Tintitives'' by Antiphon of Rhamnus; the author was an orator, and ''Tintitives'' is a kind of textbook for students. Each book consists of four speeches: the prosecutor's opening speech, the first speech for the defense, the prosecutor's reply, and the defendant's conclusion. Three of his tetralogies are known to have survived. * The traditional arrangement of the works of Plato into nine tetralogies, including some doubtful works, and the letters as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Theban Plays
Sophocles (; grc, wikt:Σοφοκλῆς, Σοφοκλῆς, , Sophoklễs; 497/6 – winter 406/5 BC)Sommerstein (2002), p. 41. is one of three classical Greece, ancient Greek tragedy, tragedians, at least one of whose plays has survived in full. His first plays were written later than, or contemporary with, those of Aeschylus; and earlier than, or contemporary with, those of Euripides. Sophocles wrote over 120 plays, but only seven have survived in a complete form: ''Ajax (play), Ajax'', ''Antigone (Sophocles play), Antigone'', ''Women of Trachis'', ''Oedipus Rex'', ''Electra (Sophocles play), Electra'', ''Philoctetes (Sophocles), Philoctetes'' and ''Oedipus at Colonus''. For almost fifty years, Sophocles was the most celebrated playwright in the dramatic competitions of the Polis, city-state of Classical Athens, Athens which took place during the religious festivals of the Lenaea and the City Dionysia, Dionysia. He competed in thirty competitions, won twenty-four, and was neve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |