|
Socket 2
Socket 2 was one of the series of CPU sockets into which various x86 microprocessors were inserted. It was an updated Socket 1 with added support for Pentium OverDrive processors. Socket 2 was a 238-pin low insertion force (LIF) or zero insertion force (ZIF) 19×19 pin grid array (PGA) socket suitable for the 5-volt, 25 to 66 MHz 486 SX, 486 DX, 486 DX2, 486 OverDrive and 63 or 83 MHz Pentium OverDrive processors. See also * List of Intel microprocessors This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of Intel's processors from the pioneering 4-bit 4004 (1971) to the present high-end offerings. Concise technical data is given for each product. Latest 13th generation Cor ... References Socket 002 {{earlysock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel Socket 2 ZIF CPU Socket For 486 And Pentium Processors
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 series of instruction sets, the instruction sets found in most personal computers (PCs). Incorporated in Delaware, Intel ranked No. 45 in the 2020 ''Fortune'' 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 fiscal years. Intel supplies microprocessors for computer system manufacturers such as Acer, Lenovo, HP, and Dell. Intel also manufactures motherboard chipsets, network interface controllers and integrated circuits, flash memory, graphics chips, embedded processors and other devices related to communications and computing. Intel (''int''egrated and ''el''ectronics) was founded on July 18, 1968, by semiconductor pioneers Gordon Moore (of Moore's law) and Robert Noyce (1927–1990) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 1
Socket 1, originally called the "OverDrive" socket, was the second of a series of standard CPU sockets created by Intel into which various x86 microprocessors were inserted. It was an upgrade to Intel's first standard 169-pin pin grid array (PGA) socket and the first with an official designation. Socket 1 was intended as a 486 upgrade socket, and added one extra pin to prevent upgrade chips from being inserted incorrectly. Socket 1 was a 169-pin low insertion force (LIF) or zero insertion force (ZIF) 17×17 pin grid array (PGA) socket suitable for the 5-volt, 16 to 33 MHz 486 SX, 486 DX, 486 DX2 and 486 OverDrive processors. See also * List of Intel microprocessors This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of Intel's processors from the pioneering 4-bit 4004 (1971) to the present high-end offerings. Concise technical data is given for each product. Latest 13th generation Cor ... References External links CPU Sockets Chart {{intelsock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827). Definition One volt is defined as the electric potential between two points of a conducting wire when an electric current of one ampere dissipates one watt of power between those points. Equivalently, it is the potential difference between two points that will impart one joule of energy per coulomb of charge that passes through it. It can be expressed in terms of SI base units ( m, kg, second, s, and ampere, A) as : \text = \frac = \frac = \frac. It can also be expressed as amperes times ohms (current times resistance, Ohm's law), webers per second (magnetic flux per time), watts per ampere (power per current), or joules per coulomb (energy per charge), which is also equivalent to electronvolts per elementary charge: : \text = \tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pin Grid Array
A pin grid array (PGA) is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or rectangular, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package. The pins are commonly spaced 2.54 mm (0.1") apart, and may or may not cover the entire underside of the package. PGAs are often mounted on printed circuit boards using the through hole method or inserted into a socket. PGAs allow for more pins per integrated circuit than older packages, such as dual in-line package (DIP). PGA variants Plastic Plastic pin grid array (PPGA) packaging was used by Intel for late-model Mendocino core Celeron processors based on Socket 370. Some pre-Socket 8 processors also used a similar form factor, although they were not officially referred to as PPGA. Flip chip A flip-chip pin grid array (FC-PGA or FCPGA) is a form of pin grid array in which the die faces downwards on the top of the substrate with the back of the die exposed. This allows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit. The integrated circuit is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock-driven, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and provides results (also in binary form) as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system. The integration of a whole CPU onto a single or a few integrated circuits using Very-Large-Scale Integration (VLSI) greatly reduced the cost of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CPU Socket
In computer hardware, a CPU socket or CPU slot contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the central processing unit (CPU) without soldering. Common sockets have retention clips that apply a constant force, which must be overcome when a device is inserted. For chips with many pins, zero insertion force (ZIF) sockets are preferred. Common sockets include Pin Grid Array (PGA) or Land Grid Array (LGA). These designs apply a compression force once either a handle (PGA type) or a surface plate (LGA type) is put into place. This provides superior mechanical retention while avoiding the risk of bending pins when inserting the chip into the socket. Certain devices use Ball Grid Array (BGA) sockets, although these require soldering and are generally not considered user replaceable. CPU sockets are used on the motherboard in desktop and serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
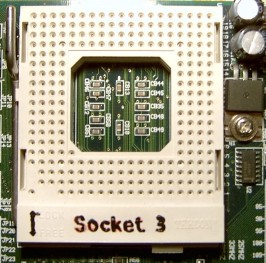
Socket 3
Socket 3 was a series of CPU sockets for various x86 microprocessors. It was sometimes found alongside a secondary socket designed for a math coprocessor chip, such as the 487. Socket 3 resulted from Intel's creation of lower voltage microprocessors. An upgrade to Socket 2, it rearranged the pin layout. Socket 3 is compatible with 168-pin socket CPUs. Socket 3 was a 237-pin low insertion force (LIF) or zero insertion force (ZIF) 19×19 pin grid array (PGA) socket suitable for the 3.3 V and 5 V, 25–50 MHz Intel 486 SX, 486 DX, 486 DX2, 486 DX4, 486 OverDrive and Pentium OverDrive processors as well as AMD Am486, Am5x86 and Cyrix Cx5x86 processors. See also * List of Intel microprocessors * List of AMD microprocessors This article gives a list of AMD microprocessors, sorted by generation and release year. If applicable and openly known, the designation(s) of each processor's core (versions) is (are) listed in parentheses. For an overview over concrete prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium OverDrive
The Pentium OverDrive was a microprocessor marketing brand name used by Intel, to cover a variety of consumer upgrade products sold in the mid-1990s. It was originally released for 486 motherboards, and later some Pentium sockets. Intel dropped the brand, as it failed to appeal to corporate buyers, and discouraged new system sales. 486 sockets The Pentium OverDrive is a heavily modified, 3.3 volt Pentium P54 core manufactured on 0.6 micrometer technology. It is fitted with a 486-compatible bus unit (though with an increased pin-count), an integrated heatsink and fan, and 32 kB of level 1 cache, double the 16 kB offered on regular P54C chips. As the data bus was effectively reduced to 32-bit width, per-clock performance was much lower than that of a 'regular' Pentium, though still substantially faster compared to a similarly clocked 486 owing to the Pentium's architectural improvements, such as the much improved FPU. It was also equipped with an integrated 3.3 volt power regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
486 OverDrive
Intel's i486 OverDrive processors are a category of various Intel 80486s that were produced with the designated purpose of being used to upgrade personal computers. The OverDrives typically possessed qualities different from 'standard' Intel 80486, i486s with the same speed steppings. Those included built-in voltage regulators, different pin-outs, CPU cache, write-back cache instead of CPU cache, write-through cache, built-in heatsinks, and fanless operation — features that made them more able to work where an ordinary edition of a particular model would not. Each 486 Overdrive typically came in two versions, ODP and ODPR variants. The ODPR chips had 168 pins and functioned as complete swap-out replacements for existing chips, whereas the ODP chips had an extra 169th pin, and were used for inserting into a special 'Overdrive' (Socket 1) socket on some 486 boards, which would disable the existing CPU without needing to remove it (in case that the existing CPU is surface-mounted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
486 DX2
The Intel i486DX2, rumored as 80486DX2 (later renamed IntelDX2) is a CPU produced by Intel that was first introduced in 1992. The i486DX2 was nearly identical to the i486DX, but it had additional clock multiplier circuitry. It was the first chip to use clock doubling, whereby the processor runs two internal logic clock cycles per external bus cycle. An i486 DX2 was thus significantly faster than an i486 DX at the same bus speed thanks to the 8K on-chip cache shadowing the slower clocked external bus. The i486DX2-66 was a very popular processor for video games enthusiasts in the early to mid-90s. Often coupled with 4 to 8 MB of RAM and a VLB video card, this CPU was capable of playing virtually every game title available for years after its release, right up to the end of the MS-DOS game era, making it a "sweet spot" in terms of CPU performance and longevity. The introduction of 3D graphics spelled the end of the 486's reign, because of their heavy use of floating point calculat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_CPU-pins_PNr°0295.jpg)