|
Soca Music
Soca music is a genre of music defined by Lord Shorty, its inventor, as the "Soul of Calypso", which has influences of African and East Indian rhythms. It was originally spelt "sokah" by its inventor but through an error in a local newspaper when reporting on the new music it was erroneously spelt "soca"; Lord Shorty confirmed the error but chose to leave it that way to avoid confusion. It is a genre of music that originated in Trinidad and Tobago in the early 1970s and developed into a range of styles during the 1980s and after. Soca was initially developed by Lord Shorty in an effort to revive traditional calypso, the popularity of which had been flagging amongst younger generations in Trinidad due to the rise in popularity of reggae from Jamaica and soul and funk from the United States. Soca is an offshoot of Calypso/Kaiso, with influences from East Indian rhythms and hooks. Soca has evolved since the 1980s primarily through musicians from various Anglophone Caribbean count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadence-lypso
Cadence-lypso is a fusion of cadence rampa from Haiti and calypso from Trinidad and Tobago that has also spread to other English speaking countries of the Caribbean. Originated in the 1970s by the Dominican band Exile One on the island of Guadeloupe, it spread and became popular in the dance clubs around the Creole world and Africa as well as the French Antilles. Genres: Caribbean and Latin America. Gordon Henderson is the leader and founder of Exile One, and the one who coined the term ''cadence-lypso''. Performing the Caribbean Experience. History Dominican contemporary music, that is the music played by the dance bands from the 1950s, has played a very important role in Dominica national life. Dominica musical landscape has seen many changes in the intervening period from 1950. In the forties and fifties, there were bands such as the Casimir Brothers of Roseau. The Swinging Stars emerged at the end of the fifties. Their music was a dance-oriented version of many kinds of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zouglou
Zouglou ( , ) is a dance oriented style of music originated from Ivory Coast during the mid-1990s. It started with students from a college of Gagnoa drawing on elements of other styles of music. Zouglou recounts the various social realities experienced by the Ivorian youth and carries messages, sometimes humorous, sometimes political, or, more often, delivers advice on life. It has since spread elsewhere, including to Burkina Faso, Cameroon and Gabon. The export of the phenomenon It was in 1989 that the zouglou as dance, language and philosophy, exports of the city of Yop to that of Abobo. Opokou N'ti, with real skills choreographic was blessed by Joe Christy to "liberate" (dance) to the city of Abobo to demand "teachers" who had invited them to fraternize. A few weeks later comes the demonstration zouglou in non-student in the hall of Kumasi, when the Ziguehi was a reality in Côte d'Ivoire, facilitated by Alain Gaston Lago and Tahi (Commissioner Tricot). The man of letters a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Caribbean Music
Indo-Caribbean music is the musical traditions of the Indo-Caribbean people of the Caribbean music area. Indo-Caribbean music is most common in Trinidad and Tobago, Guyana, Jamaica, and Suriname. Indo-Caribbean traditional music often reflects the Bhojpuri heritage of many Indo-Caribbeans; women's folk songs are especially reflective of the music of Bhojpur. These include folk songs for childbirth (''sohar''), humorous and light-hearted songs for a bride's family to insult the groom's (''gali''), funereal songs (''nirgun'') and ''matkor''. Other women's folk songs are seasonal and are performed at festivals like the ''phagwah'' and ''holi''. Instrumentation consists mostly of the ''dhantal'', a metal rod and claper, and the ''dholak'', a two-headed barrel drum. Traditional Hindu bhajans are also common. Modern Indo-Caribbean traditions include the seasonal, responsorial men's form, the ''chowtal'', and a vocal song form called '' taan-singing'', performed by a single male vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disco
Disco is a genre of dance music and a subculture that emerged in the 1970s from the United States' urban nightlife scene. Its sound is typified by four-on-the-floor beats, syncopated basslines, string sections, brass and horns, electric piano, synthesizers, and electric rhythm guitars. Disco started as a mixture of music from venues popular with Italian Americans, Hispanic and Latino Americans and Black Americans "'Broadly speaking, the typical New York discothèque DJ is young (between 18 and 30) and Italian,' journalist Vince Lettie declared in 1975. ..Remarkably, almost all of the important early DJs were of Italian extraction .. Italian Americans have played a significant role in America's dance music culture .. While Italian Americans mostly from Brooklyn largely created disco from scratch .." in Philadelphia and New York City during the late 1960s and early 1970s. Disco can be seen as a reaction by the 1960s counterculture to both the dominance of rock music ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punjabi Language
Punjabi (; ; , ), sometimes spelled Panjabi, is an Indo-Aryan language of the Punjab region of Pakistan and India. It has approximately 113 million native speakers. Punjabi is the most widely-spoken first language in Pakistan, with 80.5 million native speakers as per the 2017 census, and the 11th most widely-spoken in India, with 31.1 million native speakers, as per the 2011 census. The language is spoken among a significant overseas diaspora, particularly in Canada, the United States, and the United Kingdom. In Pakistan, Punjabi is written using the Shahmukhi alphabet, based on the Perso-Arabic script; in India, it is written using the Gurmukhi alphabet, based on the Indic scripts. Punjabi is unusual among the Indo-Aryan languages and the broader Indo-European language family in its usage of lexical tone. History Etymology The word ''Punjabi'' (sometimes spelled ''Panjabi'') has been derived from the word ''Panj-āb'', Persian for 'Five Waters', referring to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhangra (music)
Bhangra () is a type of non-traditional music of Punjab originating in the Southall area of United Kingdom. It is a type of upbeat popular music associated with the Punjabi diaspora in Britain. The style has its origins in the folk music of Punjab as well as western pop music of the 1970s and 1980s. Prior to this musical fusion, Bhangra existed only as a dance form in the native Punjab. This British music was unique in that it was not traditional nor did it seek any authenticity. While the traditional folk music of Punjab has a set of melodies that are used by various singers, Bhangra was a form of strict "band culture" in that new melodies were composed for each song. Therefore, the musicians were as important as the singers. Origins The roots of modern bhangra music date back to the British Punjabi community in Britain during the 1960s. An early pop music and modern recording artist/group of this type of music in the United Kingdom was Bhujhangy Group, founded by Tarloc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bollywood
Hindi cinema, popularly known as Bollywood and formerly as Bombay cinema, refers to the film industry based in Mumbai, engaged in production of motion pictures in Hindi language. The popular term Bollywood, is a portmanteau of "Bombay" (former name of Mumbai) and " Hollywood". The industry is a part of the larger Indian cinema, which also includes South Cinema and other smaller film industries. In 2017, Indian cinema produced 1,986 feature films, of which the largest number, 364 have been from Hindi. , Hindi cinema represented 43 percent of Indian net box-office revenue; Tamil and Telugu cinema represented 36 percent, and the remaining regional cinema constituted 21 percent. Hindi cinema has overtaken the U.S. film industry to become the largest centre for film production in the world. In 2001 ticket sales, Indian cinema (including Hindi films) reportedly sold an estimated 3.6 billion tickets worldwide, compared to Hollywood's 2.6 billion tickets sold. Earlier Hindi film ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zouk
Zouk is a musical movement pioneered by the French Antillean band Kassav' in the early 1980s. It was originally characterized by a fast tempo (120–145 bpm), a percussion-driven rhythm and a loud horn section. The fast zouk béton of Martinique and Guadeloupe faded away during the 1980s. Musicians from Martinique and Guadeloupe added MIDI instrumentation to their compas style, which developed into zouk-love. Zouk-love is effectively the French Lesser Antilles' compas.Popular Musics of the Non Western World. Peter Manuel, New York Oxford University Press, 1988, p74 Zouk gradually became indistinguishable from the genre known as compas. This light compas influenced the Cape-Verdean new generation. Zouk béton The original fast carnival style of zouk, best represented by the band Kassav', became known as "zouk béton", "zouk chiré" or "zouk hard". Zouk béton is considered a synthesis of various French Antillean dance music styles of the 20th century: kadans (cadence), konp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaiso
Kaiso is a type of music popular in Trinidad and Tobago, and other countries, especially of the Caribbean, such as Grenada, Belize, Barbados, St. Lucia and Dominica, which originated in West Africa particularly among the Efik and Ibibio people of Nigeria, and later evolved into calypso music. Kaiso music has its origins in West Africa (particularly in present-day Nigeria) and in the Kingdom of Kongo and was brought over by the enslaved Africans, who (in the early history of the art form) used it to sing about their masters. The people would also gather in "kaiso" tents where a griot or lead singer would lead them in song. Many early kaisos were sung in French Creole by an individual called a chantwell. Kaiso songs are generally narrative in form and often have a cleverly concealed political subtext. Kaiso performers are known as kaisonians. In Barbados, ''kaiso'' refers to a form of stage-presented calypso, such as at the crop over festival. Terminology The term ''kaiso' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reggae
Reggae () is a music genre that originated in Jamaica in the late 1960s. The term also denotes the modern popular music of Jamaica and its diaspora. A 1968 single by Toots and the Maytals, " Do the Reggay" was the first popular song to use the word "reggae", effectively naming the genre and introducing it to a global audience. While sometimes used in a broad sense to refer to most types of popular Jamaican dance music, the term ''reggae'' more properly denotes a particular music style that was strongly influenced by traditional mento as well as American jazz and rhythm and blues, and evolved out of the earlier genres ska and rocksteady. Reggae usually relates news, social gossip, and political commentary. It is instantly recognizable from the counterpoint between the bass and drum downbeat and the offbeat rhythm section. The immediate origins of reggae were in ska and rocksteady; from the latter, reggae took over the use of the bass as a percussion instrument. Reggae is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
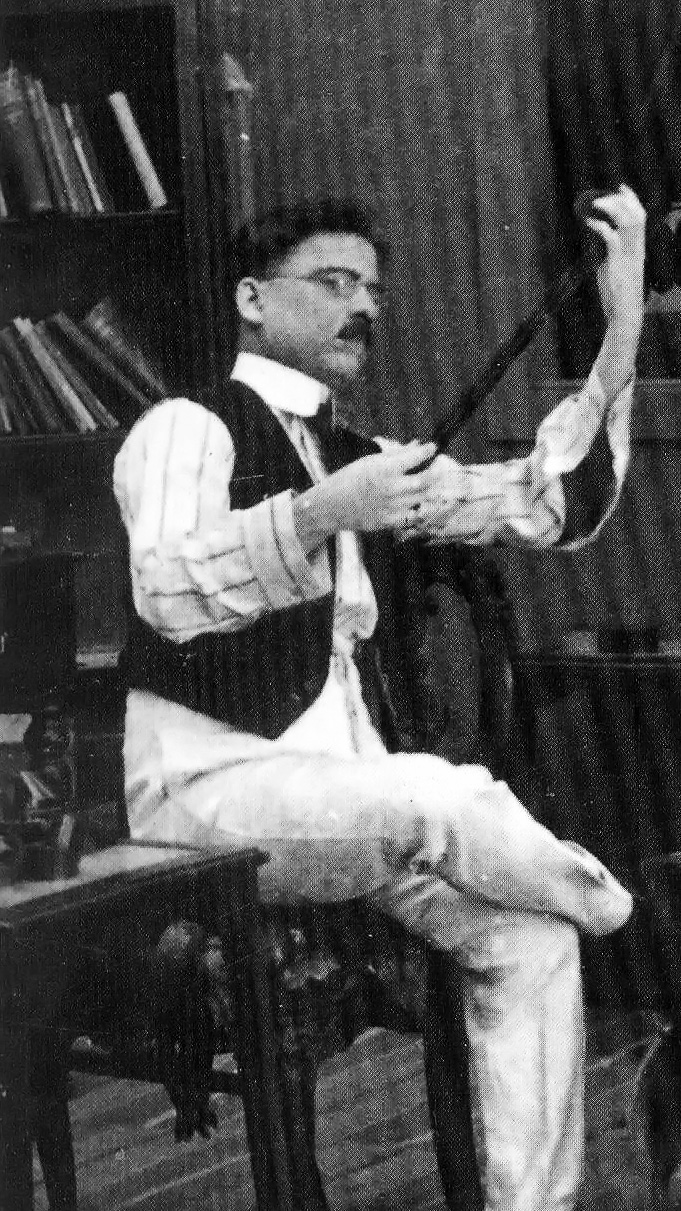
Lord Shorty
Ras Shorty I (6 October 1941 – 12 July 2000), born Garfield Blackman and also known as Lord Shorty, was a Trinidadian calypsonian and soca musician, known as the Father of Soca and The Love Man. Biography He was born Garfield Blackman in Lengua Village, Princes Town, Trinidad, and rose to fame as "Lord Shorty" with his 1963 hit "Cloak and Dagger", subsequently taking the name Ras Shorty. A prolific musician, composer and innovator, Shorty experimented with fusing calypso and the other Indian-inspired music, including chutney music, for nearly a decade before unleashing "the soul of calypso,"...soca music. Shorty was the first to really define his music and with "Indrani" in 1973 and "Endless Vibrations" (not just the song but the entire album) in 1975, calypso music really took off in another direction. On 30 August 1977 Shorty's friend and collaborator Maestro (Cecil Hume) died in an accident in Trinidad and his loss was felt by Shorty, who penned "Higher World" as a trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |