|
Sobekhotep VIII
Sekhemre Seusertawy Sobekhotep VIII was possibly the third king of the 16th Dynasty of Egypt reigning over the Theban region in Upper Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period.Kim Ryholt, The Political Situation in Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period c.1800-1550 B.C, Museum Tusculanum Press, (1997)Darrell D. Baker: The Encyclopedia of the Pharaohs: Volume I - Predynastic to the Twentieth Dynasty 3300–1069 BC, Stacey International, , 2008, p. 454 Alternatively, he may be a ruler of the 13th or 17th Dynasty. If he was a king of the 16th Dynasty, Sobekhotep VIII would be credited 16 years of reign by the Turin canon, starting c. 1650 BC, at the time of the Hyksos invasion of Egypt. __FORCETOC__ Chronological position The 2nd line of the 11th column of the Turin canon reads ''Sekhem ..e'' and refers, according to Egyptologists Kim Ryholt and Darrell Baker, to Sekhemre Seusertawy, which is Sobekhotep VIII's nomen. If this identification is correct, then Sobekhotep VIII re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hapi (Nile God)
Hapi ( Ancient Egyptian: ''ḥʿpy'') was the god of the annual flooding of the Nile in ancient Egyptian religion. The flood deposited rich silt (fertile soil) on the river's banks, allowing the Egyptians to grow crops.Wilkinson, p.106 Hapi was greatly celebrated among the Egyptians. Some of the titles of Hapi were "Lord of the Fish and Birds of the Marshes" and "Lord of the River Bringing Vegetation". Hapi is typically depicted as an androgynous figure with a prominent belly and large drooping breasts, wearing a loincloth and ceremonial false beard,Wilkinson, p.107 depicted in hieroglyphics as an intersex person. Mythology The annual flooding of the Nile occasionally was said to be the ''Arrival of Hapi''. Since this flooding provided fertile soil in an area that was otherwise desert, Hapi symbolised fertility. He had large female breasts because he was said to bring a rich and nourishing harvest. Due to his fertile nature he was sometimes considered the "father of the gods", an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labib Habachi
Labib Habachi (لبيب حبشي) (April 18, 1906 – February 18, 1984) was an influential Coptic Egyptian Egyptologist. Dr Habachi spent 30 years in the Antiquities Department of the Egyptian Government, ending his career as Chief inspector. During this period he spent an enormous amount of time in numerous dig sites in Egypt and the Sudan. He left government work to accept a position at the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago as an Archaeological Consultant to its Nubian Expedition. Tell el-Dab'a Between 1929 and 1939, Pierre Montet excavated at Tanis, finding the royal necropolis of the Twenty-first and Twenty-second Dynasties — the finds there almost equalled that of Tutankhamun's tomb in the Valley of the Kings. He believed that he found the location of Avaris, and this opinion was widely accepted at the time. Yet Habachi was not convinced. In 1941-42 he worked at Tell el-Dab'a for the Egyptian Antiquities Service and came to the conclusion th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
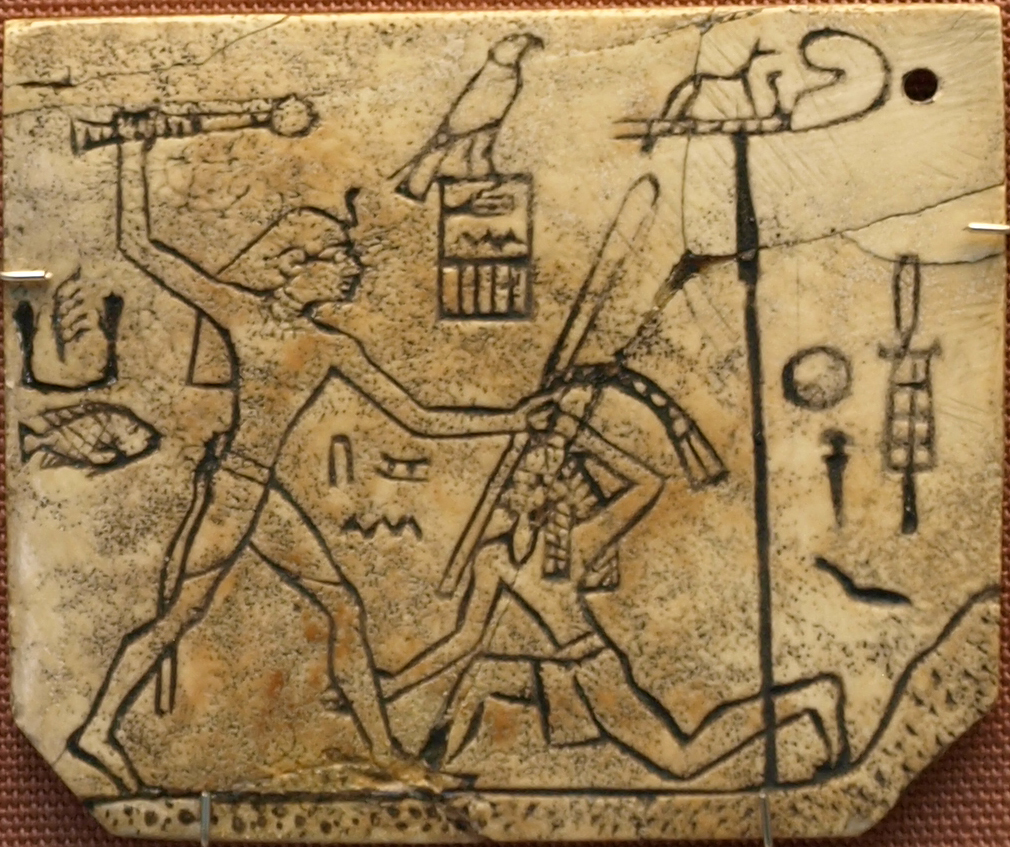
Pharaohs Of The Sixteenth Dynasty Of Egypt
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the annexation of Egypt by the Roman Empire in 30 BC. However, regardless of gender, "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom. The term "pharaoh" was not used contemporaneously for a ruler until a possible reference to Merneptah, c. 1210 BC during the Nineteenth Dynasty, nor consistently used until the decline and instability that began with the Twenty-Fifth Dynasty. In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as three titles: the Horus, the Sedge and Bee ( ''nswt-bjtj''), and the Two Ladies or Nebty ( ''nbtj'') name. The Golden Horus and the nomen and prenomen titles were added later. In Egyptian society, relig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century BC Pharaohs
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 ( MDCI), to December 31, 1700 ( MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French '' Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal court could be more easil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the annexation of Egypt by the Roman Empire in 30 BC. However, regardless of gender, "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom. The term "pharaoh" was not used contemporaneously for a ruler until a possible reference to Merneptah, c. 1210 BC during the Nineteenth Dynasty, nor consistently used until the decline and instability that began with the Twenty-Fifth Dynasty. In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as three titles: the Horus, the Sedge and Bee ( ''nswt-bjtj''), and the Two Ladies or Nebty ( ''nbtj'') name. The Golden Horus and the nomen and prenomen titles were added later. In Egyptian society, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amun
Amun (; also ''Amon'', ''Ammon'', ''Amen''; egy, jmn, reconstructed as ( Old Egyptian and early Middle Egyptian) → (later Middle Egyptian) → ( Late Egyptian), cop, Ⲁⲙⲟⲩⲛ, Amoun) romanized: ʾmn) was a major ancient Egyptian deity who appears as a member of the Hermopolitan Ogdoad. Amun was attested from the Old Kingdom together with his wife Amunet. With the 11th Dynasty ( 21st century BC), Amun rose to the position of patron deity of Thebes by replacing Montu. After the rebellion of Thebes against the Hyksos and with the rule of Ahmose I (16th century BC), Amun acquired national importance, expressed in his fusion with the Sun god, Ra, as Amun-Ra (alternatively spelled Amon-Ra or Amun-Re). Amun-Ra retained chief importance in the Egyptian pantheon throughout the New Kingdom (with the exception of the " Atenist heresy" under Akhenaten). Amun-Ra in this period (16th to 11th centuries BC) held the position of transcendental, self-created creator d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Creation Myths
Ancient Egyptian creation myths are the ancient Egyptian accounts of the creation of the world. The Pyramid Texts, tomb wall decorations, and writings, dating back to the Old Kingdom (c. 2700–2200 BCE) have provided the majority of information regarding ancient Egyptian creation myths. These myths also form the earliest religious compilations in the world. The ancient Egyptians had many creator gods and associated legends. Thus, the world or more specifically Egypt was created in diverse ways according to different parts of ancient Egypt. Some versions of the myth indicate spitting, others masturbation, as the act of creation. The earliest god, Ra and/or Atum (both being creator/sun gods), emerged from a chaotic state of the world and gave rise to Shu ( air) and Tefnut (moisture), from whose union came Geb (earth) and Nut ( sky), who in turn created Osiris, Isis, Set, and Nephthys. An extension to this basic framework was the Osiris myth involving Osiris, his consort Isis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Season Of The Harvest
The Season of the Harvest or Low Water was the third and final season of the lunar and civil Egyptian calendars. It fell after the Season of the Emergence (') and before the spiritually dangerous intercalary month ('), after which the New Year's festivities began the Season of the Inundation (''Ꜣḫt''). In the modern Coptic calendar it falls between Tobi 11 and Paoni 11. Names The Season of the Harvest was known to the Egyptians themselves as "LowWater" ( egy, Šmw), variously transliterated as Shemu or Shomu, in reference to the state of the Nile before the beginning of its annual flood. It is also referred to as Summer or the Dry Season. Lunar calendar In the lunar calendar, the intercalary month was added as needed to maintain the heliacal rising of Sirius in the fourth month of this season. This meant that the Season of the Harvest usually lasted from May to September. Because the precise timing of the flood varied, the months of "Low Water" no longer precisely re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Baines (Egyptologist)
John Robert Baines, (born 17 March 1946) is a retired British Egyptologist and academic. From 1976 to 2013, he was Professor of Egyptology at the University of Oxford and a fellow of The Queen's College, Oxford. Early life Baines was born on 17 March 1946. He is the oldest son of Edward Russell Baines and his wife Dora Margaret Jean (née O’Brien). He was educated at Winchester College, an all boys public boarding school in Winchester, Hampshire, England. He went on to study Egyptology at the University of Oxford. He graduated with a Bachelor of Arts degree (BA) in 1967, later promoted to Master of Arts (MA). He gained his Doctor of Philosophy degree (DPhil) in 1976. Academic career Baines was Professor of Egyptology at the University of Oxford from 1976 to 2013. He was one of the youngest professors at the university at the age of 30. He retired from full-time academia in 2013 but maintains his link with Oxford as a research associate. Baines is the author of multiple sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile Flood
The flooding of the Nile has been an important natural cycle in Egypt since Ancient Egypt, ancient times. It is celebrated by Egyptians as an annual holiday for two weeks starting August 15, known as ''Wafaa El-Nil''. It is also celebrated in the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, Coptic Church by ceremonially throwing a martyr's relic into the river, hence the name, The Martyr's Finger (, ). The flooding of the Nile was poetically described in myth as Isis's tears of sorrow for Osiris myth, Osiris when killed by their brother Set (deity), Set. Flooding cycle The flooding of the Nile is the result of the yearly monsoon between May and August causing enormous precipitations on the Ethiopian Highlands whose summits reach heights of up to 4550 m (14,928 ft). Most of this rainwater is taken by the Blue Nile and by the Atbarah River into the Nile, while a less important amount flows through the Sobat River, Sobat and the White Nile into the Nile. During this short period, those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercalary Month (Egypt)
The intercalary month or epagomenal days. of the ancient Egyptian calendar, Egyptian, Coptic calendar, Coptic, and Ethiopian calendars are a period of five days in common years and six days in leap years in addition to those calendars' 12 standard months, sometimes reckoned as their thirteenth month. They originated as a periodic measure to ensure that the heliacal rising of Sirius (star), Sirius would occur in the Mesori, 12th month of the Egyptian lunar calendar but became a regular feature of the civil calendar and its descendants. Coptic and Ethiopian leap days occur in the year preceding Julian calendar, Julian and Gregorian calendar, Gregorian leap years. Names The English names "intercalary month" and "epagomenal days" derive from Latin ' ("proclaimed between") and Greek language, Greek ''epagómenoi'' () or ''epagómenai'' (, "brought in" or "added on"), Latinisation of names, Latinized as '. The period is also sometimes known as the "monthless days". In ancient Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenhotep III
Amenhotep III ( egy, jmn-ḥtp(.w), ''Amānəḥūtpū'' , "Amun is Satisfied"; Hellenization, Hellenized as Amenophis III), also known as Amenhotep the Magnificent or Amenhotep the Great, was the ninth pharaoh of the Eighteenth dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty. According to different authors, he ruled Egypt from June 1386 to 1349 BC, or from June 1388 BC to December 1351 BC/1350 BC, after his father Thutmose IV died. Amenhotep was Thutmose's son by a minor wife, Mutemwiya. His reign was a period of unprecedented prosperity and splendour, when Egypt reached the peak of its artistic and international power. When he died in the 38th or 39th year of his reign he was succeeded by his son Amenhotep IV, who later changed his name to Akhenaten. Family and early life Amenhotep was the son of Thutmose IV and his minor wife Mutemwiya. He was born probably around 1401 BC. Later in his life, Amenhotep commissioned the depiction of his divine birth to be displayed at Luxor Temple. Amenh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(2865505031).jpg)


