|
Slug Moth
The Limacodidae or Eucleidae are a family of moths in the superfamily Zygaenoidea or the Cossoidea;Scoble, M.J. (1992). ''The Lepidoptera: Form, Function and Diversity.'' Oxford University Press. the placement is in dispute. They are often called slug moths because their caterpillars bear a distinct resemblance to slugs. They are also called cup moths because of the shape of their cocoons. The larvae are often liberally covered in protective stinging hairs, and are mostly tropical, but occur worldwide, with about 1800 described species and probably many more as yet undescribed species. Description Moths They are small, hairy moths, with reduced or absent mouthparts and fringed wings. They often perch with their abdomens sticking out at 90° from their thoraces and wings. North American moths are mostly cryptic browns, sometimes marked with white or green, but the hag moth mimics bees.Wagner, D.L. (2005). ''Caterpillars of Eastern North America.'' Princeton University Press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
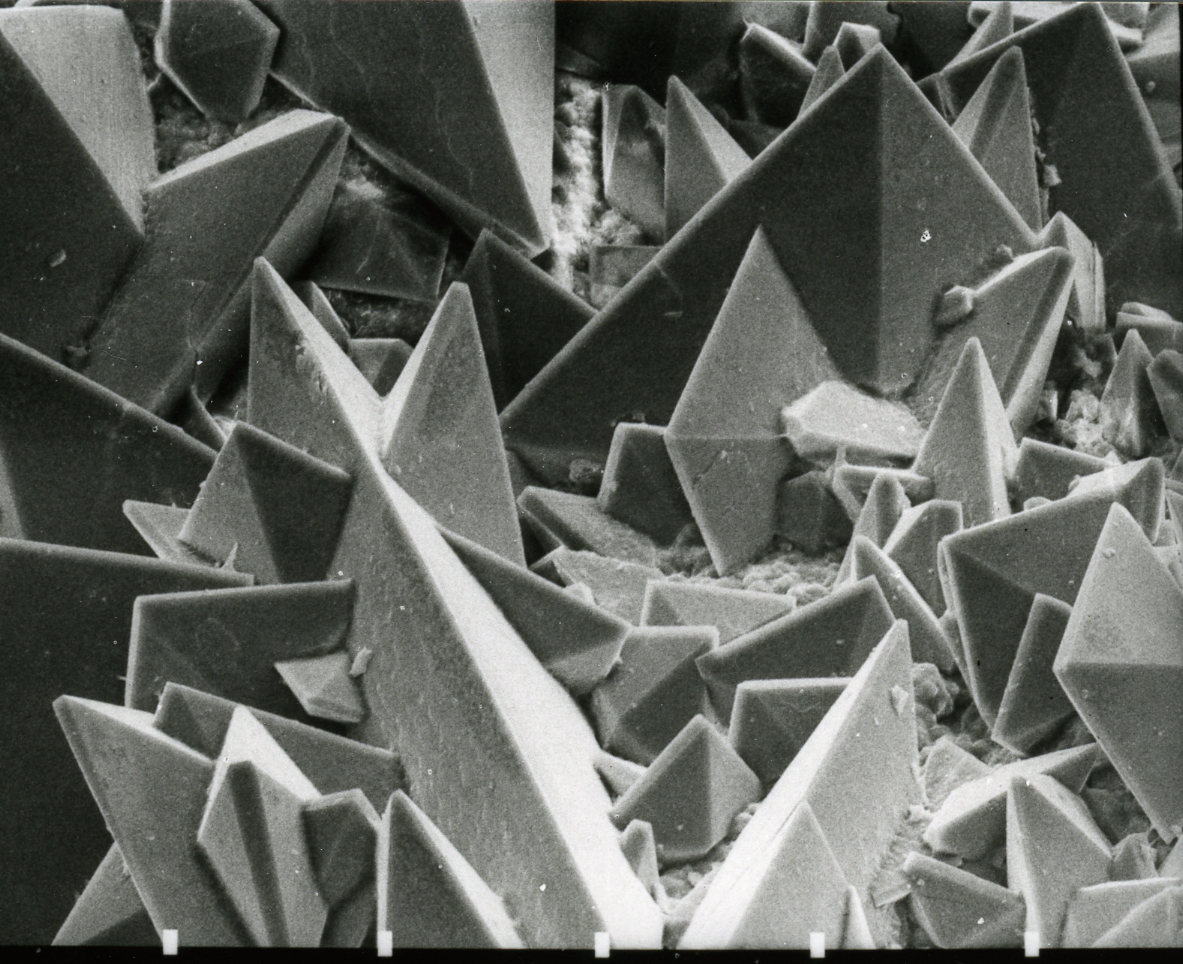
Calcium Oxalate
Calcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalic acid with the chemical formula . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' varies from 1 to 3. Anhydrous and all hydrated forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate occurs naturally as the mineral whewellite, forming envelope-shaped crystals, known in plants as raphides. The two rarer hydrates are dihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral weddellite, and trihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral caoxite, are also recognized. Some foods have high quantities of calcium oxalates and can produce sores and numbing on ingestion and may even be fatal. Tribes with diets that depend highly on fruits and vegetables high in calcium oxalate, such as in Micronesia, reduce the level of it by boiling and cooking them. They are a constituent in 76% of human kidney stones. Calcium oxalate is also found in beerstone, a scale that forms on containers used in breweries. Occurrence Many plants accumu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saddleback Caterpillar
The saddleback caterpillar (''Acharia stimulea'', formerly ''Sibine stimulea'') is the larva of a species of moth native to eastern North America. It is also found in Mexico. The species belongs to the family of slug caterpillars, Limacodidae. The larva (caterpillar) is primarily green with brown at both ends and a prominent white-ringed brown dot in the center which resembles a saddle. It has a pair of fleshy horns at both ends. These and most of the rest of the body bear urticating hairs that secrete an irritating venom. Contact with the hairs causes a painful, swollen rash and sometimes nausea in humans. In some cases, more severe reactions to the venom can occur, including a systemic condition called erucism or acute urticaria, for which severe symptoms may include migraines, gastrointestinal symptoms, asthma complications, anaphylactic shock, rupturing of erythrocytes, and hemorrhaging. The hairs should be removed from the skin immediately to prevent more venom spread. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monkey Slug
''Phobetron pithecium'', the hag moth, is a moth of the family Limacodidae. Its larva is known as the monkey slug. Lifecycle One generation a year occurs in the north, but two or more happen in the southern United States. Larva The larva is distinctive, with no close analogues, although it may be mistaken for the shed skin of a hairy spider or leaf debris. It has nine pairs of curly projections or tubercles of varying lengths from the flattened body, each densely covered in hairs. The third, fifth and seventh projection are often longer than the others. The caterpillar has been reported to cause irritation to humans. Like all limacodids, the legs are shortened and the prolegs are reduced to suction cups. The "arms" or tubercles can fall off without harming the caterpillar, aiding the larva in defense. The larvae are in length. It is solitary and is not a very significant agricultural threat, but it is a common sight in orchards. Pupa This species pupates in a cup-shaped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pubescent (botany)
Trichomes (); ) are fine outgrowths or appendages on plants, algae, lichens, and certain protists. They are of diverse structure and function. Examples are hairs, glandular hairs, scales, and papillae. A covering of any kind of hair on a plant is an indumentum, and the surface bearing them is said to be pubescent. Algal trichomes Certain, usually filamentous, algae have the terminal cell produced into an elongate hair-like structure called a trichome. The same term is applied to such structures in some cyanobacteria, such as '' Spirulina'' and ''Oscillatoria''. The trichomes of cyanobacteria may be unsheathed, as in ''Oscillatoria'', or sheathed, as in ''Calothrix''. These structures play an important role in preventing soil erosion, particularly in cold desert climates. The filamentous sheaths form a persistent sticky network that helps maintain soil structure. Plant trichomes Plant trichomes have many different features that vary between both species of plants and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichomes
Trichomes (); ) are fine outgrowths or appendages on plants, algae, lichens, and certain protists. They are of diverse structure and function. Examples are hairs, glandular hairs, scales, and papillae. A covering of any kind of hair on a plant is an indumentum, and the surface bearing them is said to be pubescent. Algal trichomes Certain, usually filamentous, algae have the terminal cell produced into an elongate hair-like structure called a trichome. The same term is applied to such structures in some cyanobacteria, such as '' Spirulina'' and ''Oscillatoria''. The trichomes of cyanobacteria may be unsheathed, as in ''Oscillatoria'', or sheathed, as in ''Calothrix''. These structures play an important role in preventing soil erosion, particularly in cold desert climates. The filamentous sheaths form a persistent sticky network that helps maintain soil structure. Plant trichomes Plant trichomes have many different features that vary between both species of plants and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Botanical Terms
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary of leaf morphology. For other related terms, see Glossary of phytopathology, Glossary of lichen terms, and List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names. A B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
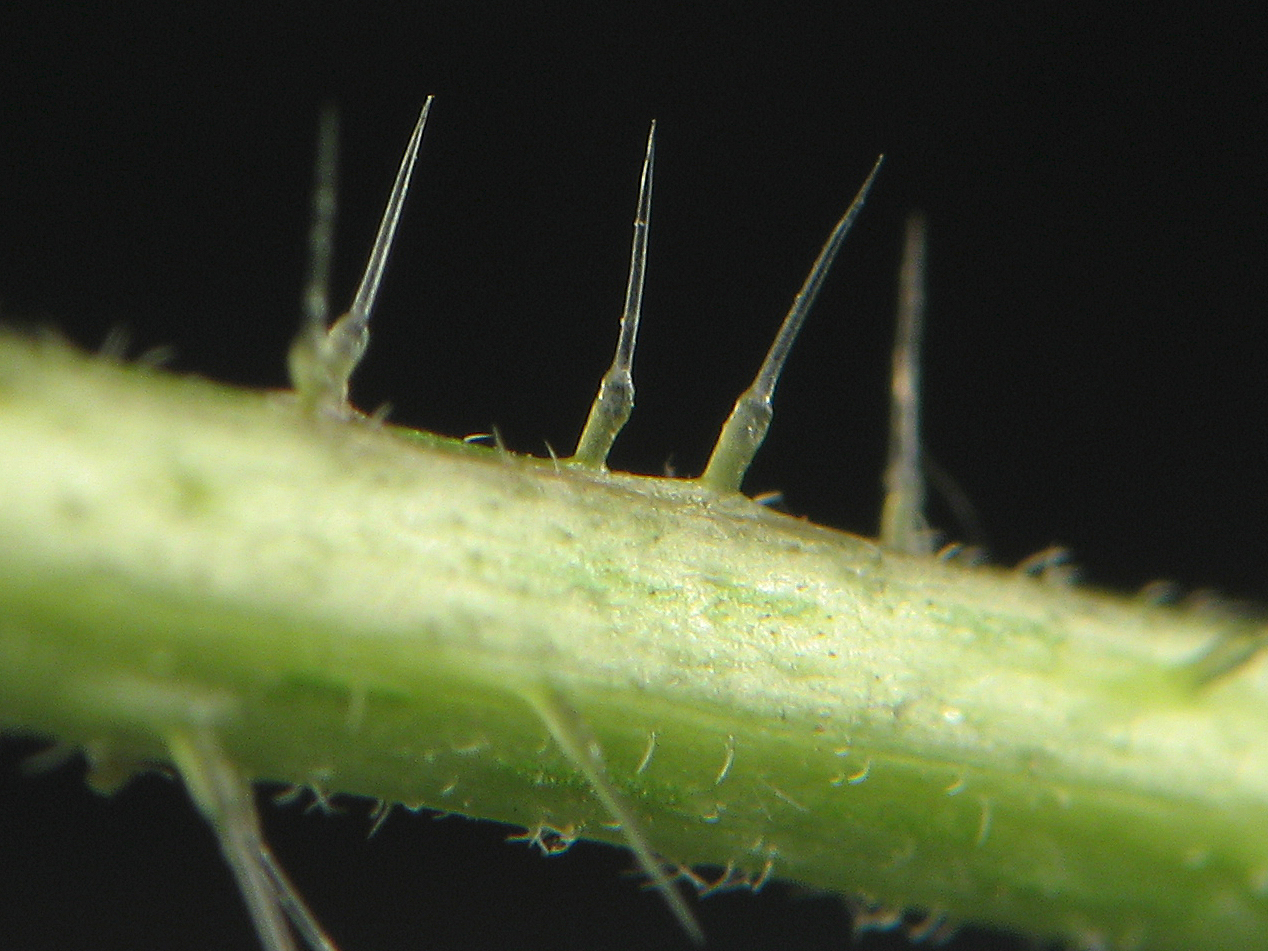
Urticating Hair
Urticating hairs or urticating bristles are one of the primary defense mechanisms used by numerous plants, almost all New World tarantulas, and various lepidopteran caterpillars. ''Urtica'' is Latin for "nettle" (stinging nettles are in the genus ''Urtica''), and bristles that urticate are characteristic of this type of plant, and many other plants in several families. This term also refers to certain types of barbed bristles that cover the dorsal and posterior surface of a tarantula's or caterpillar's abdomen. Many tarantula species eject bristles from their abdomens, directing them toward potential attackers. These bristles can embed themselves in the other animal's skin or eyes, causing physical irritation, usually to great discomfort. The term urticating hairs is a misnomer, as technically only mammals possess true hairs. In plants The most common form of urticating hairs in plants are typified by nettles, which possess sharp-pointed hollow bristles seated on a gland that s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow-shouldered Slug
''Lithacodes fasciola'', the yellow-shouldered slug or ochre-winged hag moth, is a moth of the family Limacodidae. Lifecycle One generation a year occurs in the north, but two or more in southern United States, so mature caterpillars may be found from May to November.Wagner, DL, 2005. Caterpillars of Eastern North America. Princeton University Press Larva The larva is flattened and ovoid in outline, with a short, squared off "tail". It is a bright yellow green with yellow and green stripes along its length. Small craters dot its topside. Maximum length is 15 mm. Like all limacodids, the legs are shortened and the prolegs are reduced to suction cups. A high proportion of larvae has parasitoids. Their presence can be determined before emergence by a black spot formed by the breathing siphon of the fly. Pupa This species pupates in a cup-shaped cocoon with a circular escape hatch. Adult The small (1 cm) moth is "hairy" and brown, with a white stripe bordered in black acr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setae
In biology, setae (singular seta ; from the Latin word for "bristle") are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms. Animal setae Protostomes Annelid setae are stiff bristles present on the body. They help, for example, earthworms to attach to the surface and prevent backsliding during peristaltic motion. These hairs make it difficult to pull a worm straight from the ground. Setae in oligochaetes (a group including earthworms) are largely composed of chitin. They are classified according to the limb to which they are attached; for instance, notosetae are attached to notopodia; neurosetae to neuropodia. Crustaceans have mechano- and chemosensory setae. Setae are especially present on the mouthparts of crustaceans and can also be found on grooming limbs. In some cases, setae are modified into scale like structures. Setae on the legs of krill and other small crustaceans help them to gather phytoplankton. It captures them and allows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycaenidae
Lycaenidae is the second-largest family of butterflies (behind Nymphalidae, brush-footed butterflies), with over 6,000 species worldwide, whose members are also called gossamer-winged butterflies. They constitute about 30% of the known butterfly species. The family comprises seven subfamilies, including the blues (Polyommatinae), the coppers (Lycaeninae), the hairstreaks (Theclinae), and the harvesters (Miletinae). Description, food, and life cycle Adults are small, under 5 cm usually, and brightly coloured, sometimes with a metallic gloss. Larvae are often flattened rather than cylindrical, with glands that may produce secretions that attract and subdue ants. Their cuticles tend to be thickened. Some larvae are capable of producing vibrations and low sounds that are transmitted through the substrates they inhabit. They use these sounds to communicate with ants.Pierce, N. E.; Braby, M. F.; Heath, A.; Lohman, D. J.; Mathew, J.; Rand, D. B. & Travassos, M. A. (2002)"The eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the cocoons of the larvae of the mulberry silkworm ''Bombyx mori'' reared in captivity (sericulture). The shimmering appearance of silk is due to the triangular prism-like structure of the silk fibre, which allows silk cloth to refract incoming light at different angles, thus producing different colors. Silk is produced by several insects; but, generally, only the silk of moth caterpillars has been used for textile manufacturing. There has been some research into other types of silk, which differ at the molecular level. Silk is mainly produced by the larvae of insects undergoing complete metamorphosis, but some insects, such as webspinners and raspy crickets, produce silk throughout their lives. Silk production also occurs in hymenoptera ( bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)





