|
Slavyanka, Azerbaijan
Slavyanka (russian: Славянка) is a village and the second most populous municipality after the capital Gədəbəy in the Gadabay Rayon of Azerbaijan. It has a population of 3,705. The municipality consists of the villages of Slavyanka and Maarif, Azerbaijan, Maarif. History Along with a number of other villages in northwestern Azerbaijan, Slavyanka was settled in 1844 by the Doukhobors, members of a Pacifist dissenter Christian group resettled to Transcaucasia by Nicholas I of Russia, Nicholas I from the Molochna River settlements in today's Zaporizhzhia Oblast of Ukraine. The village is said to have been named after the town of Sloviansk, Slavyansk (in today's Donetsk Oblast), where many of the ancestors of the Molochna Doukhobors had originated.Slavyanka Village (Doukhobor Genealogy Website) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
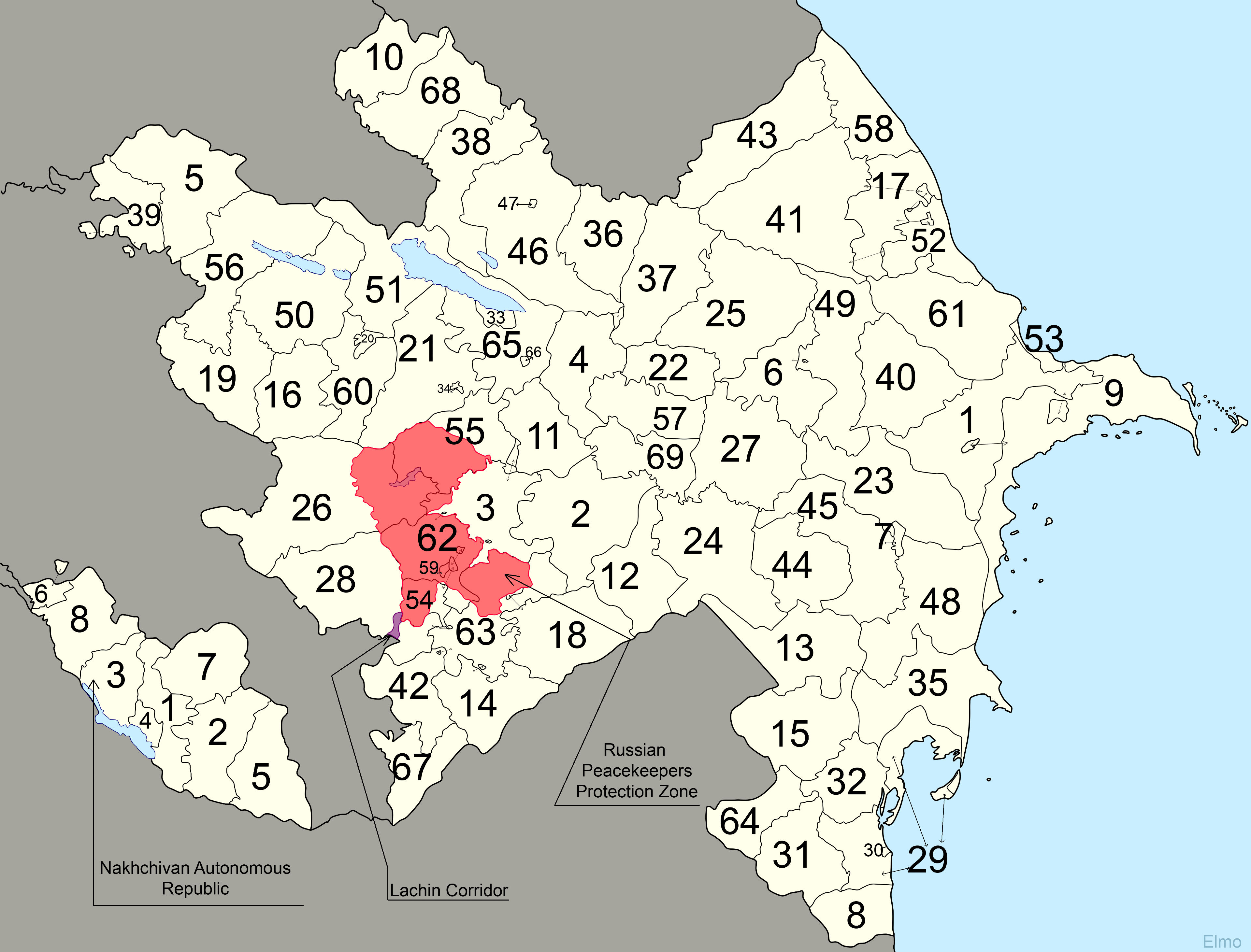
Administrative Divisions Of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 66 districts () and 11 cities () that are subordinate to the Republic. Out of these, 7 districts and 1 city is located within the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The districts are further divided into municipalities (). Additionally, the districts of Azerbaijan are grouped into 14 Economic Regions (). On July 7, 2021, the President of Azerbaijan Ilham Aliyev signed Decree "On the new division of economic regions in the Republic of Azerbaijan". Administrative divisions Contiguous Azerbaijan The territory of former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast presently consists of the districts of Khojavend, Shusha, Khojaly, the eastern portion of Kalbajar and the western portion of Tartar. The Autonomous Oblast was abolished on 26 November 1991, by the Supreme Soviet of the Azerbaijan SSR. Since then, the territory of the autonomous oblast has been administratively split between the aforementioned districts. As a result of the First N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conscription
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day under various names. The modern system of near-universal national conscription for young men dates to the French Revolution in the 1790s, where it became the basis of a very large and powerful military. Most European nations later copied the system in peacetime, so that men at a certain age would serve 1–8 years on active duty and then transfer to the reserve force. Conscription is controversial for a range of reasons, including conscientious objection to military engagements on religious or philosophical grounds; political objection, for example to service for a disliked government or unpopular war; sexism, in that historically men have been subject to the draft in the most cases; and ideological objection, for example, to a perceived vio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
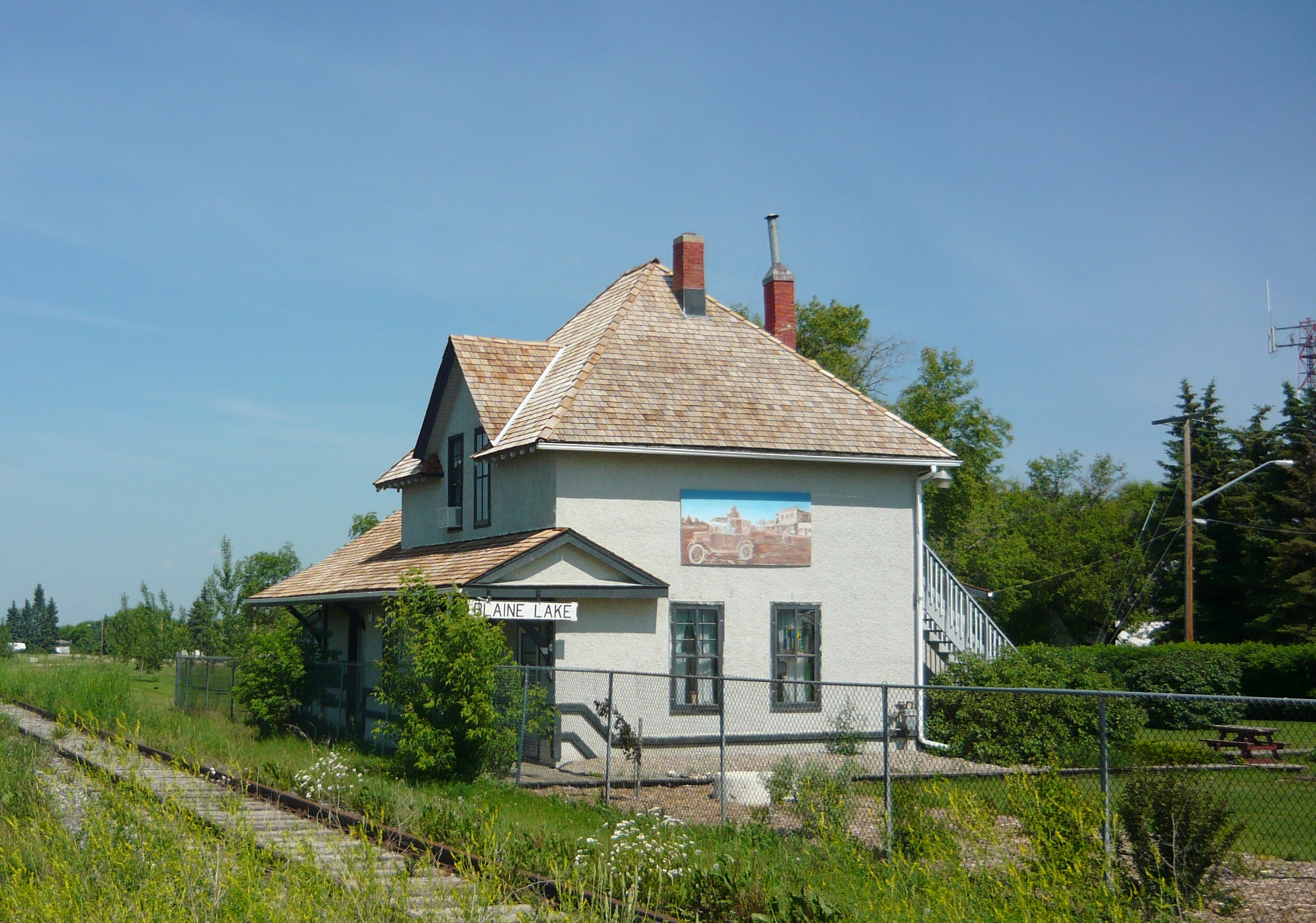
Blaine Lake, Saskatchewan
Blaine Lake is a town in central Saskatchewan, Canada. It is located 85 km north of Saskatoon, 104 km southwest of Prince Albert and 104 km east of North Battleford at the junction of Highway 12 and Highway 40. Nearby are the urban centres of Shellbrook and Rosthern. Blaine Lake is considered the "Gateway to the Northern Lakes" due to its proximity to fishing, hunting and camping sites, as well as its convenient location at a junction of two highways. History A surveyor named Blaine was drowned in the lake prior to the establishment in 1911. The historic CN train station that now houses thBlaine Lake Wapiti Libraryalong with the local town history museum. The station was built in 1912 two years after the rail line between Prince Albert and North Battleford was constructed and served the community until 1973. The Doukhobor Dugout House is a Provincial Heritage Property southeast of the town. ;Heritage properties A number of heritage buildings are located wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolkhoz
A kolkhoz ( rus, колхо́з, a=ru-kolkhoz.ogg, p=kɐlˈxos) was a form of collective farm in the Soviet Union. Kolkhozes existed along with state farms or sovkhoz., a contraction of советское хозяйство, soviet ownership or state ownership, sovetskoye khozaystvo. Russian plural: ''sovkhozy''; anglicized plural: ''sovkhozes''. These were the two components of the socialized farm sector that began to emerge in Soviet agriculture after the October Revolution of 1917, as an antithesis both to the feudal structure of impoverished serfdom and aristocratic landlords and to individual or family farming. The 1920s were characterized by spontaneous emergence of collective farms, under influence of traveling propaganda workers. Initially, a collective farm resembled an updated version of the traditional Russian "commune", the generic "farming association" (''zemledel’cheskaya artel’''), the Association for Joint Cultivation of Land (TOZ), and finally the kolkhoz. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collective Farming
Collective farming and communal farming are various types of, "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member-owners jointly engage in farming activities as a collective, and state farms, which are owned and directly run by a centralized government. The process by which farmland is aggregated is called collectivization. In some countries (including the Soviet Union, the Eastern Bloc countries, China and Vietnam), there have been both state-run and cooperative-run variants. For example, the Soviet Union had both kolkhozy (cooperative-run farms) and sovkhozy (state-run farms). Pre-20th century history A small group of farming or herding families living together on a jointly managed piece of land is one of the most common living arrangements in all of human history, having co-existed and competed with more individualistic forms of ownership (as w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rostov Oblast
Rostov Oblast ( rus, Росто́вская о́бласть, r=Rostovskaya oblast, p=rɐˈstofskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located in the Southern Federal District. The oblast has an area of and a population of 4,277,976 ( 2010 Census), making it the sixth most populous federal subject in Russia. Its administrative center is the city of Rostov-on-Don, which also became the administrative center of the Southern Federal District in 2002. Geography Rostov Oblast borders Ukraine (Donetsk and Luhansk Oblasts) and also Volgograd and Voronezh Oblasts in the north, Krasnodar and Stavropol Krais in the south, and the Republic of Kalmykia in the east. The Rostov oblast is located in the Pontic-Caspian steppe. It is directly north over the North Caucasus and west of the Yergeni hills.Google Earth It is within the Russian Southern Federal District. Rivers and lakes The Don River, one of Europe's longest rivers, flows through the oblast for part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baptists
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only ( believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul competency (the responsibility and accountability of every person before God), ''sola fide'' (salvation by just faith alone), ''sola scriptura'' (scripture alone as the rule of faith and practice) and congregationalist church government. Baptists generally recognize two ordinances: baptism and communion. Diverse from their beginning, those identifying as Baptists today differ widely from one another in what they believe, how they worship, their attitudes toward other Christians, and their understanding of what is important in Christian discipleship. For example, Baptist theology may include Arminian or Calvinist beliefs with various sub-groups holding different or competing positions, while others allow for diversity in this matter within t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molokan
The Molokans ( rus, молокан, p=məlɐˈkan or , "dairy-eater") are a Spiritual Christian sect that evolved from Eastern Orthodoxy in the East Slavic lands. Their traditions—especially dairy consumption during Christian fasts—did not conform to those of the Russian Orthodox Church, and they were regarded as heretics (''sektanty''). The term ''Molokan'' is an exonym used by their Orthodox neighbors; they tend to identify themselves as Spiritual Christians (духовные христиане: ''dukhovnye khristiane''). There are almost as many different ways among Molokans as there are Molokans. Some built chapels for worship, kept sacraments, and revered saints and icons, while others (like Ikonobortsy, "icon-wrestlers") discarded these practices in the pursuit of individual approaches to scripture. In general, they rejected the institutionalized formalism of Orthodoxy and denominations with similar doctrines in favor of more emphasis on "Original Christianity" as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elisabethpol Governorate
The Elizavetpol Governorate, also known after 1918 as the Ganja Governorate, was a province ('' guberniya'') of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire, with its capital in Yelisavetpol (present-day Ganja). The area of the governorate stretched and was composed of 1,275,131 inhabitants in 1916. The Elizavetpol Governorate bordered the Erivan Governorate to the west, the Tiflis Governorate and Zakatal Okrug to the north, the Dagestan Oblast to the northeast, the Baku Governorate to the east, and Iran to the south. Geography The area of the governorate includes the southern slope of the main Caucasus range in the northeast, where Mount Bazardüzü and other peaks rise above the snow-line; the arid steppes beside the Kura river, reaching 1000 ft. of altitude in the west and sinking to 100–200 ft. in the east, where irrigation is necessary; and the northern slopes of the Transcaucasian escarpment and portions of the Armenian Highlands, which is intersected towards it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Wikipedians%27 Notice Board/Style Guide
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''Canadian''. Canada is a multilingual and multicultural society home to people of groups of many different ethnic, religious, and national origins, with the majority of the population made up of Old World immigrants and their descendants. Following the initial period of French and then the much larger British colonization, different waves (or peaks) of immigration and settlement of non-indigenous peoples took place over the course of nearly two centuries and continue today. Elements of Indigenous, French, British, and more recent immigrant customs, languages, and religions have combined to form the culture of Canada, and thus a Canadian identity. Canada has also been strongly influenced by its linguistic, geographic, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)