|
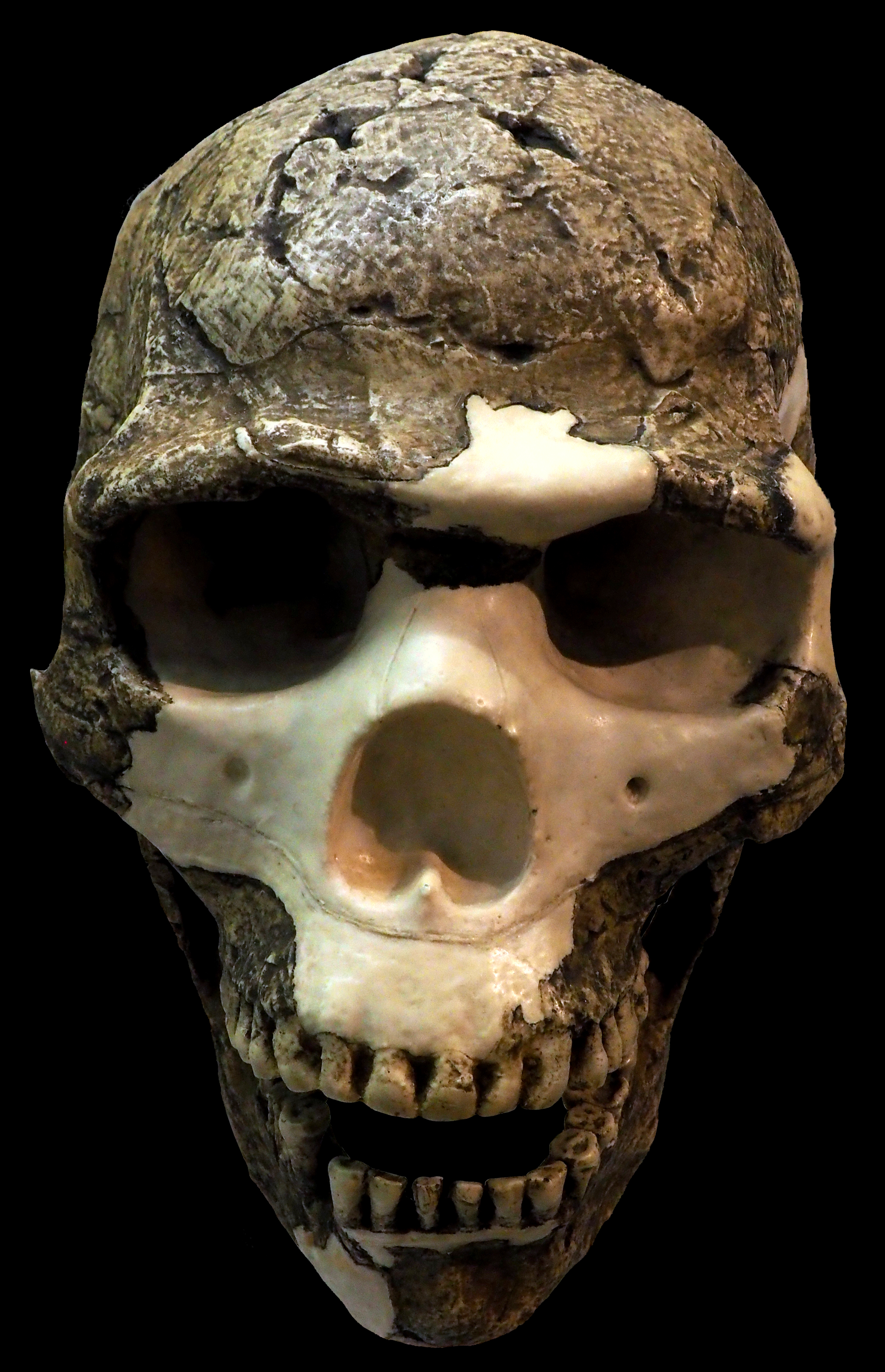
Skhul
Es-Skhul (es-Skhūl, ar, السخول; meaning ''kid'', ''young goat'') or the Skhul Cave is a prehistoric cave site situated about south of the city of Haifa, Israel, and about from the Mediterranean Sea. Together with the nearby sites of Tabun Cave, Jamal cave, and the cave at El Wad, Skhul is part of the Nahal Me'arot Nature Reserve, a national park and UNESCO World Heritage Site. The site was first excavated by Dorothy Garrod during summer of 1929. Several human skeletons were found in the cave, belonging to an ancient species of Homo sapiens. Both Neanderthals – and anatomically modern humans were present in the region from 200,000 to 45,000 years ago – around 100,000 years ago. The remains found at es-Skhul, together with those found at the other caves of Wadi el-Mughara and Mugharet el-Zuttiyeh, were classified in 1939 by Arthur Keith and as ''Palaeoanthropus palestinensis'', a descendant of ''Homo heidelbergensis''. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
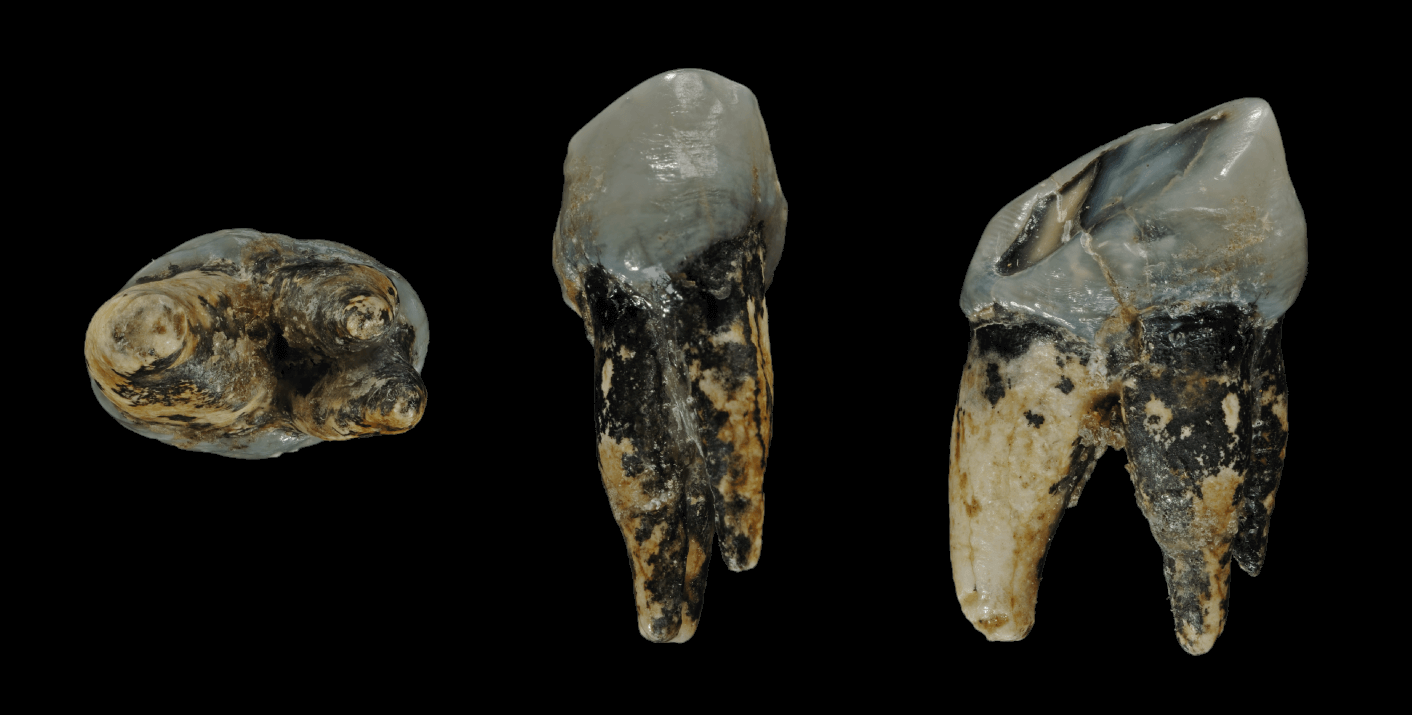
Skhul And Qafzeh Hominins
The Skhul/Qafzeh hominins or Qafzeh–Skhul early modern humans are hominin fossils discovered in Es-Skhul and Qafzeh caves in Israel. They are today classified as ''Homo sapiens'', among the earliest of their species in Eurasia. Skhul Cave is on the slopes of Mount Carmel; Qafzeh Cave is a rockshelter near Nazareth in Lower Galilee. The remains found at Es Skhul, together with those found at the Nahal Me'arot Nature Reserve and Mugharet el-Zuttiyeh, were classified in 1939 by Arthur Keith and Theodore D. McCown as ''Palaeoanthropus palestinensis'', a descendant of '' Homo heidelbergensis''. History The remains exhibit a mix of traits found in archaic and anatomically modern humans. They have been tentatively dated at about 80,000-120,000 years old using electron paramagnetic resonance and thermoluminescence dating techniques. The brain case is similar to modern humans, but they possess brow ridges and a projecting facial profile like Neanderthals. They were initially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Hominina Fossils
The following tables give an overview of notable finds of hominin fossils and remains relating to human evolution, beginning with the formation of the tribe Hominini (the divergence of the human and chimpanzee lineages) in the late Miocene, roughly 7 to 8 million years ago. As there are thousands of fossils, mostly fragmentary, often consisting of single bones or isolated teeth with complete skulls and skeletons rare, this overview is not complete, but show some of the most important findings. The fossils are arranged by approximate age as determined by radiometric dating and/or incremental dating and the species name represents current consensus; if there is no clear scientific consensus the other possible classifications are indicated. The early fossils shown are not considered ancestors to ''Homo sapiens'' but are closely related to ancestors and are therefore important to the study of the lineage. After 1.5 million years ago (extinction of ''Paranthropus''), all fossils sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Carmel
Mount Carmel ( he, הַר הַכַּרְמֶל, Har haKarmel; ar, جبل الكرمل, Jabal al-Karmil), also known in Arabic as Mount Mar Elias ( ar, link=no, جبل مار إلياس, Jabal Mār Ilyās, lit=Mount Saint Elias/ Elijah), is a coastal mountain range in northern Israel stretching from the Mediterranean Sea towards the southeast. The range is a UNESCO biosphere reserve. A number of towns are situated there, most notably the city of Haifa, Israel's third largest city, located on the northern and western slopes. Etymology The word ''karmel'' means "garden-land" and is of uncertain origin. It is either a compound of ''kerem'' and ''el'', meaning "vineyard of God" or a clipping of ''kar male,'' meaning "full kernel." Martin Jan Mulder suggested a third etymology, that of ''kerem + l'' with the lamed a sufformative, but this is considered unlikely as evidence for the existence of a lamed sufformative is weak. Geography and geology The phrase "Mount Carmel" has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qafzeh Cave
Qafzeh Cave, also known by other names, is a prehistoric archaeological site located at the bottom of Mount Precipice in the Jezreel Valley of Lower Galilee south of Nazareth. Important remains of prehistoric people were discovered on the site - some of the oldest examples in the world, outside of Africa, of virtually anatomically modern human beings. These were discovered on the ledge just outside the cave, where 18 layers from the Middle Paleolithic era were identified. The interior of the cave contains layers ranging from the Neolithic era to the Bronze Age. Names The Arabic name of the mountain is Jebel el-Qafzeh, 'Mount of the Leap', and the cave's name is derived from it, Qafzeh Cave, sometimes spelled Qafza Cave, with article becoming al-Kafza (Cave). By translation to Hebrew, the name becomes Meʿarat Har HaKfitza, 'Leap Mount Cave', or sometimes Mt. HaKfitza Cave, HaKfitza(h) Cave, or Meʿarat Qafzeh. Another Hebrew name is Meʿarat Kedumim or Kedumim Cave. The various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahal Me'arot Nature Reserve
The Caves of Nahal Me’arot / Wadi el-Mughara ("Caves Creek"), named here by the Hebrew and Arabic name of the valley where they are located, are a UNESCO Site of Human Evolution in the Carmel mountain range near Haifa in northern Israel. UNESCO website The four UNESCO-listed caves are: * Tabun cave, Tabun or Tanur cave (lit.: "Oven") * Gamal or el-Jamal cave ("Camel") * El Wad or Nahal cave ("Stream") * Skhul or Gedi cave ("Kid") The four caves were proclaimed a site of "outstanding universal value" by UNESCO in 2012. They are prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabun Cave
The Tabun Cave is an excavated site located at Nahal Me'arot Nature Reserve, Israel and is one of the Human Evolution sites at Mount Carmel, which were proclaimed as having universal value by UNESCO in 2012. History Together with the nearby sites of El Wad cave, Jamal cave, and Skhul cave, Tabun is part of the Nahal Me'arot Nature Reserve, a national park and UNESCO World Heritage Site. The cave was occupied intermittently during the Lower and Middle Paleolithic (500,000 to around 40,000 years ago). In the course of this period, deposits of sand, silt and clay of up to accumulated in the cave. Excavations suggest that it features one of the longest sequences of human occupation in the Levant. Dorothy Garrod led excavations in 1929 over 22 months that established the sequence of occupation of this and other sites in the area. It was during these excavations that a woman, Yusra, recruited from a local village, was credited with the discovery of the Tabun 1 Neanderthal sku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Heidelbergensis
''Homo heidelbergensis'' (also ''H. sapiens heidelbergensis''), sometimes called Heidelbergs, is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human which existed during the Middle Pleistocene. It was subsumed as a subspecies of '' H. erectus'' in 1950 as ''H. e. heidelbergensis'', but towards the end of the century, it was more widely classified as its own species. It is debated whether or not to constrain ''H. heidelbergensis'' to only Europe or to also include African and Asian specimens, and this is further confounded by the type specimen (Mauer 1) being a jawbone, because jawbones feature few diagnostic traits and are generally missing among Middle Pleistocene specimens. Thus, it is debated if some of these specimens could be split off into their own species or a subspecies of ''H. erectus''. Because the classification is so disputed, the Middle Pleistocene is often called the "muddle in the middle." ''H. heidelbergensis'' is regarded as a chronospecies, evolving from an Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mugharet El-Zuttiyeh
Mugharet el-Zuttiyeh ("Cave of the Robbers") is a prehistoric archaeological site in Upper Galilee, Israel. It is situated from the Nahal Amud outlet, approximately above the wadi bed ( below sea level). It was found to house a fossil today known as the "Galilee skull" or "The Yabrudian Man". History Discovered in 1925, the skull was the first fossilised archaic human found in Western Asia. Together with the remains found at Es Skhul and the Wadi el-Mughara Caves, this find was classified in 1939 by Arthur Keith and as ''Palaeoanthropus palestinensis''. Today its taxonomy is that of '' Homo heidelbergensis''. Zuttiyeh cave is at the opening of a limestone ravine where Nahal Amud turns eastward, above a smaller cave known as Mugharet el-Emireh (Cave of the Princess). The cave was excavated from 1925 to 1926 by Francis Turville-Petre. It was the first paleontological excavation in the region. Turville-Petre discovered a skull, referred to as the ''Galilee Skull'', that was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neanderthals
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the "causes of Neanderthal disappearance about 40,000 years ago remain highly contested," demographic factors such as small population size, inbreeding and genetic drift, are considered probable factors. Other scholars have proposed competitive replacement, assimilation into the modern human genome (bred into extinction), great climatic change, disease, or a combination of these factors. It is unclear when the line of Neanderthals split from that of modern humans; studies have produced various intervals ranging from 315,000 to more than 800,000 years ago. The date of divergence of Neanderthals from their ancestor '' H. heidelbergensis'' is also unclear. The oldest potential Neanderthal bones date to 430,000 years ago, but the classifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorothy Garrod
Dorothy Annie Elizabeth Garrod, CBE, FBA (5 May 1892 – 18 December 1968) was an English archaeologist who specialised in the Palaeolithic period. She held the position of Disney Professor of Archaeology at the University of Cambridge from 1939 to 1952, and was the first woman to hold a chair at either Oxford or Cambridge. Early life and education Garrod was the daughter of the physician Sir Archibald Garrod and Laura Elizabeth Smith, daughter of the surgeon Sir Thomas Smith, 1st Baronet. She was born in Chandos Street, London, and was educated at home. Her first teacher was Isabel Fry as governess. Garrod recalled Fry teaching her, at age nine, in Harley Street with the daughter of Walter Jessop. She later attended Birklands School in St Albans. In 1913, Garrod entered Newnham College, Cambridge, and in that year became a Roman Catholic convert. She read history there, completing the course in 1916. She had three brothers, two of whom were killed in action in WW I and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fossil Sites
This list of fossil sites is a worldwide list of localities known well for the presence of fossils. Some entries in this list are notable for a single, unique find, while others are notable for the large number of fossils found there. Many of the entries in this list are considered Lagerstätten (sedimentary deposits that exhibits extraordinary fossils with exceptional preservation—sometimes including preserved soft tissues). Lagerstätten are indicated by a note () in the noteworthiness column. Fossils may be found either associated with a geological formation or at a single geographic site. Geological formations consist of rock that was deposited during a specific period of time. They usually extend for large areas, and sometimes there are different important sites in which the same formation is exposed. Such sites may have separate entries if they are considered to be more notable than the formation as a whole. In contrast, extensive formations associated with large areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Wad
El Wad is an Epipalaeolithic archaeological site in Mount Carmel, Israel. The site has two components: El Wad Cave, also known as Mugharat el-Wad or HaNahal Cave ( he, מערת הנחל); and El Wad Terrace, located immediately outside the cave. Together with the nearby sites of Tabun Cave, Jamal Cave, and Es-Skhul Cave, El Wad is part of the Nahal Me'arot Nature Reserve, a national park and UNESCO World Heritage Site. Background and research history El Wad is one of a number of significant prehistoric archaeological sites in the caves of Wadi el-Mughara in Mount Carmel, now protected as the national nature reserve and UNESCO World Heritage Site. However in the 1920s, very little was known of the prehistory of the region, and the sites were threatened by quarrying for the construction of the Port of Haifa. In 1928, British archaeologist Charles Lambert conducted a trial excavation at El Wad on behalf of the Department of Antiquities of Mandatory Palestine to assess the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_1928_Natufian_culture_discovery.jpg)