|
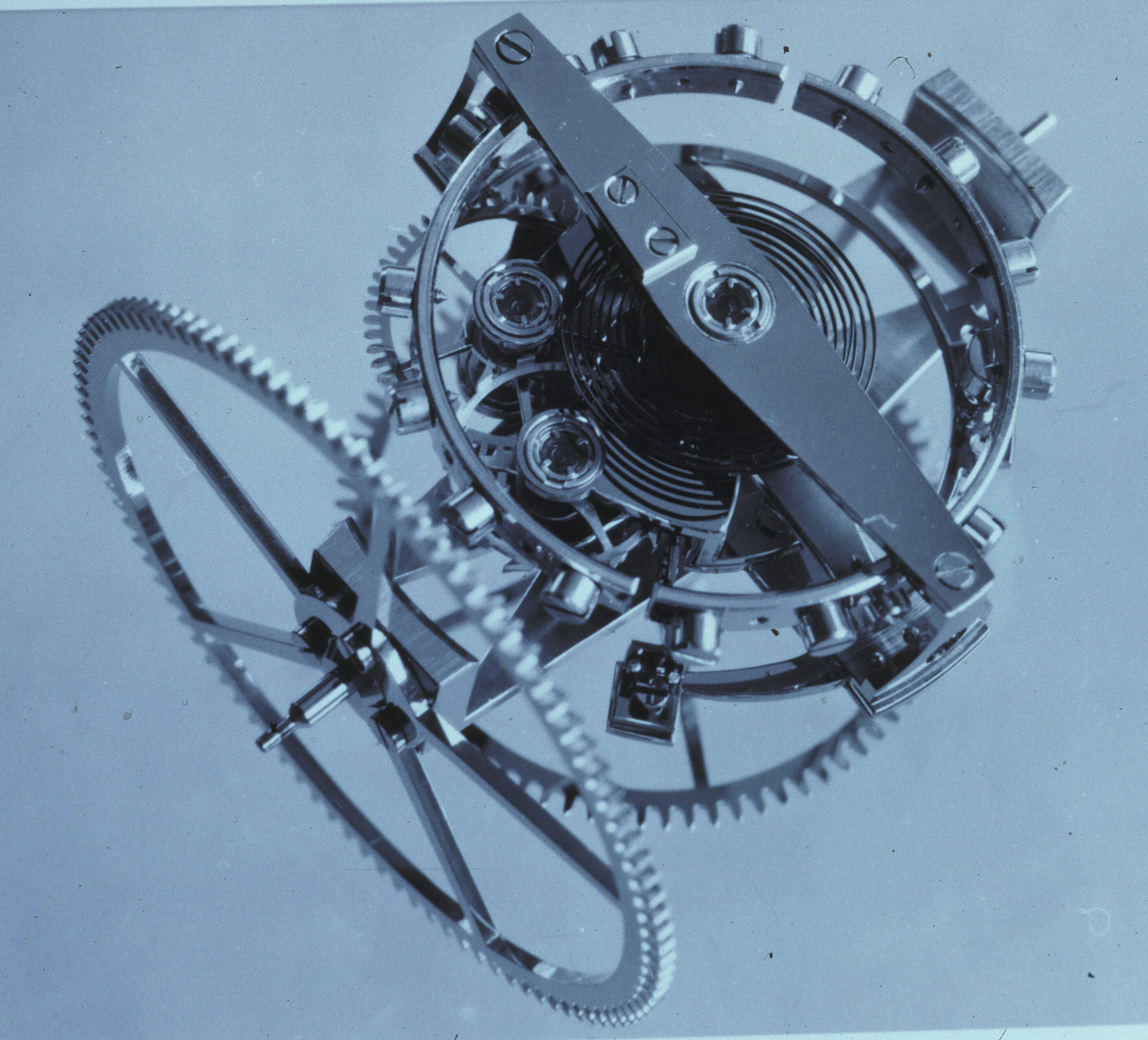
Skeleton Clock
A skeleton clock is any clock or Watch, wristwatch, though typically mechanical in nature, in which the parts that usually conceal the inner workings of the mechanism have been removed or significantly modified so as to display these inner parts. It is considered to be a showcase design and intentionally exposes to plain view the various gears, wheels and Spring (device), springs within the Movement (clockwork), movement itself. There is no official definition of a skeleton clock ''per se'', but a major portion of the main parts of the timepiece should be openly visible from the front of the clock and most often from the back as well in order for it to be considered and accepted as a skeleton clock. The parts most commonly showcased by a skeleton design are those exhibiting either the most movement or the most attractive design. These may include, but are not limited to the escapement, balance wheel and balance spring, mainspring, and tourbillon. Generally there is either no di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapphire Crystal
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, chromium, vanadium, or magnesium. The name sapphire is derived via the Latin "sapphirus" from the Greek "sappheiros", which referred to Lapis lazuli, lapis lazuli. It is typically blue, but natural "fancy" sapphires also occur in yellow, purple, orange, and green colors; "parti sapphires" show two or more colors. Red corundum stones also occur, but are called ruby, rubies rather than sapphires. Pink-colored corundum may be classified either as ruby or sapphire depending on locale. Commonly, natural sapphires are cut and polished into gemstones and worn in jewellery, jewelry. They also may be created synthetically in laboratories for industrial or decorative purposes in large boule (crystal), crystal boules. Because of the remarkable hardness of sapphires 9 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, Mohs scale (the third hardest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Chester, Pennsylvania
West Chester is a borough and the county seat of Chester County, Pennsylvania. Located within the Philadelphia metropolitan area, the borough had a population of 18,461 at the 2010 census. West Chester is the mailing address for most of its neighboring townships. When calculated by mailing address, the population as of the 2010 U.S. Census was 108,696, which would make it the 10th largest city by mailing address in the state of Pennsylvania. Much of the West Chester University of Pennsylvania North Campus and the Chester County government are located within the borough. The center of town is located at the intersection of Market and High Streets. History The area was originally known as Turk's Head—after the inn of the same name located in what is now the center of the borough. West Chester has been the seat of government in Chester County since 1786 when the seat was moved from nearby Chester in what is now Delaware County. The borough was incorporated in 1799. In the heart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remontoire
In mechanical horology, a remontoire (from the French ''remonter'', meaning 'to wind') is a small secondary source of power, a weight or spring, which runs the timekeeping mechanism and is itself periodically rewound by the timepiece's main power source, such as a mainspring. It was used in a few precision clocks and watches to place the source of power closer to the escapement, thereby increasing the accuracy by evening out variations in drive force caused by unevenness of the friction in the geartrain. In spring-driven precision clocks, a gravity remontoire is sometimes used to replace the uneven force delivered by the mainspring running down by the more constant force of gravity acting on a weight. In turret clocks, it serves to separate the large forces needed to drive the hands from the modest forces needed to drive the escapement which keeps the pendulum swinging. A remontoire should not be confused with a ''maintaining power spring'', which is used only to keep the timepiec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Going Barrel
{{unreferenced, date=September 2009 Used in mechanical watches and clocks, a barrel is a cylindrical metal box closed by a cover, with a ring of gear teeth around it, containing a spiral spring called the mainspring, which provides power to run the timepiece. The barrel turns on an arbor (axle). The spring is hooked to the barrel at its outer end and to the arbor at its inner end. The barrel teeth engage the first pinion of the wheel train of the watch, usually the center wheel. Barrels rotate slowly: for a watch mainspring barrel, the rate is usually one rotation every 8 hours. This construction allows the mainspring to be wound (by turning the arbour) without interrupting the tension of the spring driving the timepiece. Types ; Plain barrel: I.e. without teeth, used in fusee watches and clocks. A chain, or cord, was wound around the plain barrel, connecting it to the fusee. ; Going barrel: The form used in modern watches, is wound by turning the arbor and drives the watch m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusee (horology)
Used in antique spring-powered mechanical watches and clocks, a fusee (from the French ''fusée'', wire wound around a spindle) is a cone-shaped pulley with a helical groove around it, wound with a cord or chain which is attached to the mainspring barrel. Fusees were used from the 15th century to the early 20th century to improve timekeeping by equalizing the uneven pull of the mainspring as it ran down. Gawaine Baillie stated of the fusee, "Perhaps no problem in mechanics has ever been solved so simply and so perfectly." History The origin of the fusee is not known. Many sources erroneously credit clockmaker Jacob Zech of Prague with inventing it around 1525. The earliest definitely dated fusee clock was made by Zech in 1525, but the fusee actually appeared earlier, with the first spring driven clocks in the 15th century., p.127-128, p.121 The idea probably did not originate with clockmakers, since the earliest known example is in a crossbow windlass shown in a 1405 mili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escapement
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy to the clock's timekeeping element (usually a pendulum or balance wheel) to replace the energy lost to friction during its cycle and keep the timekeeper oscillating. The escapement is driven by force from a coiled spring or a suspended weight, transmitted through the timepiece's gear train. Each swing of the pendulum or balance wheel releases a tooth of the escapement's ''escape wheel'', allowing the clock's gear train to advance or "escape" by a fixed amount. This regular periodic advancement moves the clock's hands forward at a steady rate. At the same time, the tooth gives the timekeeping element a push, before another tooth catches on the escapement's pallet, returning the escapement to its "locked" state. The sudden stopping of the esc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffolk
Suffolk () is a ceremonial county of England in East Anglia. It borders Norfolk to the north, Cambridgeshire to the west and Essex to the south; the North Sea lies to the east. The county town is Ipswich; other important towns include Lowestoft, Bury St Edmunds, Newmarket, and Felixstowe which has one of the largest container ports in Europe. The county is low-lying but can be quite hilly, especially towards the west. It is also known for its extensive farming and has largely arable land with the wetlands of the Broads in the north. The Suffolk Coast & Heaths and Dedham Vale are both nationally designated Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty. History Administration The Anglo-Saxon settlement of Suffolk, and East Anglia generally, occurred on a large scale, possibly following a period of depopulation by the previous inhabitants, the Romanised descendants of the Iceni. By the fifth century, they had established control of the region. The Anglo-Saxon inhabitants later b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
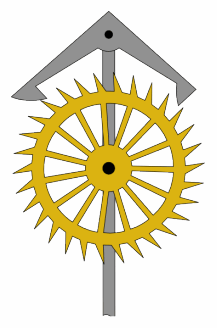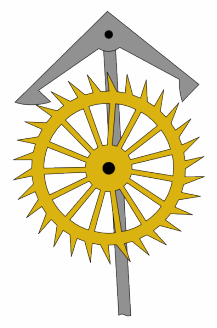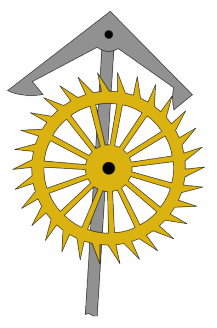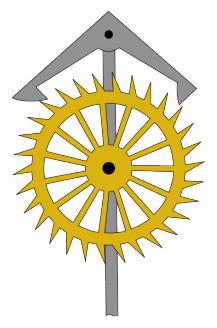
Great Wheel Skeleton Clock
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements * Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size * Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent People * List of people known as "the Great" *Artel Great (born 1981), American actor Other uses * ''Great'' (1975 film), a British animated short about Isambard Kingdom Brunel * ''Great'' (2013 film), a German short film * Great (supermarket), a supermarket in Hong Kong * GReAT, Graph Rewriting and Transformation, a Model Transformation Language * Gang Resistance Education and Training Gang Resistance Education And Training, abbreviated G.R.E.A.T., provides a school-based, police officer instructed program that includes classroom instruction and various learning activities. Their intention is to teach the students to avoid gang ..., or GREAT, a school-based and police officer-instructed program * Global Research and Analysis Team (GReAT), a cybersecurity team at Kaspersky Lab *'' Great!'', a 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Skeleton Clock By Smith & Sons
English usually refers to: * English language * English people English may also refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England ** English national identity, an identity and common culture ** English language in England, a variant of the English language spoken in England * English languages (other) * English studies, the study of English language and literature * ''English'', an Amish term for non-Amish, regardless of ethnicity Individuals * English (surname), a list of notable people with the surname ''English'' * People with the given name ** English McConnell (1882–1928), Irish footballer ** English Fisher (1928–2011), American boxing coach ** English Gardner (b. 1992), American track and field sprinter Places United States * English, Indiana, a town * English, Kentucky, an unincorporated community * English, Brazoria County, Texas, an unincorporated community * Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourbillon
In horology, a tourbillon (; "whirlwind") is an addition to the mechanics of a watch escapement to increase accuracy. It was developed around 1795 and patented by the Swiss-French watchmaker Abraham-Louis Breguet on June 26, 1801. In a tourbillon the escapement and balance wheel are mounted in a rotating cage, with the goal of eliminating errors of poise in the balance giving a uniform weight. Tourbillons are still included in some modern wristwatches, the mechanism is usually exposed on the watch's face to showcase it. Types of tourbillon Single axis tourbillon Patented by Breguet in 1801, the single axis tourbillon minimizes the difference in rate between positions caused by poise errors. The tourbillon was invented to complement the split bi-metallic balance which was inherently difficult to poise. In the most common implementation of this, the tourbillon carriage is carried by the fourth pinion, within a stationary fourth wheel. The escape pinion is engaged with this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock
A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and the year. Devices operating on several physical processes have been used over the millennia. Some predecessors to the modern clock may be considered as "clocks" that are based on movement in nature: A sundial shows the time by displaying the position of a shadow on a flat surface. There is a range of duration timers, a well-known example being the hourglass. Water clocks, along with the sundials, are possibly the oldest time-measuring instruments. A major advance occurred with the invention of the verge escapement, which made possible the first mechanical clocks around 1300 in Europe, which kept time with oscillating timekeepers like balance wheels., pp. 103–104., p. 31. Traditionally, in horology, the term ''clock'' was used for a stri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |