|
Sinophoneus
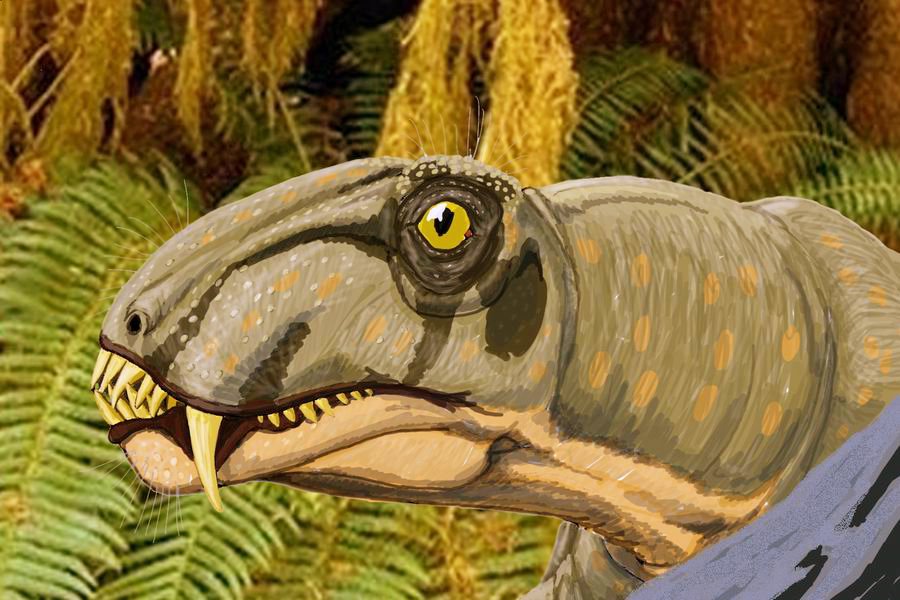
''Sinophoneus'' is an extinct genus of carnivorous dinocephalian therapsid belonging to the family Anteosauridae. It lived 272 to 270 million years ago at the beginning of the Middle Permian (Lower Roadian) in what is now the Gansu Province in northern China. It is known by a skull of an adult individual (the holotype GMV1601), as well as by many skulls of juvenile specimens. The latter were first considered as belonging to a different animal, named ''Stenocybus'', before being reinterpreted as immature ''Sinophoneus''. ''Sinophoneus'' shows a combination of characters present in other anteosaurs. Its bulbous profile snout and external nostrils located in front of the canine are reminiscent of the basal anteosaur ''Archaeosyodon'', while its massive transerse pterygoids processes with enlarged distal ends are more similar to the more derived anteosaurs ''Anteosaurus'' and ''Titanophoneus''. First phylogenetic analyzes identified ''Sinophoneus'' as the most basal Anteosaurinae. A mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinophoneus09
''Sinophoneus'' is an extinct genus of carnivorous dinocephalian therapsid belonging to the family Anteosauridae. It lived 272 to 270 million years ago at the beginning of the Middle Permian (Lower Roadian) in what is now the Gansu Province in northern China. It is known by a skull of an adult individual (the holotype GMV1601), as well as by many skulls of juvenile specimens. The latter were first considered as belonging to a different animal, named ''Stenocybus'', before being reinterpreted as immature ''Sinophoneus''. ''Sinophoneus'' shows a combination of characters present in other anteosaurs. Its bulbous profile snout and external nostrils located in front of the canine are reminiscent of the basal anteosaur ''Archaeosyodon'', while its massive transerse pterygoids processes with enlarged distal ends are more similar to the more derived anteosaurs ''Anteosaurus'' and ''Titanophoneus''. First phylogenetic analyzes identified ''Sinophoneus'' as the most basal Anteosaurinae. A mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anteosaurus
''Anteosaurus'' (meaning "Antaeus reptile") is an extinct genus of large carnivorous dinocephalian synapsid. It lived at the end of the Guadalupian (= Middle Permian) during the Capitanian stage, about 265 to 260 million years ago in what is now South Africa. It is mainly known by cranial remains and few postcranial bones. With its skull reaching in length and a body size estimated at more than in length, and in weight, ''Anteosaurus'' was the largest known carnivorous non-mammalian synapsid and the largest terrestrial predator of the Permian period. Occupying the top of the food chain in the Middle Permian, its skull, jaws and teeth show adaptations to capture large prey like the giants titanosuchids and tapinocephalids dinocephalians and large pareiasaurs. As in many other dinocephalians the cranial bones of ''Anteosaurus'' are pachyostosed, but to a lesser extent than in tapinocephalid dinocephalians. In ''Anteosaurus'', pachyostosis mainly occurs in the form of horn-sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
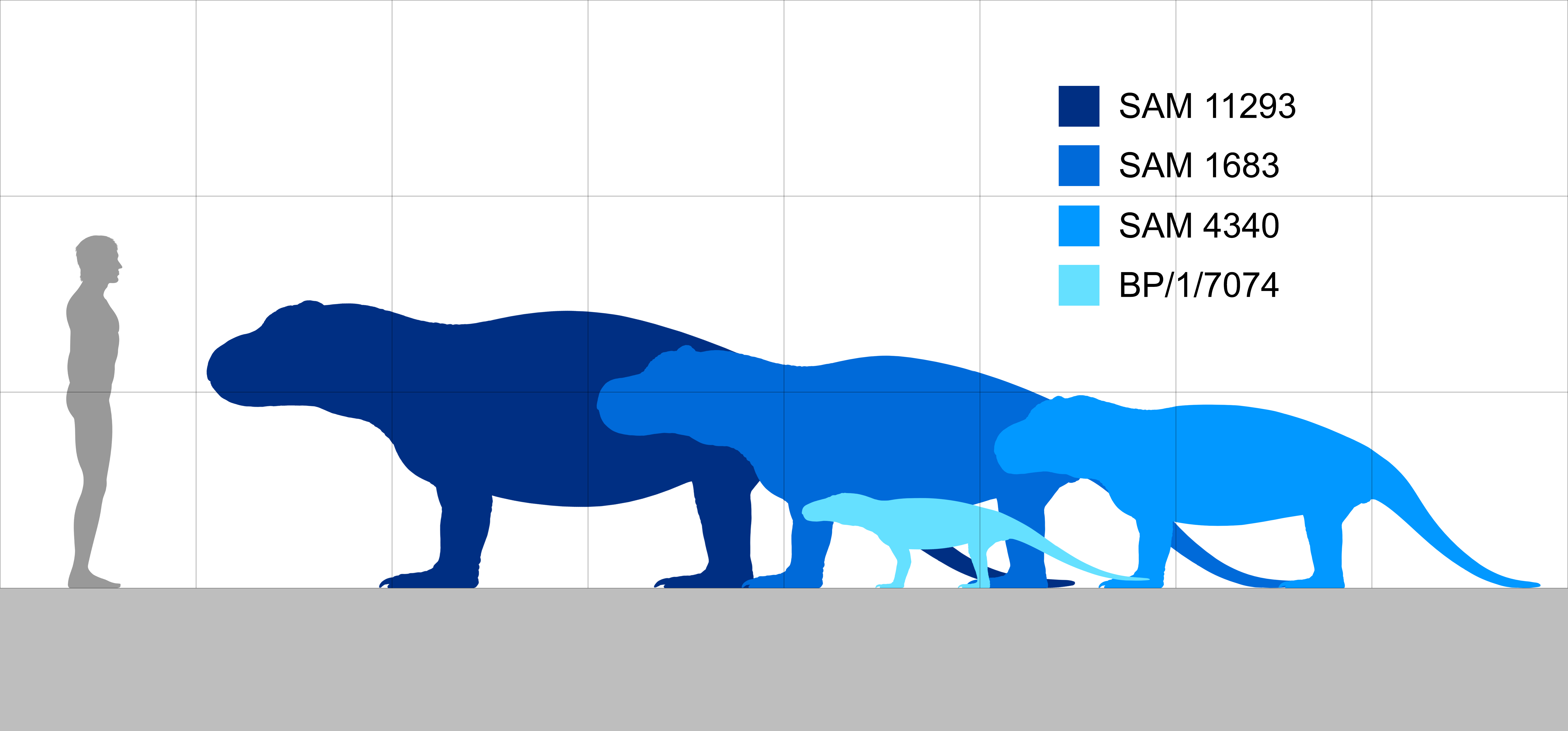
Anteosaurinae
Anteosaurinae is an extinct subfamily of dinocephalian therapsids. It is one of two subfamilies in the family Anteosauridae, the other being Syodontinae. Description These are very specialized, very large anteosaurs. The postcanine teeth are further reduced. Deepening of the postorbital region of the skull (behind the eyes) produced a larger temporal opening, indicating more muscle mass. The boss on the angular (rear of the jaw) has become very prominent, again, another sign of powerful jaw muscles. These huge animals were clearly formidable predators. In the Anteosaurinae, pachyostosis is taken to extremes. The dorsal (upper) surface of the nasal, frontal, and postfrontals (around and between/above the eyes) is thickened and rugose in the same manner as the tapinocephalids. Nevertheless these animals are too specialized and too late in time to have been the ancestors of the herbivorous tapinocephalids, so these characteristics evolved independently. Boonstra notes that the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anteosauridae
Anteosauridae is an extinct family of large carnivorous dinocephalian therapsids that are known from the Middle Permian of Asia, Africa, and South America.These animals were by far the largest predators of the Permian period, with skulls reaching 80 cm in length in adult individuals, far larger than the biggest gorgonopsian. Description Anteosaurids are characterized by very large pointed incisors and canines, bulbous spatulate (spoon shaped) postcanines, a very strongly upturned margin of the premaxilla, so the front of mouth curves strongly upwards, and a long, very robust lower jaw (Boonstra 1963). Anteosaurids distinguished from ''Brithopus'' and other non-anteosaurid anteosaurians by the presence of a large thickened region or "boss" on the side of the angle of the lower jaw; this was probably used in intraspecific behaviour. In '' Doliosauriscus'' and ''Anteosaurus'', not only was this boss very prominent, but the bones were very thick and rugose. The same situation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syodontinae
Syodontinae is a group of dinocephalian therapsids. It is one of two subfamilies in the family Anteosauridae, the other being Anteosaurinae. They are known from the Middle Permian Period of what is now Russia and South Africa. One of the best known syodontines is ''Syodon'' from Russia. The South African form ''Australosyodon'', is one of the earliest known Gondwanan anteosaurs. Description Syodontines lack the boss on the lower jaw that characterises the related anteosaurines, and they have often been considered more primitive in this respect. Classification Below is a cladogram showing syodontine relationships from a 2012 phylogenetic In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ... study of anteosaurians: References Anteosaurs Guadalupian first appearances Guada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium ( facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachyostosis
Pachyostosis is a non-pathological condition in vertebrate animals in which the bones experience a thickening, generally caused by extra layers of lamellar bone. It often occurs together with bone densification (osteosclerosis), reducing inner cavities. This joint occurrence is called pachyosteosclerosis. However, especially in the older literature, "pachyostosis" is often used loosely, referring to all osseous specializations characterized by an increase in bone compactness and/or volume. It occurs in both terrestrial and, especially, aquatic or semi-aquatic vertebrates. In aquatic animals, such as seacows (manatees and dugongs), ''Thalassocnus'', and plesiosaurs, pachyostosis in the thoracic region provides (or provided) ballast against the air-filled lungs. This maintains neutral buoyancy in aquatic habitats. Most giant deer showed pronounced pachyostosis of the mandible and skull. It has been suggested that this served to store minerals for antler growth. Many Pachycephalosau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontogeny
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the study of the entirety of an organism's lifespan. Ontogeny is the developmental history of an organism within its own lifetime, as distinct from phylogeny, which refers to the evolutionary history of a species. Another way to think of ontogeny is that it is the process of an organism going through all of the developmental stages over its lifetime. The developmental history includes all the developmental events that occur during the existence of an organism, beginning with the changes in the egg at the time of fertilization and events from the time of birth or hatching and afterward (i.e., growth, remolding of body shape, development of secondary sexual characteristics, etc.). While developmental (i.e., ontogenetic) processes can influence sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterygoid Bone
The pterygoid is a paired bone forming part of the palate of many vertebrates, behind the palatine bone In anatomy, the palatine bones () are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxillae, they comprise the hard palate. (''Palate'' is derived from the Latin ''pa ...s. It is a flat and thin lamina, united to the medial side of the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone, and to the perpendicular lamina of the palatine bone. Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process (anatomy)
In anatomy, a process ( la, processus) is a projection or outgrowth of tissue from a larger body. For instance, in a vertebra, a process may serve for muscle attachment and leverage (as in the case of the transverse and spinous processes), or to fit (forming a synovial joint), with another vertebra (as in the case of the articular processes).Moore, Keith L. et al. (2010) ''Clinically Oriented Anatomy'', 6th Ed, p.442 fig. 4.2 The word is used even at the microanatomic level, where cells can have processes such as cilia or pedicels. Depending on the tissue, processes may also be called by other terms, such as ''apophysis'', ''tubercle'', or ''protuberance''. Examples Examples of processes include: *The many processes of the human skull: ** The mastoid and styloid processes of the temporal bone ** The zygomatic process of the temporal bone ** The zygomatic process of the frontal bone ** The orbital, temporal, lateral, frontal, and maxillary processes of the zygomatic bone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |