|
Sinningia Speciosa
''Sinningia speciosa'', sometimes known in the horticultural trade as gloxinia, is a Tuber, tuberous member of the flowering plant native to Brazil within the family Gesneriaceae. Originally included in the genus ''Gloxinia (genus), Gloxinia'' in 1817, it was reclassified to ''Sinningia''. Showy ''S. speciosa'' hybrids are still sometimes referred to simply as "gloxinia", although this name is now technically incorrect. The name florist's gloxinia is now sometimes used to distinguish it from the Rhizome, rhizomatous species now included in the genus ''Gloxinia (genus), Gloxinia''. Another common name is Brazilian gloxinia. The plants produce large, velvety, brightly colored flowers and are popular Houseplant, houseplants. Cultural requirements are similar to those of Streptocarpus sect. Saintpaulia, African violets except that ''S. speciosa'' generally requires more light and often has a Dormancy, dormant period, when the tuber should be kept cool and dry until it resprouts. Cul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Ernest Baillon
Henri Ernest Baillon was a French botanist and physician. He was born in Calais on 30 November 1827 and died in Paris on 19 July 1895. Baillon spent his professional life as a professor of natural history, and he published numerous works on botany. He was appointed to the Légion d'honneur in 1867 and joined the Royal Society in 1894. Baillon put together the "Dictionnaire de botanique", for which Auguste Faguet produced the wood engravings. The plant genus '' Baillonia'' (family Verbenaceae) was named in his honor by Henri Théophile Bocquillon Henri Théophile Bocquillon (5 June 1834, Crugny – 15 May 1884, Paris) was a French botanist. In Paris, he successively worked as an instructor at the Lycée Napoleon (from 1858), Lycée Louis-le-Grand (from 1862), Lycée Henri-IV (from .... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuber
Tubers are a type of enlarged structure used as storage organs for nutrients in some plants. They are used for the plant's perennation (survival of the winter or dry months), to provide energy and nutrients for regrowth during the next growing season, and as a means of asexual reproduction. ''Stem tubers'' form thickened rhizomes (underground stems) or stolons (horizontal connections between organisms); well known species with stem tubers include the potato and yam. Some writers also treat modified lateral roots (''root tubers'') under the definition; these are found in sweet potatoes, cassava, and dahlias. Terminology The term originates from the Latin , meaning "lump, bump, swelling". Some writers define the term "tuber" to mean only structures derived from stems; others use the term for structures derived from stems or roots., p. 124 Stem tubers A stem tuber forms from thickened rhizomes or stolons. The top sides of the tuber produce shoots that grow into typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowering Plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants that produce their seeds enclosed within a fruit. They are by far the most diverse group of land plants with 64 orders, 416 families, approximately 13,000 known genera and 300,000 known species. Angiosperms were formerly called Magnoliophyta (). Like gymnosperms, angiosperms are seed-producing plants. They are distinguished from gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within their seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from the common ancestor of all living gymnosperms before the end of the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. The closest fossil relatives of flowering plants are uncertain and contentious. The earliest angiosperm fossils ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population, seventh most populous. Its capital is Brasília, and List of cities in Brazil by population, its most populous city is São Paulo. The federation is composed of the union of the 26 States of Brazil, states and the Federal District (Brazil), Federal District. It is the largest country to have Portuguese language, Portuguese as an List of territorial entities where Portuguese is an official language, official language and the only one in the Americas; one of the most Multiculturalism, multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass Immigration to Brazil, immigration from around the world; and the most populous Catholic Church by country, Roman Catholic-major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gesneriaceae
Gesneriaceae, the gesneriad family, is a family of flowering plants consisting of about 152 genera and ca. 3,540 species in the tropics and subtropics of the Old World (almost all Didymocarpoideae) and the New World (most Gesnerioideae), with a very small number extending to temperate areas. Many species have colorful and showy flowers and are cultivated as ornamental plants. Etymology The family name is based on the genus '' Gesneria'', which honours Swiss naturalist and humanist Conrad Gessner. Description Most species are herbaceous perennials or subshrubs but a few are woody shrubs or small trees. The phyllotaxy is usually opposite and decussate, but leaves have a spiral or alternate arrangement in some groups. As with other members of the Lamiales the flowers have a (usually) zygomorphic corolla whose petals are fused into a tube and there is no one character that separates a gesneriad from any other member of Lamiales. Gesneriads differ from related families o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloxinia (genus)
''Gloxinia'' is a genus containing three species of tropical rhizomatous herbs in the flowering plant family Gesneriaceae. The species are primarily found in the Andes of South America, but ''Gloxinia perennis'' is also found in Central America and the West Indies, where it has probably escaped from cultivation. ''Gloxinia perennis'' is the original (type) species of the genus, and for much of its history the genus consisted of only ''G. perennis'' and a very small number of other species. The classification of ''Gloxinia'' later changed reflect the 1976 classification of Hans Wiehler, who took a broader view of the genus. A recent analysis of ''Gloxinia'' and related genera based on molecular and morphological work has determined that Wiehler's circumscription of the genus was unnatural, both phylogenetically and morphologically. The analyses demonstrated that the genera ''Anodiscus'' and ''Koellikeria'', each with a single species, were more closely related to ''Gloxinia per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinningia
''Sinningia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Gesneriaceae. It is named after Wilhelm Sinning (1792–1874), a gardener of the Botanische Gärten der Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn. There are about 65 species of tuberous herbaceous perennials, all occurring in Central and South America, with the greatest concentration of species occurring in southern Brazil. The best-known species, '' Sinningia speciosa'', was originally introduced in cultivation as ''Gloxinia speciosa'' and is still commonly known to gardeners and in the horticultural trade as "gloxinia", although this is now considered incorrect. The true genus '' Gloxinia'' is distinguished by having scaly rhizomes rather than tubers. ''Sinningia'' species often grow on rocks or cliffs and most are pollinated by hummingbirds or bees but ''Sinningia brasiliensis'' is bat-pollinated, and ''Sinningia tubiflora'', with large, powerfully fragrant tubular white flowers, is apparently pollinated by sphinx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizome
In botany and dendrology, a rhizome (; , ) is a modified subterranean plant stem that sends out roots and shoots from its nodes. Rhizomes are also called creeping rootstalks or just rootstalks. Rhizomes develop from axillary buds and grow horizontally. The rhizome also retains the ability to allow new shoots to grow upwards. A rhizome is the main stem of the plant that runs underground horizontally. A stolon is similar to a rhizome, but a stolon sprouts from an existing stem, has long internodes, and generates new shoots at the end, such as in the strawberry plant. In general, rhizomes have short internodes, send out roots from the bottom of the nodes, and generate new upward-growing shoots from the top of the nodes. A stem tuber is a thickened part of a rhizome or stolon that has been enlarged for use as a storage organ. In general, a tuber is high in starch, e.g. the potato, which is a modified stolon. The term "tuber" is often used imprecisely and is sometimes applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houseplant
A houseplant, sometimes known as a pot plant, potted plant, or an indoor plant, is an ornamental plant that is grown indoors. As such, they are found in places like residences and offices, mainly for decorative purposes. Common houseplants are usually tropical or semi-tropical, and are often epiphytes, succulents or cacti. Cultural history Early history The history of houseplants is intertwined with the history of container gardening in general. Ancient Egyptians and Sumerians grew ornamental and fruiting plants in decorative containers. Ancient Greeks and the Romans cultivated laurel trees in earthenware vessels. In ancient China, potted plants were shown at garden exhibitions over 2,500 years ago. In the medieval era, gillyflowers were displayed in containers. Early modern era In the Renaissance, plant collectors and affluent merchants from Italy, the Netherlands and Belgium imported plants from Asia Minor and the East Indies. Creeping groundsel was introduced in Malt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptocarpus Sect
''Streptocarpus'' ("twisted fruit" from Greek στρεπτός (''streptos'') "twisted" and καρπός (''carpos'') "fruit") is an Afrotropical genus of flowering plants in the family Gesneriaceae. The genus is native to Afromontane biotopes from central, eastern and southern Africa, including Madagascar and the Comoro Islands. The flowers are five-petalled, salverform tubes, almost orchid-like in appearance, and hover or arch over the plant, while the pointed, elongate fruit is of a helical form similar to that of the "tusk" of a narwhal. In the wild, species can be found growing on shaded rocky hillsides or cliffs, on the ground, in rock crevices, and almost anywhere the seed can germinate and grow. For the home, there are now many hybrids of various colours and forms available. Although generally referred to simply as "Streptocarpus" or "Streps", the common name for subgenus ''Streptocarpus'' is Cape primrose, referring to the nativity of several species to South Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dormancy
Dormancy is a period in an organism's life cycle when growth, development, and (in animals) physical activity are temporarily stopped. This minimizes metabolic activity and therefore helps an organism to conserve energy. Dormancy tends to be closely associated with environmental conditions. Organisms can synchronize entry to a dormant phase with their environment through predictive or consequential means. Predictive dormancy occurs when an organism enters a dormant phase ''before'' the onset of adverse conditions. For example, photoperiod and decreasing temperature are used by many plants to predict the onset of winter. Consequential dormancy occurs when organisms enter a dormant phase ''after'' adverse conditions have arisen. This is commonly found in areas with an unpredictable climate. While very sudden changes in conditions may lead to a high mortality rate among animals relying on consequential dormancy, its use can be advantageous, as organisms remain active longer an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
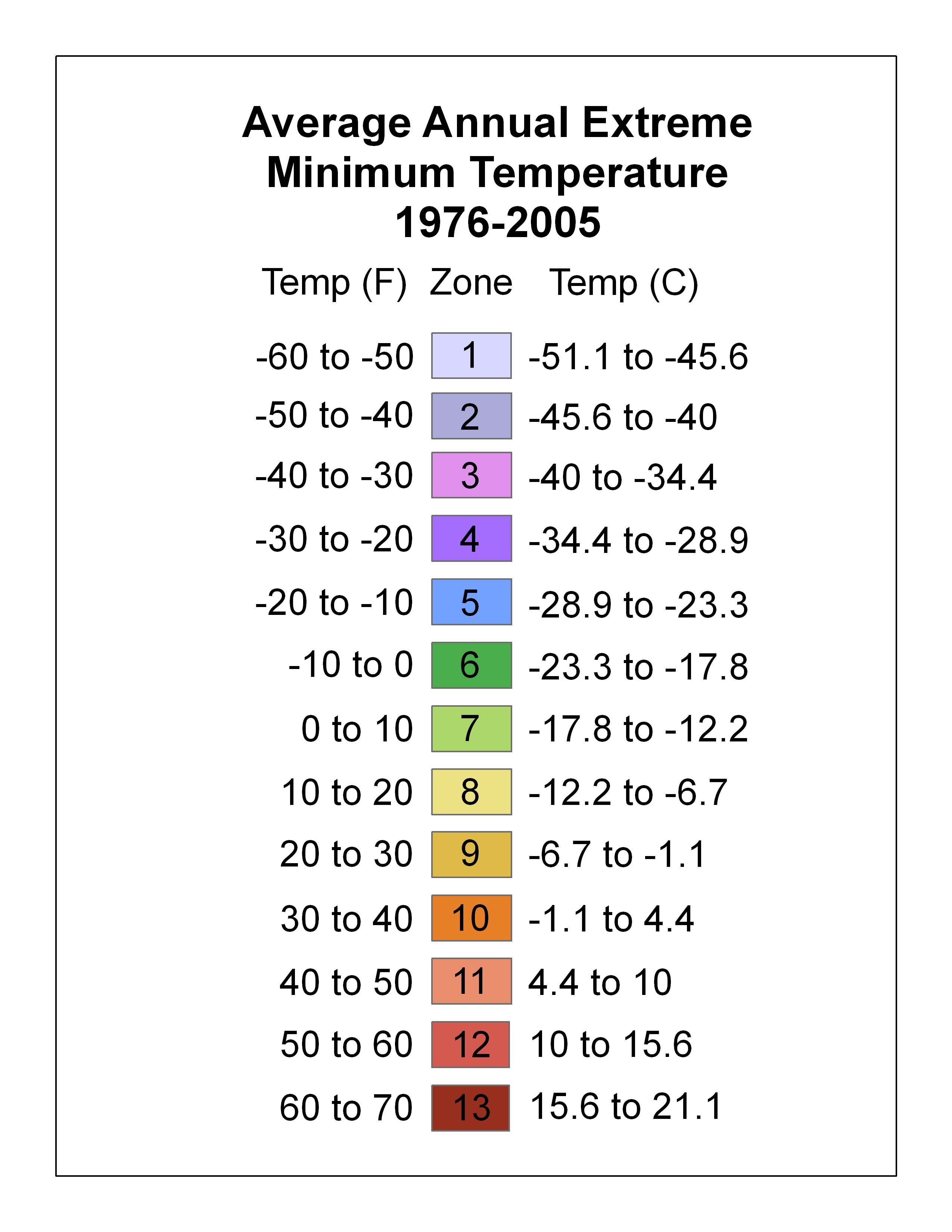
Hardiness Zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely used system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a rough guide for landscaping and gardening, defines 13 zones by long-term average annual extreme minimum temperatures. It has been adapted by and to other countries (such as Canada) in various forms. Unless otherwise specified, in American contexts "hardiness zone" or simply "zone" usually refers to the USDA scale. For example, a plant may be described as "hardy to zone 10": this means that the plant can withstand a minimum temperature of 30 °F (−1.1 °C) to 40 °F (4.4 °C). Other hardiness rating schemes have been developed as well, such as the UK Royal Horticultural Society and US Sunset Western Garden Book systems. A heat zone (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)