|
Singus
Singus or Singos ( grc, Σίγγος) was a town of Sithonia in the Chalcidice in ancient Macedonia, upon the gulf to which it gave its name, the Singitic Gulf (Σιγγιτικὸς κόλπος). It is cited by Herodotus as one of the cities, along with Assa, Pilorus and Sarta, located near Mount Athos, which Xerxes had ordered to open a channel through which his fleet passed. From these cities he recruited troops, in his expedition of the year 480 BCE against Greece. It belonged to the Delian League since it appears in the tribute registry of Athens from 454/3 to 433/2 BCE. In the Peace of Nicias of 421 BCE it was stipulated that the inhabitants of Mecyberna, Sane and Singus would live in their own cities under the same conditions as the Olyntihans and Acanthians, which has been interpreted by some historians as Singus was one of the cities that had undergone synoecism with Olynthus in the revolt that took place in the year 432 BCE, and that in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilorus
Pilorus or Piloros ( grc, Πίλωρος) was a town of Sithonia in the Chalcidice in ancient Macedonia, upon the Singitic Gulf between Sane and Singus. It is cited by Herodotus as one of the cities, along with Assa, Singus, and Sarta, located near Mount Athos which Xerxes had ordered to open a channel through which his fleet passed. From these cities he recruited troops, in his expedition of the year 480 BCE against Greece. It belonged to the Delian League since it appears in the tribute registry of Athens in 434/3 BCE. Its site is located near modern Pyrgadikia Pyrgadikia ( el, Πυργαδίκια) is a Greek village in the Chalkidiki peninsula. It is located in the south-east part of Chalkidiki (approximately 110 km south-east of Thessaloniki), built on the coast of Siggitikos bay (part of Aegean s .... References Populated places in ancient Macedonia Former populated places in Greece Geography of ancient Chalcidice Members of the Delian League [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarta (Chalcidice)
Sarta or Sarte ( grc, Σάρτη) was a maritime town on the Sithonia peninsula of Chalcidice, in ancient Macedonia, on the Singitic Gulf between Singus and the promontory of Ampelus. It is cited by Herodotus as one of the cities—together with Pilorus, Singus, and Assa—located near Mount Athos, which Xerxes ordered to open a channel through which his fleet passed, and from which he recruited troops in his expedition of the year 480 BCE against Greece. It belonged to the Delian League, since it appears in the tribute registry of Athens from 434/3 to 415/4 BCE. Its site is located about south of modern Sarti The Italian language surname Sarti is derived from the occupation of tailor. Notable people with the surname include: *Adolfo Sarti (1928–1992), Italian Christian Democrat politician *Alessio Sarti (born 1979), Italian football (soccer) goalkee .... References Populated places in ancient Macedonia Former populated places in Greece Geography of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assa (Chalcidice)
Assa ( grc, Ἄσσα), also known as Assera (Ἄσσηρα), was a town of Chalcidice, in ancient Macedonia, on the Singitic Gulf. It is cited by Herodotus as one of the cities—together with Pilorus, Singus and Sarte—located near Mount Athos which Xerxes ordered to open a channel through which his fleet passed, and from which he recruited troops in his expedition of the year 480 BCE against Greece. It belonged to the Delian League since it appears in the tribute registry of Athens from 454/3 to 433/2 BCE. Pliny the Elder calls the town Cassera, and its territory was called Assyrytis (Ἀσσυρῦτις) by Aristotle.Aristotle Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ..., ''Hist. An.'' 3.12 Here was a river which was called the Psychrus or Psychros (Ψ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sithonia
Sithonia ( el, Σιθωνία), also known as Longos, is a peninsula of Chalkidiki, which itself is located on a larger peninsula within Greece. The Kassandra Peninsula lies to the west of Sithonia and the Mount Athos peninsula to the east. Sithonia is also a municipality, covering the Sithonia peninsula. The seat of the municipality is the town Nikiti. Geography Gulfs that surround the peninsula are the Singitic Gulf to the east and the Toronean Gulf to the west. The peaks of Itamos and Dragoudelis are in the center of the peninsula. The landscape is covered with vineyards, forests, grasslands, shrubland and mountains. Amongst the many historic places in Sithonia is the ancient city, the castle and the church of Agios Athanasios in Toroni, the windmills in Sykia and the 16th century church in Nikiti. In the northern part of the peninsula are the popular beaches of Ai Giannis, Kalogria, Elia and Lagomandra on the west coast and Livrochios, Karidi, Kavourotripes and Platani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
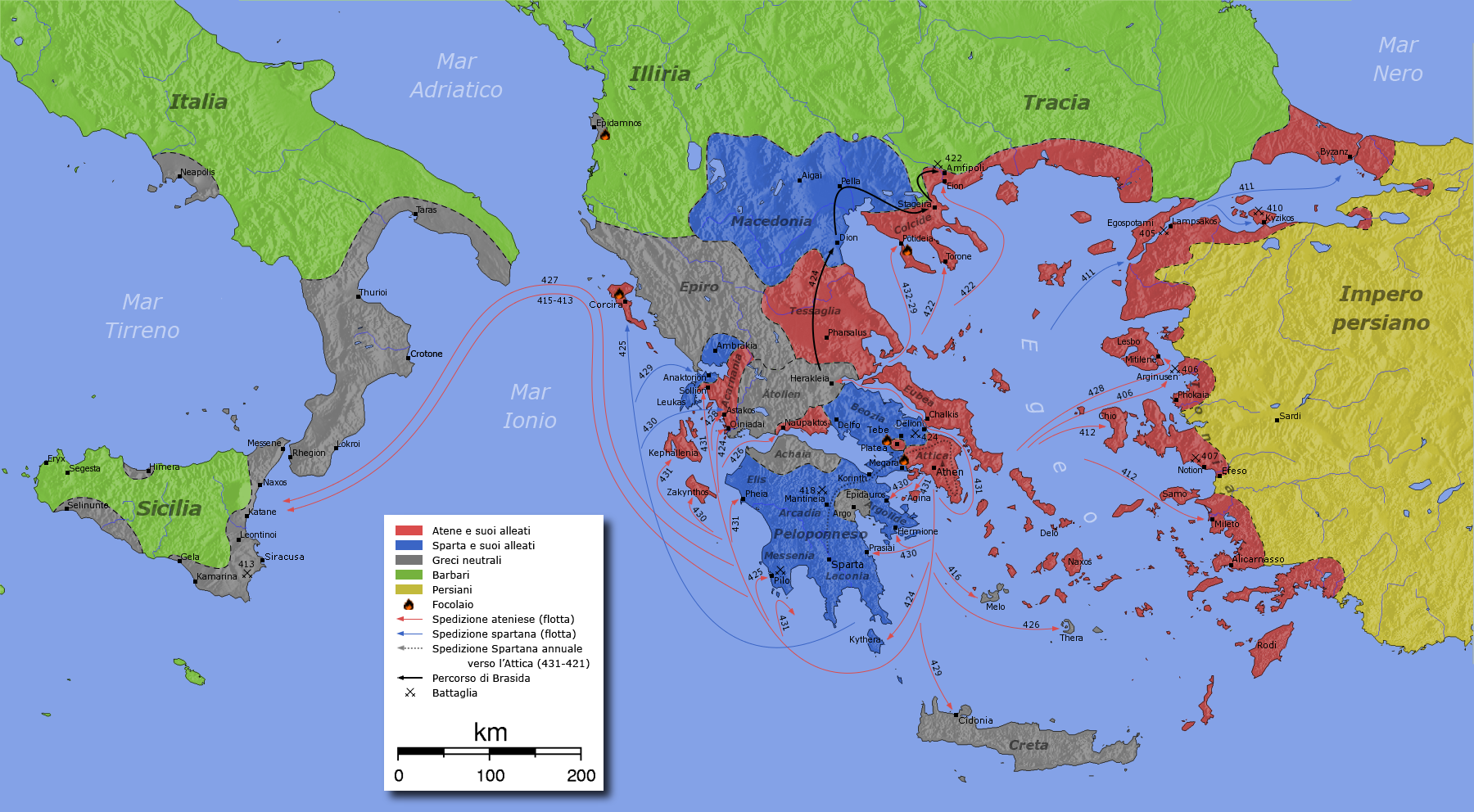
Peace Of Nicias
The Peace of Nicias was a peace treaty signed between the Greek city-states of Athens and Sparta in March 421 BC that ended the first half of the Peloponnesian War. In 425 BC, the Spartans had lost the battles of Pylos and Sphacteria, a severe defeat resulting in the Athenians holding 292 prisoners. At least 120 were Spartiates, who had recovered by 424 BC, when the Spartan general Brasidas captured Amphipolis. In the same year, the Athenians suffered a major defeat in Boeotia at the Battle of Delium, and in 422 BC, they were defeated again at the Battle of Amphipolis in their attempt to take back that city. Both Brasidas, the leading Spartan general, and Cleon, the leading politician in Athens, were killed at Amphipolis. By then, both sides were exhausted and ready for peace. The negotiations were started by Pleistoanax, King of Sparta, and Nicias, an Athenian general. The most amicable proposal was to return everything to the prewar state except for Nisaea and Plataea. Athens w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Greece
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Ancient Macedonia
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agios Nikolaos, Chalkidiki
Agios Nikolaos ( el, Άγιος Νικόλαος, meaning Saint Nicholas) is a village located 110 kilometers south-east of Thessaloniki on the Chalkidiki peninsula in Macedonia, Greece. Geography The village Agios Nikolaos itself is 2 km inland from the Singitic Gulf. However, its territory is quite extensive. To the north-east it borders the village of Pyrgadikia at Salonikiou Beach (8 km from Agios Nikolaos). To the north it borders the village of Metangitsi. In the west and south-west it is neighboring the village of Nikiti (9 km from Agios Nikolaos). To the south it borders the village of Sarti at Armenistis Beach (28 km from Agios Nikolaos). Landscapes Agios Nikolaos' landscapes show a substantial variability. In the plains east and south-east of the village agriculture predominates with olive trees as the main cultivated plant. Toward the south, rises the Itamos mountain range of Sithonia and is completely covered with pine forest. Towards its northeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see things at great distance as if they were nearby was also called "Strabo". (; el, Στράβων ''Strábōn''; 64 or 63 BC 24 AD) was a Greek geographer, philosopher, and historian who lived in Asia Minor during the transitional period of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. Life Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus (in present-day Turkey) in around 64BC. His family had been involved in politics since at least the reign of Mithridates V. Strabo was related to Dorylaeus on his mother's side. Several other family members, including his paternal grandfather had served Mithridates VI during the Mithridatic Wars. As the war drew to a close, Strabo's grandfather had turned several Pontic fortress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synoecism
Synoecism or synecism ( ; grc, συνοικισμóς, ''sunoikismos'', ), also spelled synoikism ( ), was originally the amalgamation of villages in Ancient Greece into ''poleis'', or city-states. Etymologically the word means "dwelling together (''syn'') in the same house (''oikos'')." Subsequently, any act of civic union between polities of any size was described by the word ''synoikismos''. The closest analogy today is the incorporation of a city; in fact, "incorporation" is often used to translate synoikismos, in addition to the Latinized synoecism. Synoecism is opposed to Greek dioecism (διοικισμóς, ''dioikismos''), the creation of independent communities within the territory of a polis. Synoecism is the result of a few major factors, mainly an increase in population density of adjacent settlements, with an incorporation proposed for economic, political or ideological advantages, such as the synoecism of the communities of Attica into Athens, or by imposition o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthus (Greece)
Akanthos ( grc, Ἄκανθος; la, Acanthus) was an ancient Greek city on the Athos peninsula, on the narrow neck of land between the sacred mountain and the mainland, to the northwest of the Xerxes Canal. It was founded in the 7th century BCE as a colony of Andros, itself a colony of Chalcis in Euboea. Chalcidice was multi-cultural. The archaeology of the region suggests that some Hellenes were already there. The site is on the north-east side of Akti, on the most eastern peninsula of Chalcidice. The ancient city extended along a ridge comprising three hills bordering the south-east of modern Ierissos about from it. The ridge dominates the landscape. It is terminated on the north by the coastal road (Vasileos Konstantinou) and the beach between Ierissos and its harbor. The modern city is about equal in size to the ancient site, which is now partially wooded. Remains of an high circuit wall, a citadel, and Hellenistic buildings are visible embedded in the terrain, along w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olynthus
Olynthus ( grc, Ὄλυνθος ''Olynthos'', named for the ὄλυνθος ''olunthos'', "the fruit of the wild fig tree") was an ancient city of Chalcidice Chalkidiki (; el, Χαλκιδική , also spelled Halkidiki, is a peninsula and regional unit of Greece, part of the region of Central Macedonia, in the geographic region of Macedonia in Northern Greece. The autonomous Mount Athos region c ..., built mostly on two flat-topped hills 30–40m in height, in a fertile plain at the head of the Gulf of Torone, near the neck of the peninsula of Pallene, Chalcidice, Pallene, about 2.5 kilometers from the sea, and about 60 ''stadia'' (c. 9–10 kilometers) from Potidaea, Poteidaea. Artefacts found during the excavations of the site are exhibited in the Archaeological Museum of Olynthos. History Olynthus (mythology), Olynthus, son of Heracles, or the river god Strymon (mythology), Strymon, was considered the mythological founder of the town. The South Hill bore a small Neo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |