|
Single Port Laparoscopy
Single-port laparoscopy (SPL) is a recently developed technique in laparoscopic surgery. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which the surgeon operates almost exclusively through a single entry point, typically the patient's navel. Unlike a traditional multi-port laparoscopic approach, SPL leaves only a single small scar. Technique, equipment and training SPL is accomplished through a single 20 mm incision in the navel (umbilicus or belly button), or through only an 11 mm incision in the navel, minimizing the scarring and incisional pain associated with the multiple points of entry used during traditional laparoscopic surgery. Specialized equipment for SPL surgery falls into two broad categories; access ports and hand instruments. There are a number of different access ports, including GelPOINT system from Applied Medical, the SILS device from Covidien, the TriPort+, TriPort15 and QuadPort+ a from Advanced Surgical Concepts and the Uni-X from Pnavel. Hand ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SILS Gastric Banding
Single-incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS) is an advanced, minimally invasive (keyhole) procedure in which the surgeon operates almost exclusively through a single entry point, typically the patient's umbilicus (navel). Special articulating instruments and access ports eliminate the need to place trochars externally for triangulation, thus allowing the creation of a small, solitary portal of entry into the abdomen. SILS has been used for several common surgical procedures including hernia repair, cholecystectomy and nephrectomy. The SILS technique has also been used in weight-loss surgery for both sleeve gastrectomy and – more recently – for laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB). __TOC__ The adjustable gastric band The development of the adjustable gastric band in the mid-1980s was a watershed in the treatment of obesity. The father of the gastric band is generally agreed to have been Lubomyr Kuzmak (1929–2006), a Ukrainian born surgeon who had emigrated to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
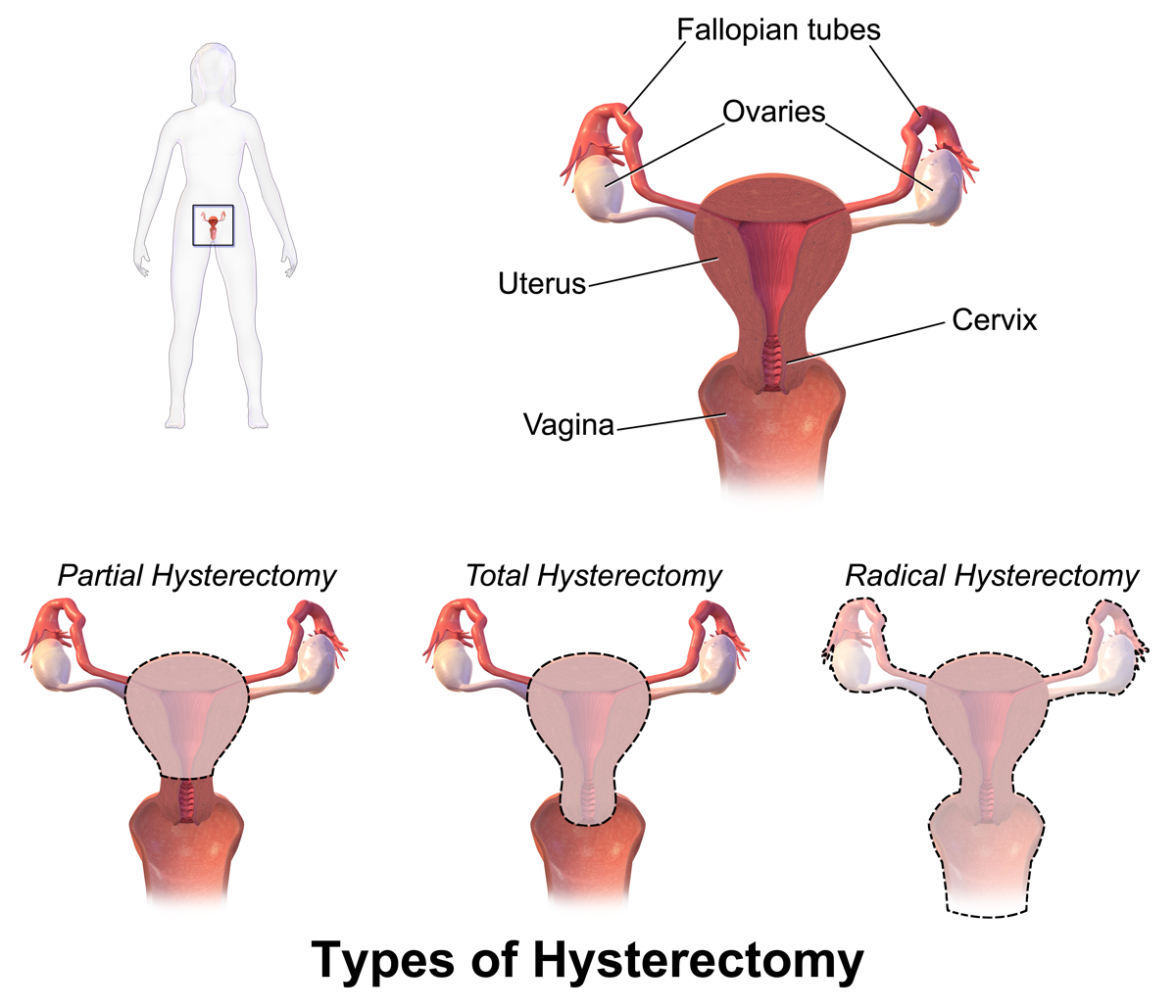
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus. It may also involve removal of the cervix, ovaries (oophorectomy), Fallopian tubes (salpingectomy), and other surrounding structures. Usually performed by a gynecologist, a hysterectomy may be total (removing the body, fundus, and cervix of the uterus; often called "complete") or partial (removal of the uterine body while leaving the cervix intact; also called "supracervical"). Removal of the uterus renders the patient unable to bear children (as does removal of ovaries and fallopian tubes) and has surgical risks as well as long-term effects, so the surgery is normally recommended only when other treatment options are not available or have failed. It is the second most commonly performed gynecological surgical procedure, after cesarean section, in the United States. Nearly 68 percent were performed for conditions such as endometriosis, irregular bleeding, and uterine fibroids. It is expected that the frequency of hysterectom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are inserted directly into the organ. There are many types of endoscopies. Depending on the site in the body and type of procedure, an endoscopy may be performed by either a doctor or a surgeon. A patient may be fully conscious or anaesthesia, anaesthetised during the procedure. Most often, the term ''endoscopy'' is used to refer to an examination of the upper part of the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract, known as an esophagogastroduodenoscopy. For nonmedical use, similar instruments are called borescopes. History Adolf Kussmaul was fascinated by sword swallowers who would insert a sword down their throat without gagging. This drew inspiration to insert a camera, the next problem to solve was how to insert a source of light, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Orifice Translumenal Endoscopic Surgery
Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) is a surgical technique whereby "scarless" abdominal operations can be performed with an endoscope passed through a natural orifice (mouth, urethra, anus, vagina, etc.) then through an internal incision in the stomach, vagina, bladder or colon, thus avoiding any external incisions or scars. Memic's hominis robotic system is the first and only FDA-authorized surgical robotic platform for NOTES procedures. The system is currently at use for transvaginal hysterectomies through the Rectouterine pouch - the removal of the uterus, along with one or both of the fallopian tubes and ovaries, in cases where there is no cancer present, as well as with the removal of ovarian cysts See also * Single port laparoscopy Single-port laparoscopy (SPL) is a recently developed technique in laparoscopic surgery. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which the surgeon operates almost exclusively through a single entry point, typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland Clinic is a nonprofit American academic medical center based in Cleveland, Ohio. Owned and operated by the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, an Ohio nonprofit corporation established in 1921, it runs a 170-acre (69 ha) campus in Cleveland, as well as 11 affiliated hospitals, 19 family health centers in Northeast Ohio, and hospitals in Florida and Nevada. International operations include the Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi hospital in the United Arab Emirates and Cleveland Clinic Canada, which has two executive health and sports medicine clinics in Toronto."Facts & Figures" Cleveland Clinic. Another hospital campus in the United Kingdom, Cleveland Clinic London, opened to outpatients in 2021 and is scheduled to fully open in 2022. Tomislav Mihaljevic is the president and CEO. Cleveland Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrocolpopexy
Uterine prolapse is when the uterus descends towards or through the opening of the vagina. Symptoms may include vaginal fullness, pain with sex, trouble urinating, urinary incontinence, and constipation. Often it gets worse over time. Low back pain and vaginal bleeding may also occur. Risk factors include pregnancy, childbirth, obesity, constipation, and chronic coughing. Diagnosis is based on examination. It is a form of pelvic organ prolapse, together with bladder prolapse, large bowel prolapse, and small bowel prolapse. Preventive efforts include managing chronic breathing problems, not smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight. Mild cases may be treated with a pessary together with hormone replacement therapy. More severe cases may require surgery such as a vaginal hysterectomy. About 14% of women are affected. It occurs most commonly after menopause. Causes The most common cause of uterine prolapse is trauma during childbirth, in particular multiple or difficult bir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephrectomy
A nephrectomy is the surgical removal of a kidney, performed to treat a number of kidney diseases including kidney cancer. It is also done to remove a normal healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor, which is part of a kidney transplant procedure. History The first recorded nephrectomy was performed in 1861 by Erastus B. Wolcott in Wisconsin. The patient had had a large tumor and the operation was initially successful, but the patient died fifteen days later. The first planned nephrectomy was performed by the German surgeon Gustav Simon on August 2, 1869, in Heidelberg. Simon practiced the operation beforehand in animal experiments. He proved that one healthy kidney can be sufficient for urine excretion in humans. Indications There are various indications for this procedure, including renal cell carcinoma, a non-functioning kidney (which may cause high blood pressure) and a congenitally small kidney (in which the kidney is swelling, causing it to press on nerves, which ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
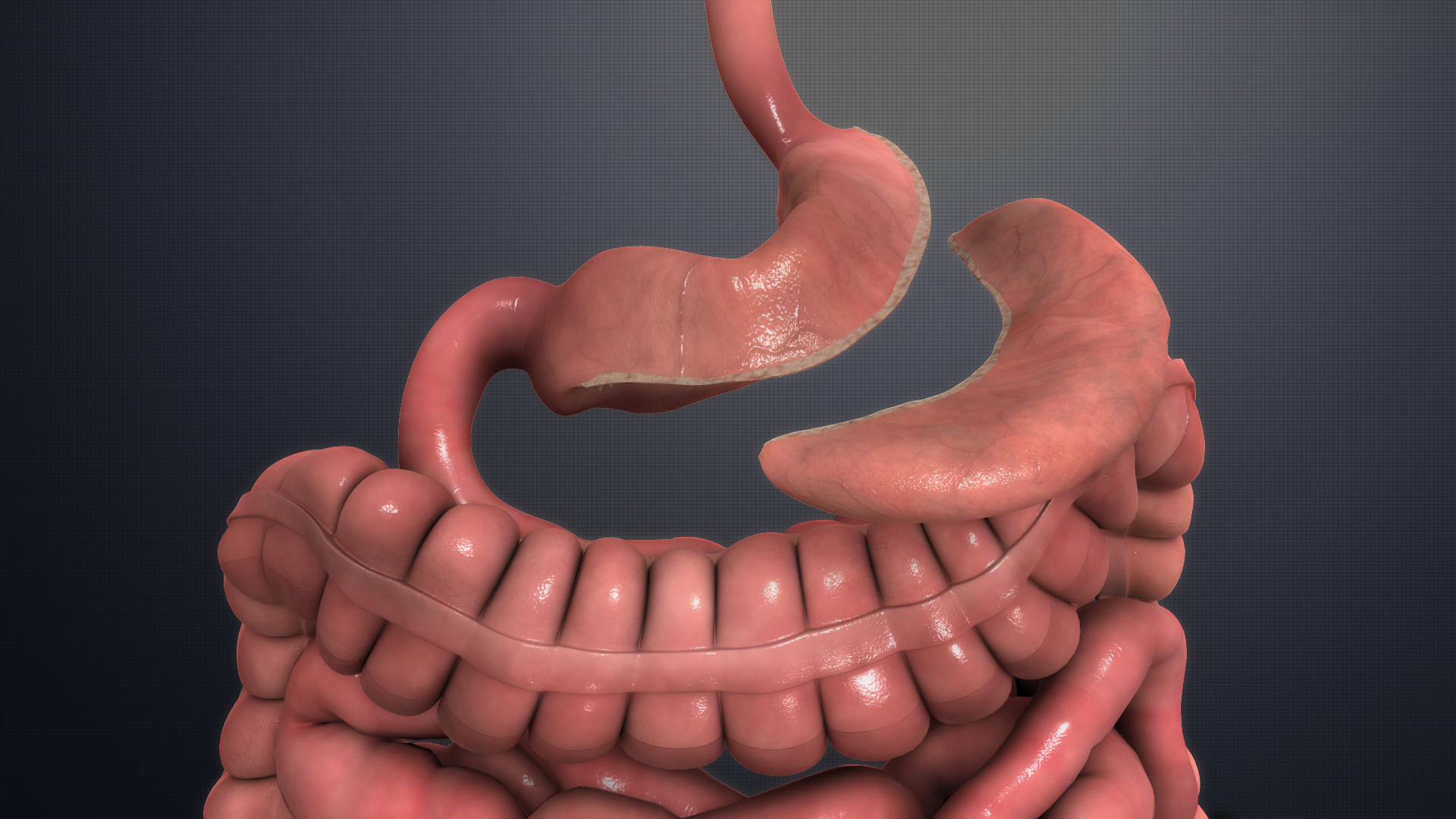
Sleeve Gastrectomy
Sleeve gastrectomy is a surgical weight-loss procedure in which the stomach is reduced to about 15% of its original size, by surgical removal of a large portion of the stomach along the greater curvature. The result is a sleeve or tube like structure. The procedure permanently reduces the size of the stomach, although there could be some dilation of the stomach later on in life. The procedure is generally performed laparoscopically and is irreversible. A meta-analysis of 174,772 participants published in The Lancet in 2021 found that bariatric surgery was associated with 59% and 30% reduction in all-cause mortality among obese adults with or without type 2 diabetes respectively. This meta-analysis also found that median life-expectancy was 9.3 years longer for obese adults with diabetes who received bariatric surgery as compared to routine (non-surgical) care, whereas the life expectancy gain was 5.1 years longer for obese adults without diabetes. Procedure Sleeve gastrectomy w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colectomy
Colectomy ('' col-'' + '' -ectomy'') is bowel resection of the large bowel ( colon). It consists of the surgical removal of any extent of the colon, usually segmental resection (partial colectomy). In extreme cases where the entire large intestine is removed, it is called total colectomy, and proctocolectomy ('' procto-'' + ''colectomy'') denotes that the rectum is included. Indications Some of the most common indications for colectomy are: * Colon cancer * Diverticulitis and diverticular disease of the large intestine * Trauma * Inflammatory bowel disease such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease. Colectomy neither cures nor eliminates Crohn's disease, instead only removing part of the entire diseased large intestine. A colectomy is considered a "cure" for ulcerative colitis because the disease attacks only the large intestine and therefore will not be able to flare up again if the entire large intestine (cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon and si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.MedlinePlus > Laparoscopy Update Date: 21 August 2009. Updated by: James Lee, MD // No longer valid Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive procedure, bandaid surgery, or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique. There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus an exploratory laparotomy. These include reduced pain due to smaller incisions, reduced hemorrhaging, and shorter recovery time. The key element is the use of a laparoscope, a long fiber optic cable system that allows viewing of the affected area by snaking the cable from a more distant, but more easily accessible location. Laparoscopic surgery includes operations within the abdominal or pelvic cavities, whereas keyhole surgery perfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
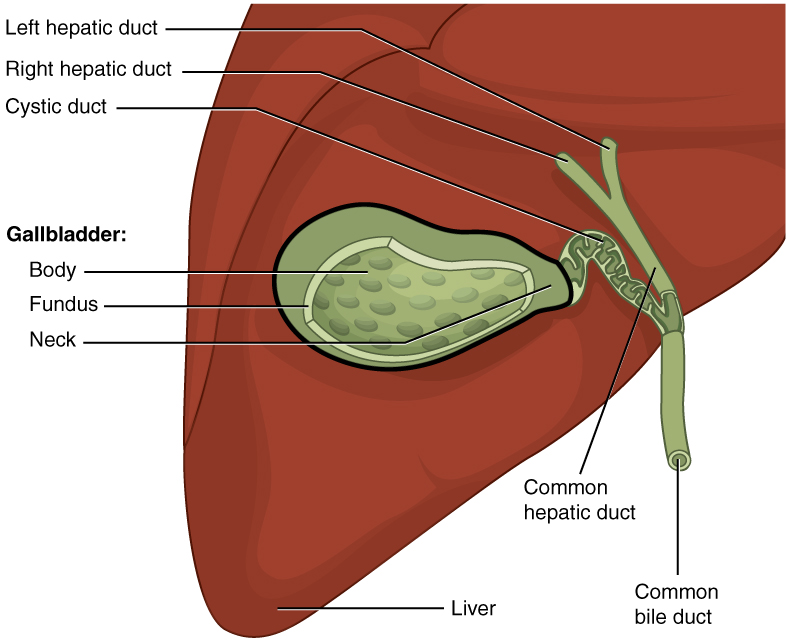
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. In 2011, cholecystectomy was the eighth most common operating room procedure performed in hospitals in the United States. Cholecystectomy can be performed either laparoscopically, or via an open surgical technique. The surgery is usually successful in relieving symptoms, but up to 10 percent of people may continue to experience similar symptoms after cholecystectomy, a condition called postcholecystectomy syndrome. Complications of cholecystectomy include bile duct injury, wound infection, bleeding, retained gallstones, abscess formation and stenosis (narrowing) of the bile duct. Medical use Pain and complications caused by gallstones are the most common reasons for removal of the gallbladder. The gallbladder can also be removed in order to treat biliary dyskinesia or gallbladder cancer. Gallstones are very common but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appendectomy
An appendectomy, also termed appendicectomy, is a Surgery, surgical operation in which the vermiform appendix (a portion of the intestine) is removed. Appendectomy is normally performed as an urgent or emergency procedure to treat complicated acute appendicitis. Appendectomy may be performed Laparoscopic surgery, laparoscopically (as minimally invasive surgery) or as an open operation. Over the 2010s, surgical practice has increasingly moved towards routinely offering laparoscopic appendicectomy; for example in the United Kingdom over 95% of adult appendicectomies are planned as laparoscopic procedures. Laparoscopy is often used if the diagnosis is in doubt, or in order to leave a less visible surgical scar. Recovery may be slightly faster after laparoscopic surgery, although the laparoscopic procedure itself is more expensive and resource-intensive than open surgery and generally takes longer. Advanced pelvic sepsis occasionally requires a lower midline laparotomy. Complicated ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |