|
Simsapa Tree
The Simsapa tree (Pali: ) is mentioned in ancient Buddhist discourses traditionally believed to have been delivered 2,500 years ago. The tree has been identified as either ''Dalbergia sissoo'', a rosewood tree common to India and southeast Asia, or '' Amherstia nobilis'', another South Asian tree, of the family Caesalpiniaceae. Buddhist scriptural references In Buddhism's Pali Canon, there is a discourse entitled, "The Simsapa Grove" ( Samyutta Nikaya 56.31). This discourse is described as having been delivered by the Buddha to monks while dwelling beneath a simsapa grove in the city of Kosambi. In this discourse, the Buddha compares a few simsapa leaves in his hand with the number of simsapa leaves overhead in the grove to illustrate what he teaches (in particular, the Four Noble Truths) and what he does not teach (things unrelated to the holy life). Elsewhere in the Pali Canon, simsapa groves are mentioned in the "Payasi Sutta" (Digha Nikaya 23) and in the "Hatthaka Discours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
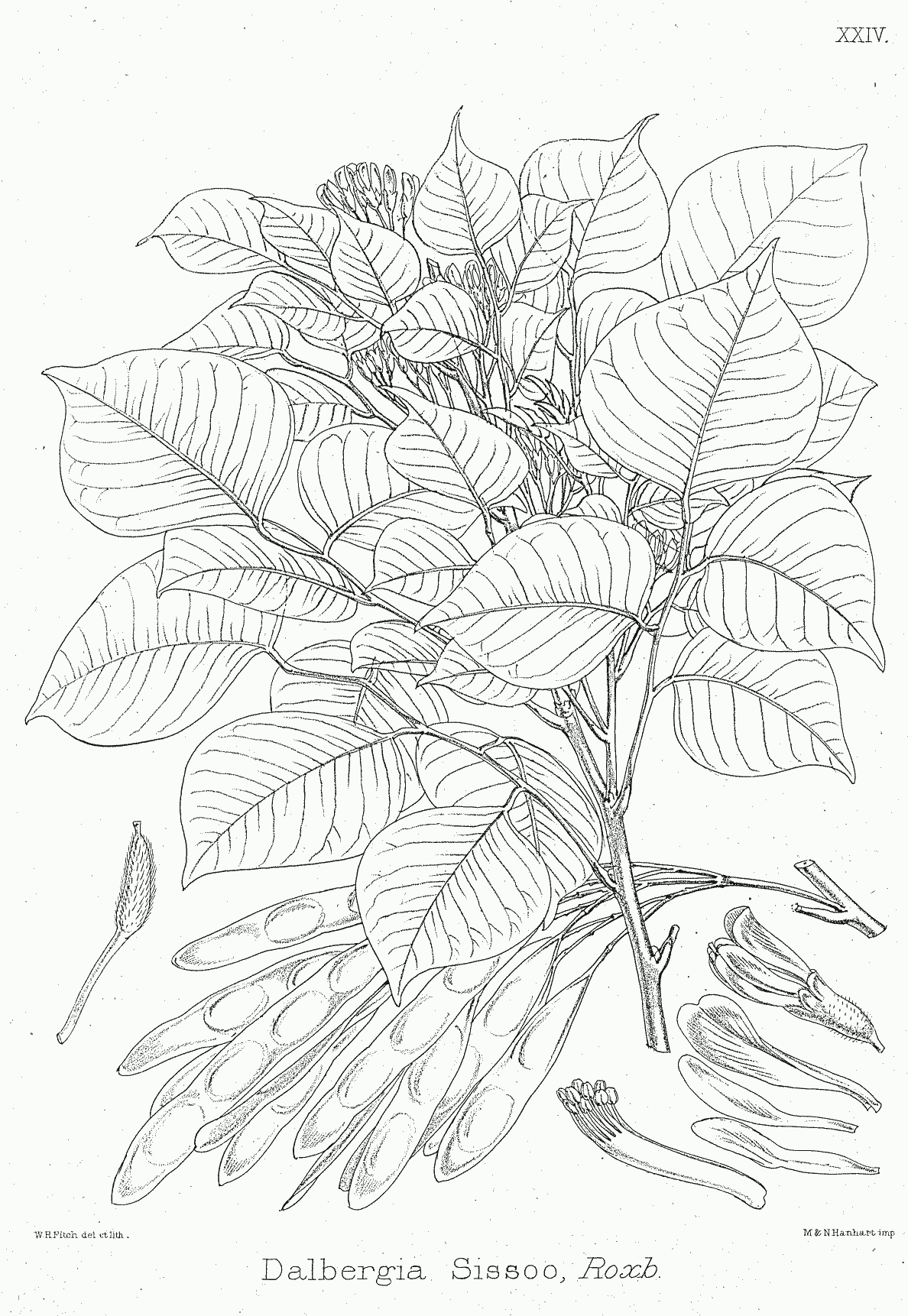
Dalbergia Sissoo Bra24
''Dalbergia'' is a large genus of small to medium-size trees, shrubs and lianas in the pea family, Fabaceae, subfamily Faboideae. It was recently assigned to the informal monophyletic ''Dalbergia'' clade (or tribe): the Dalbergieae. The genus has a wide distribution, native to the tropical regions of Central and South America, Africa, Madagascar and southern Asia. Fossil record A fossil †''Dalbergia phleboptera'' seed pod has been found in a Chattian deposit, in the municipality of Aix-en-Provence in France. Fossils of †''Dalbergia nostratum'' have been found in rhyodacite tuff of Lower Miocene age in Southern Slovakia near the town of Lučenec. Fossil seed pods of †''Dalbergia mecsekense'' have been found in a Sarmatian deposit in Hungary. †''Dalbergia lucida'' fossils have been described from the Xiaolongtan Formation of late Miocene age in Kaiyuan County, Yunnan Province, China. Uses Many species of ''Dalbergia'' are important timber trees, valued for their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosambi
Kosambi (Pali) or Kaushambi (Sanskrit) was an important city in ancient India. It was the capital of the Vatsa kingdom, one of the sixteen mahajanapadas. It was located on the Yamuna River about southwest of its confluence with the Ganges at Prayaga (modern Prayagraj). History During 2nd millennium BCE Ochre Coloured Pottery culture spread in the region. Kosambi was one of the greatest cities in India from the late Vedic period until the end of Maurya Empire with occupation continuing until the Gupta Empire. As a small town, it was established in the late Vedic period, by the rulers of Kuru Kingdom as their new capital. The initial Kuru capital Hastinapur was destroyed by floods, and the Kuru King transferred his entire capital with the subjects to a new capital that he built near the Ganga-Jamuma confluence, which was 56 km away from the southernmost part of the Kuru Kingdom now as Prayagraj previously called Allahabad.During the period prior the Maurya Empire, Kosambi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Publication Society
The Buddhist Publication Society (BPS) is a publishing house with charitable status whose objective is to disseminate the teaching of Gautama Buddha. It was founded in Kandy, Sri Lanka in 1958 by two Sri Lankan lay Buddhists, A.S. Karunaratna and Richard Abeyasekera, and a European-born Buddhist monk, Nyanaponika Thera. Originally conceived as a limited effort to publish small, affordable books on fundamental Buddhist topics, the Society expanded in scope in response to the reception of their early publishing efforts. The Buddhist Publication society's publications reflect the perspective of the Theravada denomination of Buddhism, drawing heavily from the Pāli Canon for source material. The BPS supplies Buddhist literature to over 3,000 subscriber members throughout 80 countries. Its titles have been translated into many languages, including German, French, Spanish, Portuguese, Czech, Hindi, and Chinese. Publications The Buddhist Publication Society publishes a variety of wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pali Text Society
The Pali Text Society is a text publication society founded in 1881 by Thomas William Rhys Davids "to foster and promote the study of Pāli texts". Pāli is the language in which the texts of the Theravada school of Buddhism are preserved. The Pāli texts are the oldest collection of Buddhist scriptures preserved in the language in which they were written down. The society first compiled, edited, and published Latin script versions of a large corpus of Pāli literature, including the Pāli Canon, as well as commentarial, exegetical texts, and histories. It publishes translations of many Pāli texts. It also publishes ancillary works including dictionaries, concordances, books for students of Pāli and a journal. History Thomas William Rhys Davids was one of three British civil servants who were posted to Sri Lanka, in the 19th century, the others being George Turnour, and Robert Caesar Childers (1838–1876). At this time Buddhism in Sri Lanka (then Ceylon) was struggling un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhikkhu Bodhi
Bhikkhu Bodhi (born December 10, 1944), born Jeffrey Block, is an American Theravada Buddhist monk, ordained in Sri Lanka and currently teaching in the New York and New Jersey area. He was appointed the second president of the Buddhist Publication Society and has edited and authored several publications grounded in the Theravada Buddhist tradition. Life In 1944, Block was born in Brooklyn, New York, to Jewish parents. He grew up in Borough Park, where he attended elementary school P.S. 160. In 1966, he obtained a B.A. in philosophy from Brooklyn College. In 1972, he obtained a PhD in philosophy from Claremont Graduate University. In 1967, while still a graduate student, Bodhi was ordained as a sāmaṇera (novitiate) in the Vietnamese Mahayana order. In 1972, after graduation, Bodhi traveled to Sri Lanka where, under Balangoda Ananda Maitreya Thero, he received sāmaṇera ordination in the Theravada Order and, in 1973, he received full ordination (Upasampadā) as a Therav� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atthakatha
Aṭṭhakathā (Pali for explanation, commentary) refers to Pali-language Theravadin Buddhist commentaries to the canonical Theravadin Tipitaka. These commentaries give the traditional interpretations of the scriptures. The major commentaries were based on earlier ones, now lost, in Prakrit and Sinhala, which were written down at the same time as the Canon, in the last century BCE. Some material in the commentaries is found in canonical texts of other schools of Buddhism, suggesting an early common source. According to K.R. Norman: There is no direct evidence that any commentarial material was in fact recited at the first council, but there is clear evidence that some parts of the commentaries are very old, perhaps even going back to the time of the Buddha, because they afford parallels with texts which are regarded as canonical by other sects, and must therefore pre-date the schisms between the sects. As has already been noted, some canonical texts include commentarial pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosala
The Kingdom of Kosala (Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indian kingdom with a rich culture, corresponding to the area within the region of Awadh in present-day Uttar Pradesh to Western Odisha. It emerged as a janapada, small state during the late Vedic period, with connections to the neighbouring realm of Videha. Kosala belonged to the Northern Black Polished Ware culture (c. 700–300 BCE), and the Kosala region gave rise to the Sramana movements, including Jainism and Buddhism. It was culturally distinct from the Painted Grey Ware culture of the Vedic period of Kuru Kingdom, Kuru-Pañcāla, Panchala west of it, following independent development toward Second Urbanisation, urbanisation and the use of iron. During the 5th century BCE, Kosala incorporated the territory of the Shakya clan, to which the Buddha belonged. According to the Buddhist text ''Aṅguttara Nikāya'' and the Jaina text, the ''Vyākhyāprajñapti, Bhagavati Sutra'', Kosala was one of the ''Solasa'' (sixteen) Mahaj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digha Nikaya
Digha is a seaside resort town in the state of West Bengal, India. It lies in Purba Medinipur district and at the northern end of the Bay of Bengal. It has a low gradient with a shallow sand beach. It is a popular sea resort in West Bengal. History Originally, there was a place called ''Beerkul'', where Digha lies today. This name was referred in Warren Hastings's letters (1780) as Brighton of the East. An English businessman John Frank Snaith started living here in 1923 and his writings provided a good exposure to this place. He convinced West Bengal Chief Minister Bidhan Chandra Roy to develop this place to be a beach resort. An old church can be seen near the Old Digha Main gate. This place is also known as Alankarpur Digha. A new mission has been developed in New Digha which is known as Sindhur Tara which is beside Amrabati Park its a Church where it is possible to wish for the welfare of family and loved ones. The best way to visit is to book a local van rickshaw. There ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashoka Tree '' is sometimes called the "false ashoka"
Holy tree of the ancient Jains as well as Hindus.
{{Plant common name ...
Ashoka tree is a common name for two plants which are frequently confused with each other: *''Saraca asoca'', native to South Asia and western Myanmar *''Saraca indica'', native to eastern Myanmar and Southeast Asia *''Monoon longifolium ''Monoon longifolium'', the false ashoka, also commonly known by its synonym ''Polyalthia longifolia'', is an Asian small tree species in the family Annonaceae. It is native to southern India and Sri Lanka, but has been widely introduced els ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Noble Truths
In Buddhism, the Four Noble Truths (Sanskrit: ; pi, cattāri ariyasaccāni; "The four Arya satyas") are "the truths of the Noble Ones", the truths or realities for the "spiritually worthy ones".[aFour Noble Truths: BUDDHIST PHILOSOPHY Encyclopaedia Britannica, Quote: "Although the term Four Noble Truths is well known in English, it is a misleading translation of the Pali term Chattari-ariya-saccani (Sanskrit: Chatvari-arya-satyani), because noble (Pali: ariya; Sanskrit: arya) refers not to the truths themselves but to those who recognize and understand them. A more accurate rendering, therefore, might be “four truths for the [spiritually] noble” [...]";[''Arhat (Buddhism)'' Encyclopædia Britannica The truths are: * '' dukkha'' (literally "suffering"; here "unsatisfactoriness") is an innate characteristic of existence in the realm of '' samsara''; [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


