|
Silvicultural
Silviculture is the practice of controlling the growth, composition/structure, as well as quality of forests to meet values and needs, specifically timber production. The name comes from the Latin ('forest') and ('growing'). The study of forests and woods is termed '' silvology''. Silviculture also focuses on making sure that the treatment(s) of forest stands are used to conserve and improve their productivity. Generally, silviculture is the science and art of growing and cultivating forest crops based on a knowledge of silvics, the study of the life history and general characteristics of forest trees and stands, with reference to local/regional factors. The focus of silviculture is the control, establishment and management of forest stands. The distinction between forestry and silviculture is that silviculture is applied at the stand-level, while forestry is a broader concept. Adaptive management is common in silviculture, while forestry can include natural/conserved land wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selection Cutting
Selection cutting, also known as selection system, is the silvicultural practice of harvesting trees in a way that moves a stand level modelling, forest stand towards an uneven-aged or all-aged condition, or 'structure'. Using stocking models derived from the study of old growth forests, selection cutting, also known as 'selection system', or 'selection silviculture', manages the establishment, continued growth and final harvest of multiple age classes (usually three, but 5 or even 10 are possible) of trees within a stand. A closely related approach to forest management is Continuous Cover Forestry (CCF), which makes use of selection systems to achieve a permanently irregular stand structure. Selection cutting or systems are generally considered to be more challenging to implement and maintain than even-aged timber management, even-aged management, due to the difficulty of managing multiple age classes in a shared space, but there are significant ecological benefits associated wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shelterwood Cutting
Shelterwood cutting removes part of the old forest stand to allow for a natural establishment of seedlings under the cover of the remaining trees. Initial cuttings give just enough light to allow for the regeneration of desired species. Subsequent cuttings give the new seedlings more light and fully pass the growing space to the new generation.Welford, Lana; Williams, Allie (2016)"3.4. Regeneration Methods: Shelterwood" ''SFA Silviculture''. Retrieved 2024-02-24."Module 2: Harvesting Systems , Natural Resources and Renewables , Government of Nova Scotia" ''Government of Nova Scotia.'' Retrieved 2024-02-24. Shelterwood systems have many variations and can be adapted to site conditions and the goals of the landowner. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coppice
Coppicing is the traditional method in woodland management of cutting down a tree to a tree stump, stump, which in many species encourages new Shoot (botany), shoots to grow from the stump or roots, thus ultimately regrowing the tree. A forest or grove that has been subject to coppicing is called a copse or coppice, in which young tree stems are repeatedly cut down to near ground level. The resulting living stumps are called Living stump, stools. New growth emerges, and after a number of years, the coppiced trees are harvested, and the cycle begins anew. Pollarding is a similar process carried out at a higher level on the tree in order to prevent grazing animals from eating new shoots. ''Daisugi'' (台杉, where ''sugi'' refers to Japanese cedar) is a similar Japanese technique. Many silviculture practices involve cutting and regrowth; coppicing has been of significance in many parts of lowland temperate Europe. The widespread and long-term practice of coppicing as a landscape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silvology
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests and woodlands for associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. The science of forestry has elements that belong to the biological, physical, social, political and managerial sciences. Forest management plays an essential role in the creation and modification of habitats and affects ecosystem services provisioning. Modern forestry generally embraces a broad range of concerns, in what is known as multiple-use management, including: the provision of timber, fuel wood, wildlife habitat, natural water quality management, recreation, landscape and community protection, employment, aesthetically appealing landscapes, biodiversity management, watershed management, erosion control, and preserving forests as " sinks" for atmospheric carbon dioxide. Forest ecosystems have come to be seen as the most important co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests and woodlands for associated resources for human and Natural environment, environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural Stand level modelling, stands. The science of forestry has elements that belong to the biological, physical, social, political and managerial sciences. Forest management plays an essential role in the creation and modification of habitats and affects ecosystem services provisioning. Modern forestry generally embraces a broad range of concerns, in what is known as multiple-use management, including: the provision of timber, fuel wood, wildlife habitat, natural Water resources, water quality management, recreation, landscape and community protection, employment, aesthetically appealing landscapes, biodiversity management, watershed management, erosion control, and preserving forests as "Carbon dioxide sink, sinks" for Earth's atmosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thinning
In agricultural sciences, thinning is the removal of some plants, or parts of plants, to make room for the growth of others. Selective removal of parts of a plant such as branches, buds, or roots is typically known as '' pruning''. In forestry, thinning is the selective removal of trees, primarily undertaken to improve the growth rate or health of the remaining trees. Overcrowded trees are under competitive stress from their neighbors. Thinning may be done to increase the resistance of the stand to environmental stress such as drought, insect infestation, extreme temperature, or wildfire. In forestry Tree thinning may be practised in forestry to make a stand more profitable in an upcoming final felling, or to advance ecological goals such as increasing biodiversity or accelerating the development of desired structural attributes such as large diameter trees with long tree crowns. Early thinning, e.g. after 20 years, rather than late thinning, e.g. after 50 years, has dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
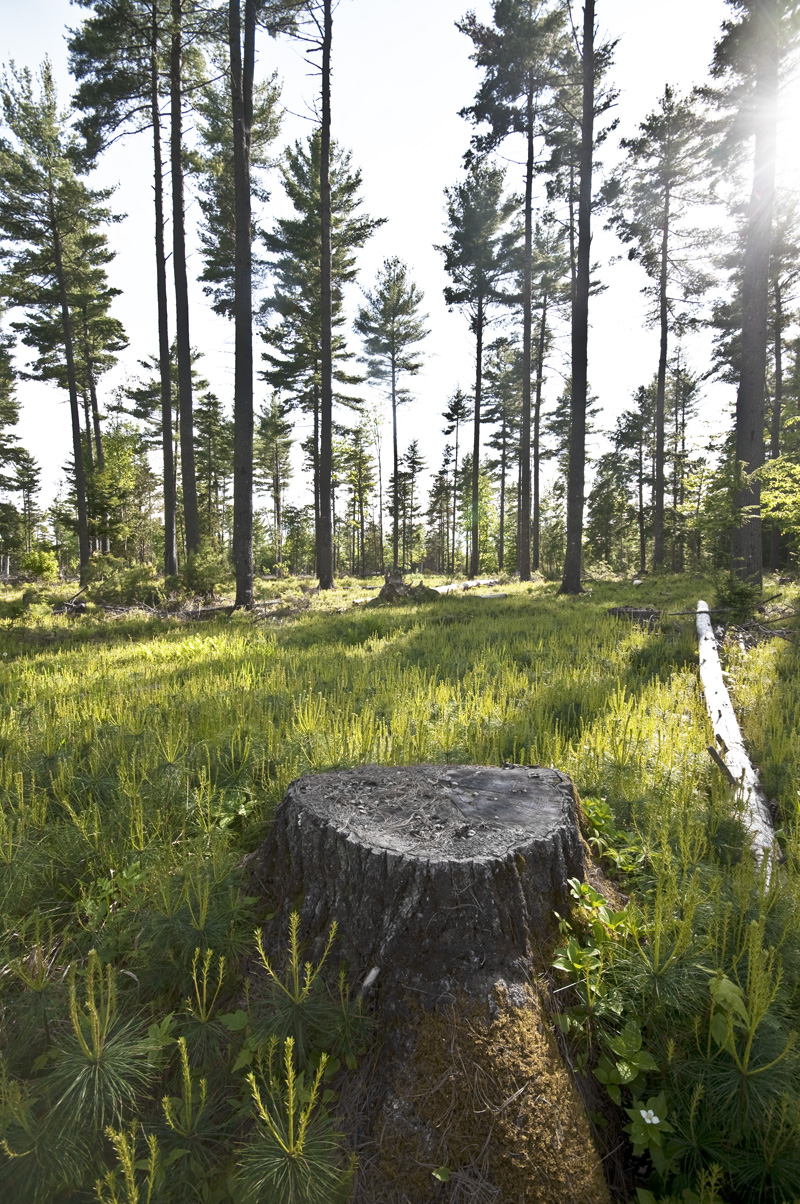
Clear Cutting
Clearcutting, clearfelling or clearcut logging is a forestry/logging practice in which most or all trees in an area are uniformly cut down. Along with Shelterwood cutting, shelterwood and Seed tree, seed tree harvests, it is used by foresters to create certain types of forest ecosystems and to promote select species that require an abundance of sunlight or grow in large, even-age stand level modelling, stands. Clearcutting is a forestry practice that mimics the stand initiation stage of forest succession after a natural disturbance such as Wildfire, stand replacing fire or Windthrow, wind-throw, and is successful for regeneration of fast growing, Douglas fir, sun tolerant tree species and wildlife species that readily regenerate in post-stand replacing sites. Logging companies and forest-worker unions in some countries support the practice for scientific, safety and economic reasons, while detractors consider it a form of deforestation that habitat destruction, destroys natural h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satoyama
is a Japanese language, Japanese term applied to the border zone or area between mountain foothills and arable flat land. Literally, ''sato'' () means village, and ''yama'' () means hill or mountain. Satoyama have been developed through centuries of small-scale agricultural and forestry use. The concept of satoyama has several definitions. The first definition is the management of forests through local agricultural communities, using coppicing. During the Edo era, young and fallen leaves were gathered from community forests to use as fertilizer in wet rice paddy fields. Villagers also used wood for construction, cooking and heating. More recently, satoyama has been defined not only as mixed community forests, but also as entire landscapes that are used for agriculture. According to this definition, satoyama contains a mosaic of mixed forests, paddy field, rice paddy fields, dry rice fields, grasslands, streams, ponds, and reservoirs for irrigation. Farmers use the grasslands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
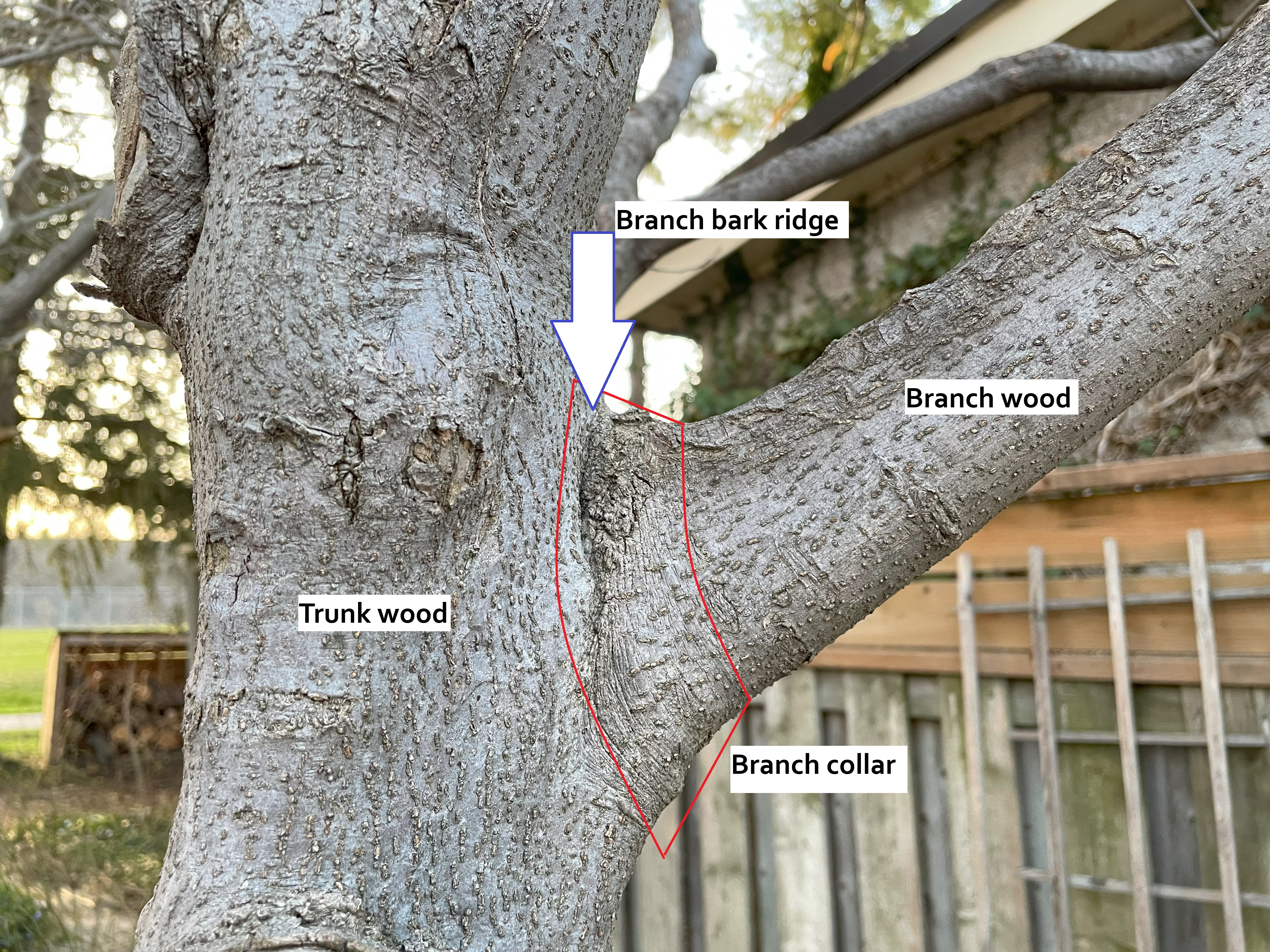
Pruning
Pruning is the selective removal of certain parts of a plant, such as branches, buds, or roots. It is practiced in horticulture (especially fruit tree pruning), arboriculture, and silviculture. The practice entails the targeted removal of diseased, damaged, dead, non-productive, structurally unsound, or otherwise unwanted plant material from crop and landscape plants. In general, the smaller the branch that is cut, the easier it is for a woody plant to compartmentalize the wound and thus limit the potential for pathogen intrusion and decay. It is therefore preferable to make any necessary formative structural pruning cuts to young plants, rather than removing large, poorly placed branches from mature plants. Woody plants may undergo a process referred to as ''self-pruning'', where they will drop twigs or branches which are no longer producing more energy than they require. It is theorized that this process can also occur in response to lack of water, in order to reduce the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forests
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a canopy cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds ''in situ''. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, '' Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020'' found that forests covered , or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020. Forests are the largest terrestrial ecosystems of Earth by area, and are found around the globe. 45 percent of forest land is in the tropical latitudes. The next largest share of forests are found in subarctic climates, followed by temperate, and subtrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |