|
Silver Compounds
Silver is a relatively unreactive metal, although it can form several compounds. The common oxidation states of silver are (in order of commonness): +1 (the most stable state; for example, silver nitrate, AgNO3); +2 (highly oxidising; for example, silver(II) fluoride, AgF2); and even very rarely +3 (extreme oxidising; for example, potassium tetrafluoroargentate(III), KAgF4). The +3 state requires very strong oxidising agents to attain, such as fluorine or peroxodisulfate, and some silver(III) compounds react with atmospheric moisture and attack glass.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 1188 Indeed, silver(III) fluoride is usually obtained by reacting silver or silver monofluoride with the strongest known oxidizing agent, krypton difluoride.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 903 Oxides and chalcogenides Oxides Silver and gold have rather low chemical affinities for oxygen, lower than copper, and it is therefore expected that silver oxides are thermally quite unstable. Soluble silver(I) salts precip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Oxide
Silver oxide is the chemical compound with the formula Ag2O. It is a fine black or dark brown powder that is used to prepare other silver compounds. Preparation Silver oxide can be prepared by combining aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and an alkali hydroxide. This reaction does not afford appreciable amounts of silver hydroxide due to the favorable energetics for the following reaction: :2 AgOH -> Ag2O + H2O ( p''K'' = 2.875) With suitably controlled conditions, this reaction can be used to prepare Ag2O powder with properties suitable for several uses including as a fine grained conductive paste filler. Structure and properties Ag2O features linear, two-coordinate Ag centers linked by tetrahedral oxides. It is isostructural with Cu2O. It "dissolves" in solvents that degrade it. It is slightly soluble in water due to the formation of the ion and possibly related hydrolysis products. It is soluble in ammonia solution, producing active compound of Tollens' reagent. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Silver Halide Precipitates
Common may refer to: Places * Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts * Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts * Clapham Common, originally common land, now a park in London, UK * Common Moss, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Lexington Common, a common land area in Lexington, Massachusetts * Salem Common Historic District, a common land area in Salem, Massachusetts People * Common (rapper) (born 1972), American hip hop artist, actor, and poet * Andrew Ainslie Common (born 1841), English amateur astronomer * Andrew Common (born 1889), British shipping director * John Common, American songwriter, musician and singer * Thomas Common (born 1850), Scottish translator and literary critic Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Common'' (film), a 2014 BBC One film, written by Jimmy McGovern, on the UK's Joint Enterprise Law * Dol Common, a character in ''The Alchemist'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Defect
A crystallographic defect is an interruption of the regular patterns of arrangement of atoms or molecules in crystalline solids. The positions and orientations of particles, which are repeating at fixed distances determined by the unit cell parameters in crystals, exhibit a periodic crystal structure, but this is usually imperfect.Ehrhart, P. (1991Properties and interactions of atomic defects in metals and alloys, volume 25 of Landolt-Börnstein, New Series III, chapter 2, p. 88, Springer, Berlin Several types of defects are often characterized: point defects, line defects, planar defects, bulk defects. Topological homotopy establishes a mathematical method of characterization. Point defects Point defects are defects that occur only at or around a single lattice point. They are not extended in space in any dimension. Strict limits for how small a point defect is are generally not defined explicitly. However, these defects typically involve at most a few extra or missing atoms. La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monochrome Photography
Monochrome photography is photography where each position on an image can record and show a different ''amount'' of light, but not a different hue. It includes all forms of black-and-white photography, which produce images containing shades of neutral grey ranging from black to white. Other hues besides grey, such as sepia, cyan, blue, or brown can also be used in monochrome photography. In the contemporary world, monochrome photography is mostly used for artistic purposes and certain technical imaging applications, rather than for visually accurate reproduction of scenes. Description Although methods for photographing in color emerged slowly starting in the 1850s, monochrome imagery dominated photography until the mid–twentieth century. From the start, photographic recording processes such as the daguerreotype, the paper negative and the glass collodion negative did not render the color of light (although they were sensitive to some colors more than others). The result was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surfaces with which it comes into contac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosensitive
Photosensitivity is the amount to which an object reacts upon receiving photons, especially visible light. In medicine, the term is principally used for abnormal reactions of the skin, and two types are distinguished, photoallergy and phototoxicity. The photosensitive ganglion cells in the mammalian eye are a separate class of light-detecting cells from the photoreceptor cells that function in vision. Skin reactions Human medicine Sensitivity of the skin to a light source can take various forms. People with particular skin types are more sensitive to sunburn. Particular medications make the skin more sensitive to sunlight; these include most of the tetracycline antibiotics, heart drugs amiodarone, and sulfonamides. Some dietary supplements, such as St. John's Wort, include photosensitivity as a possible side effect. Particular conditions lead to increased light sensitivity. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus experience skin symptoms after sunlight exposure; some types o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
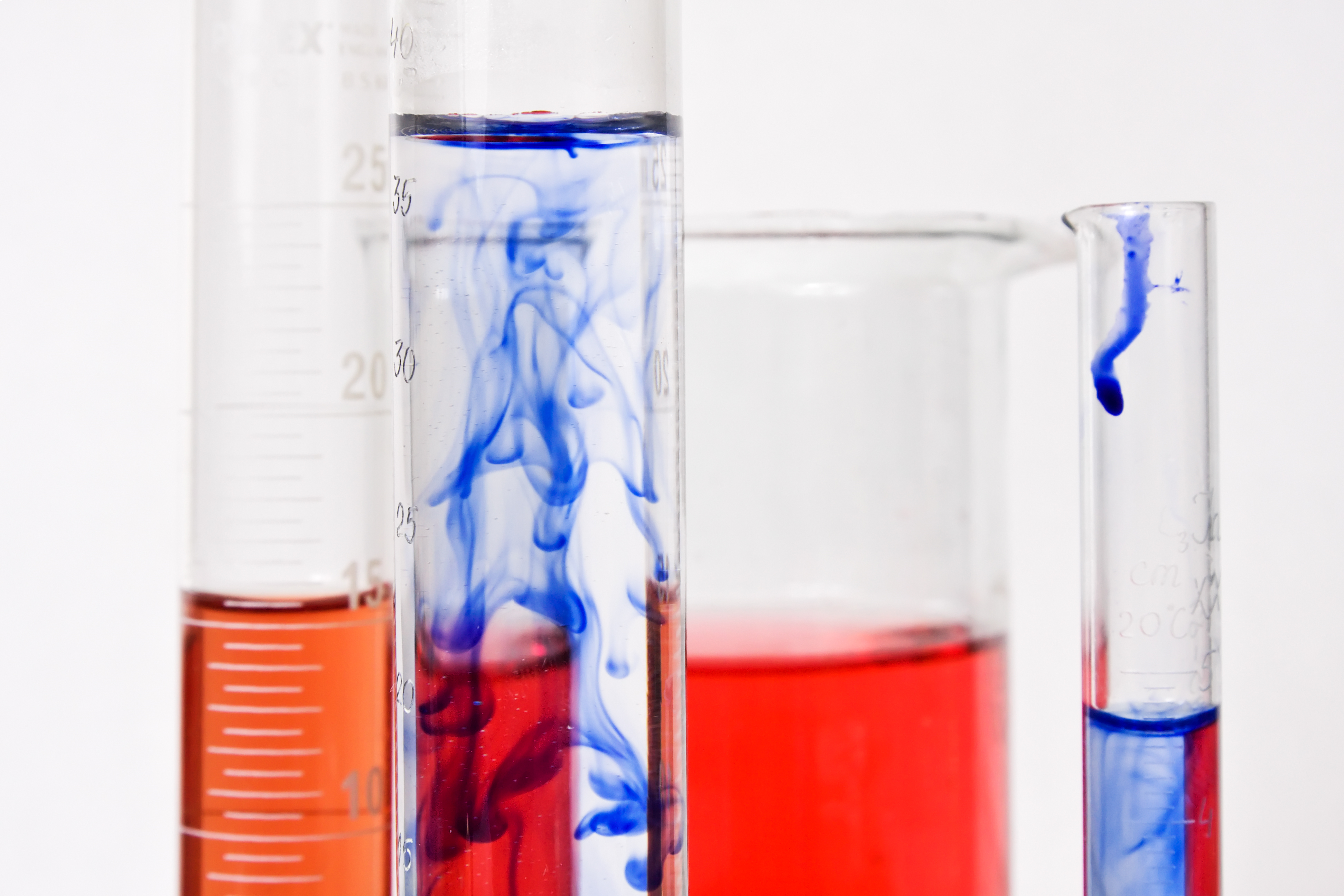
Wet Chemistry
Wet chemistry is a form of analytical chemistry that uses classical methods such as observation to analyze materials. It is called wet chemistry since most analyzing is done in the liquid phase. Wet chemistry is also called bench chemistry since many tests are performed at lab benches. Materials Wet chemistry commonly uses laboratory glassware such as beakers and graduated cylinders to prevent materials from being contaminated or interfered with by unintended sources. Gasoline, Bunsen burners, and crucibles may also be used to evaporate and isolate substances in their dry forms. Wet chemistry is not performed with any advanced instruments since most automatically scan substances. Although, simple instruments such as scales are used to measure the weight of a substance before and after a change occurs. Many high school and college laboratories teach students basic wet chemistry methods. History Before the age of theoretical and computational chemistry, wet chemistry was the predom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvation
Solvation (or dissolution) describes the interaction of a solvent with dissolved molecules. Both ionized and uncharged molecules interact strongly with a solvent, and the strength and nature of this interaction influence many properties of the solute, including solubility, reactivity, and color, as well as influencing the properties of the solvent such as its viscosity and density. If the attractive forces between the solvent and solute particles are greater than the attractive forces holding the solute particles together, the solvent particles pull the solute particles apart and surround them. The surrounded solute particles then move away from the solid solute and out into the solution. Ions are surrounded by a concentric shell of solvent. Solvation is the process of reorganizing solvent and solute molecules into solvation complexes and involves bond formation, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces. Solvation of a solute by water is called hydration. Solubility of soli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-transfer Complex
In chemistry, a charge-transfer (CT) complex or electron-donor-acceptor complex describes a type of supramolecular assembly of two or more molecules or ions. The assembly consists of two molecules that self-attract through electrostatic forces, i.e., one has at least partial negative charge and the partner has partial positive charge, referred to respectively as the electron acceptor and electron donor. In some cases, the degree of charge transfer is "complete", such that the CT complex can be classified as a salt. In other cases, the charge-transfer association is weak, and the interaction can be disrupted easily by polar solvents. Examples Electron donor-acceptor complexes A number of organic compounds form charge-transfer complex, which are often described as electron-donor-acceptor complexes (EDA complexes). Typical acceptors are nitrobenzenes or tetracyanoethylene. The strength of their interaction with electron donors correlates with the ionization potentials of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Blende
Sphalerite (sometimes spelled sphaelerite) is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in sedimentary exhalative, Mississippi-Valley type, and volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. It is found in association with galena, chalcopyrite, pyrite (and other sulfides), calcite, dolomite, quartz, rhodochrosite, and fluorite. German geologist Ernst Friedrich Glocker discovered sphalerite in 1847, naming it based on the Greek word ''sphaleros'', meaning "deceiving", due to the difficulty of identifying the mineral. In addition to zinc, sphalerite is an ore of cadmium, gallium, germanium, and indium. Miners have been known to refer to sphalerite as ''zinc blende'', ''black-jack'', and ''ruby blende''. Marmatite is an opaque black variety with a high iron content. Crystal habit and structure Sphalerite crystallizes in the face-centered cubic Cubic crystal system#Zincb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
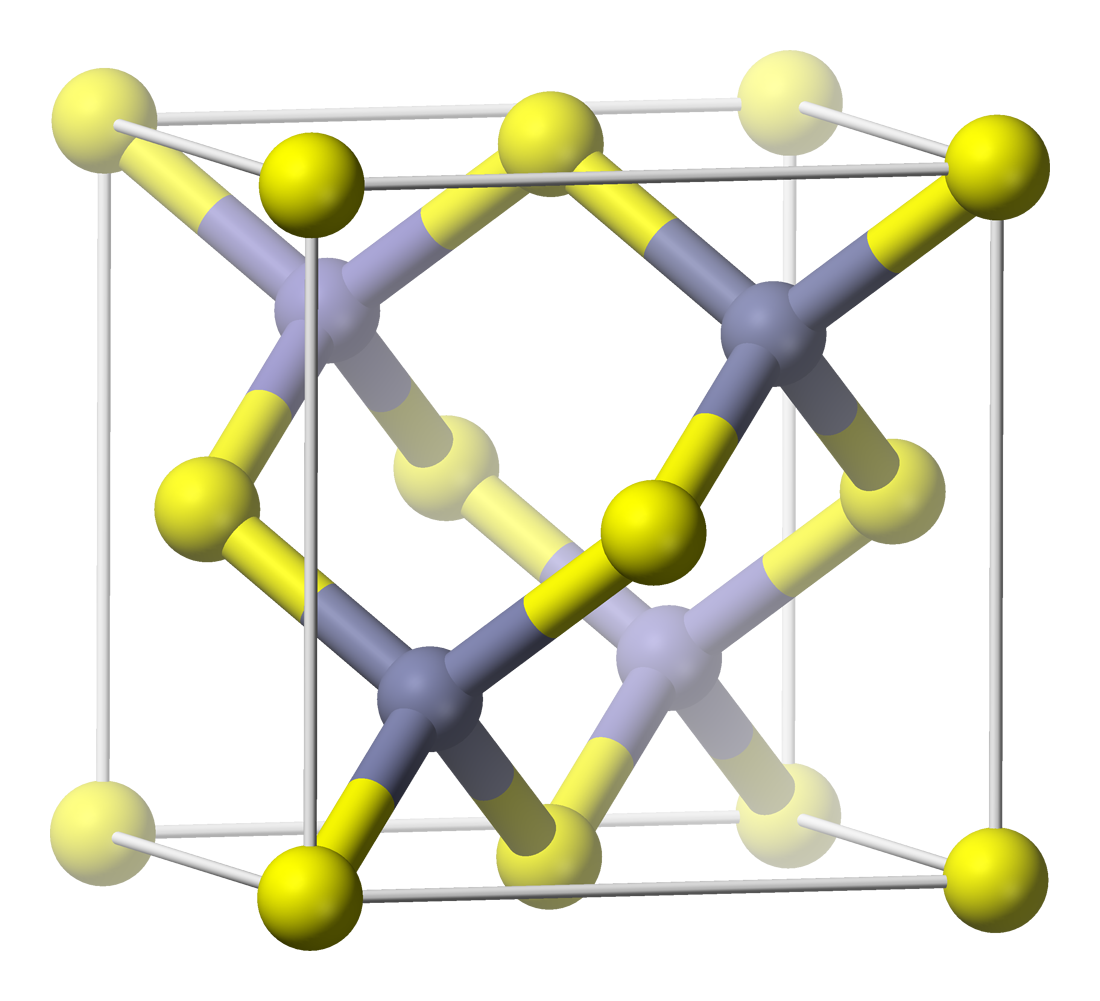
Silver Iodide
Silver iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula Ag I. The compound is a bright yellow solid, but samples almost always contain impurities of metallic silver that give a gray coloration. The silver contamination arises because AgI is highly photosensitive. This property is exploited in silver-based photography. Silver iodide is also used as an antiseptic and in cloud seeding. Structure The structure adopted by silver iodide is temperature dependent: *Below 420 K, the β phase of AgI, with the wurtzite structure, is most stable. This phase is encountered in nature as the mineral iodargyrite. *Above 420 K, the α phase becomes more stable. This motif is a body-centered cubic structure which has the silver centers distributed randomly between 6 octahedral, 12 tetrahedral and 24 trigonal sites. At this temperature, Ag+ ions can move rapidly through the solid, allowing fast ion conduction. The transition between the β and α forms represents the melting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Bromide
Silver bromide (AgBr) is a soft, pale-yellow, water-insoluble salt well known (along with other silver halides) for its unusual sensitivity to light. This property has allowed silver halides to become the basis of modern photographic materials. AgBr is widely used in photographic films and is believed by some to have been used for making the Shroud of Turin. The salt can be found naturally as the mineral bromargyrite. Preparation Although the compound can be found in mineral form, AgBr is typically prepared by the reaction of silver nitrate with an alkali bromide, typically potassium bromide: :AgNO3(aq) + KBr(aq) → AgBr(s)+ KNO3(aq) Although less convenient, the compound can also be prepared directly from its elements. Modern preparation of a simple, light-sensitive surface involves forming an emulsion of silver halide crystals in a gelatine, which is then coated onto a film or other support. The crystals are formed by precipitation in a controlled environment to produce small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |