|
Silk 700S
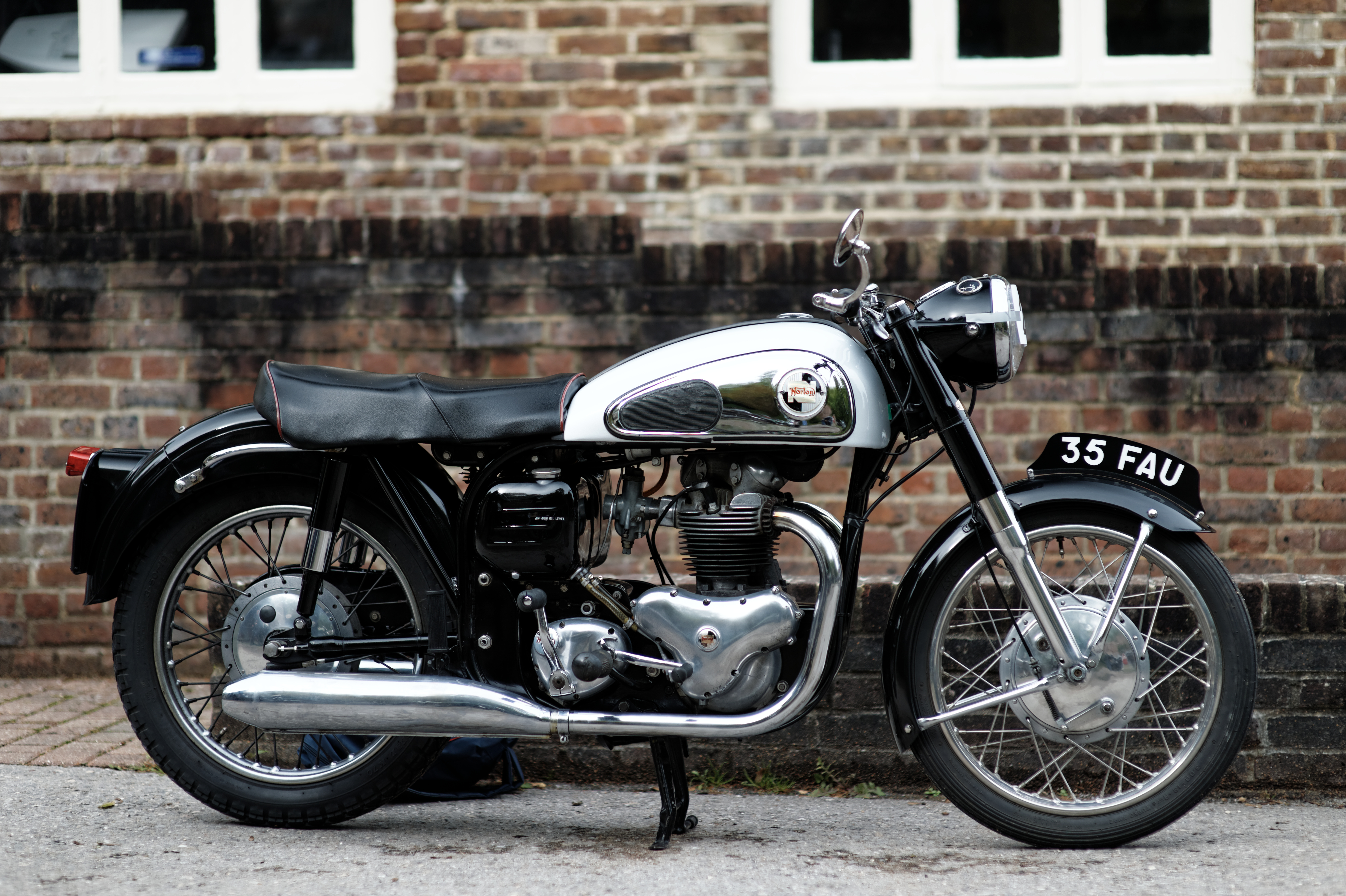
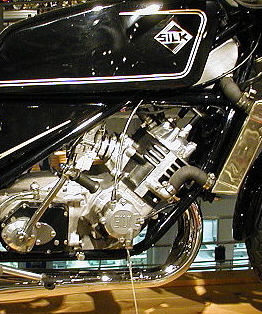
The Silk 700S was a British motorcycle made by Silk Engineering between 1975 and 1979 in Darley Abbey, Derbyshire, UK. Development The Silk 700S was launched in 1975 and featured a new engine based on the two stroke engine from the Scott Flying Squirrel in a specially designed steel tubular frame made by Spondon of Derbyshire, who also made the forks. At a cost of £1355 it was more expensive than most other production motorcycles of the time. Right from the start the Silk 700S featured state of the art electronic ignition and had a power-to-weight ratio combined with excellent handling that enabled it to compete with some of the best road bikes of the time. Top speed was an impressive 110 mph. The bike did not have an electric start; the kick-starting technique took some practice. The 700S continued to be developed at the Darley Abbey works in Derbyshire, along with the SPR Production Racing version. Production was slow, with just two motorcycles a week coming off the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silk Engineering
Silk Engineering was a British motorcycle manufacturer established by George Silk and Maurice Patey and based at Darley Abbey, Derbyshire. They produced Silk 700S two-stroke motorcycles until 1979. Problems with spare parts and rising costs led to the company ceasing manufacture. History Silk was founded in the late 1960s by George Silk, a Scott motorcycle enthusiast who worked for Derbyshire Scott specialist Tom Ward. George Silk developed a racing motorcycle by fitting a Scott engine into a Spondon frame. Following some success with a Silk Special at the Barbon Hill Climb in 1970, Silk began planning a road-going prototype with his business partner Maurice Patey. They set up Silk Engineering and began providing a spares and repair service for Scott motorcycle owners. They also offered a range of modifications to improve the reliability and performance of Scotts, as well as improving the lubrication and gas flow. Silk exhibited the prototype at the Racing and Sporting Mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is dominated by a maritime climate with narrow temperature differences between seasons. The 60% smaller island of Ireland is to the west—these islands, along with over 1,000 smaller surrounding islands and named substantial rocks, form the British Isles archipelago. Connected to mainland Europe until 9,000 years ago by a landbridge now known as Doggerland, Great Britain has been inhabited by modern humans for around 30,000 years. In 2011, it had a population of about , making it the world's third-most-populous island after Java in Indonesia and Honshu in Japan. The term "Great Britain" is often used to refer to England, Scotland and Wales, including their component adjoining islands. Great Britain and Northern Ireland now const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle steered by a handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: long-distance travel, commuting, cruising, sport (including racing), and off-road riding. Motorcycling is riding a motorcycle and being involved in other related social activity such as joining a motorcycle club and attending motorcycle rallies. The 1885 Daimler Reitwagen made by Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach in Germany was the first internal combustion, petroleum-fueled motorcycle. In 1894, Hildebrand & Wolfmüller became the first series production motorcycle. Globally, motorcycles are comparably popular to cars as a method of transport. In 2021, approximately 58.6 million new motorcycles were sold around the world, fewer than the 66.7 million cars sold over the same period. In 2014, the three top motorcycle producers globally by volume were Honda (28%), Yama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darley Abbey
Darley Abbey is a former historic mill village, now a suburb of the city of Derby, England. It is located approximately north of the city centre, on the west bank of the River Derwent, and forms part of the Darley ward along with Little Chester and the West End. The settlement dates back to the medieval era, when it was the site of an Augustinian monastery. In the 18th century, the Evans family developed their planned industrial mill village in the area; Darley Abbey is now part of the Derwent Valley Mills World Heritage Site. The area has been a part of the city (originally borough) of Derby since 1968 and is counted as part of Darley Ward. History Darley Abbey (Monastery) The Augustinian monastery of Darley Abbey has a rather confused foundation. In 1154, Robert de Ferrers, 2nd Earl of Derby made a donation to St Helen's Priory, Derby for them to establish a new religious house. He donated the churches of Uttoxeter and Crich, an oratory and cemetery at Osmaston, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derbyshire
Derbyshire ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands, England. It includes much of the Peak District National Park, the southern end of the Pennine range of hills and part of the National Forest. It borders Greater Manchester to the north-west, West Yorkshire to the north, South Yorkshire to the north-east, Nottinghamshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south-east, Staffordshire to the west and south-west and Cheshire to the west. Kinder Scout, at , is the highest point and Trent Meadows, where the River Trent leaves Derbyshire, the lowest at . The north–south River Derwent is the longest river at . In 2003, the Ordnance Survey named Church Flatts Farm at Coton in the Elms, near Swadlincote, as Britain's furthest point from the sea. Derby is a unitary authority area, but remains part of the ceremonial county. The county was a lot larger than its present coverage, it once extended to the boundaries of the City of Sheffield district in South Yorkshire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two Stroke
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of the crankshaft. A four-stroke engine requires four strokes of the piston to complete a power cycle during two crankshaft revolutions. In a two-stroke engine, the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happen simultaneously, with the intake and exhaust (or scavenging) functions occurring at the same time. Two-stroke engines often have a high power-to-weight ratio, power being available in a narrow range of rotational speeds called the power band. Two-stroke engines have fewer moving parts than four-stroke engines. History The first commercial two-stroke engine involving cylinder compression is attributed to Scottish engineer Dugald Clerk, who patented his design in 1881. However, unlike most later tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scott Flying Squirrel
The Scott Flying Squirrel was a motorcycle made by The Scott Motorcycle Company between 1926 and the outbreak of World War II. Development The ''Squirrel'' name was used for Scott motorcycles since 1921 but with the death of the founder Alfred Angas Scott in 1923 the unorthodox Scott two-stroke motorcycles began to become more conventional. Development of the three-speed Scott Flying Squirrel began in 1922 as the company was in severe debt and faced receivership. Launched at the 1926 Earls Court motorcycle show, the Flying Squirrel was expensive - nearly twice the cost of a sporting four-stroke motorcycle of the time. The unique water-cooled circulation used a convection method known as the thermosyphon system. The bottom end block was painted either green or red for racing or road respectively and featured a centrally positioned flywheel, twin inboard main bearings, overhung crankpins and doors to enable ease of access to the engine. The redesigned three-speed gearbox, multi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SILK 700 S Engine 02
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the cocoons of the larvae of the mulberry silkworm '' Bombyx mori'' reared in captivity ( sericulture). The shimmering appearance of silk is due to the triangular prism-like structure of the silk fibre, which allows silk cloth to refract incoming light at different angles, thus producing different colors. Silk is produced by several insects; but, generally, only the silk of moth caterpillars has been used for textile manufacturing. There has been some research into other types of silk, which differ at the molecular level. Silk is mainly produced by the larvae of insects undergoing complete metamorphosis, but some insects, such as webspinners and raspy crickets, produce silk throughout their lives. Silk production also occurs in hymenop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocette Venom
The Velocette Venom was a 499 cc single-cylinder four-stroke British motorcycle made by Velocette at Hall Green in Birmingham. A total of 5,721 machines were produced between 1955 and 1970. In 1961 a factory-prepared faired Velocette Venom and a team of riders set the 24-hour world record at a speed of at the Autodrome de Linas-Montlhéry, a banked oval racetrack in France. It was the first motorcycle to average over 100 mph continuously for 24 hours and no 500cc or single-cylinder motorcycle has broken this record. In 1965, the Velocette Venom was further developed with a full racing kit to create the range-topping Velocette Thruxton, with a special cylinder head developed by American flat-track racers, and adapted by Velocette to create a new production racer. It was a very popular and successful clubman racer, winning the 1967 Isle of Man Production TT. The Thruxton became the most popular Velocette model, but could not save the Velocette company from bankruptcy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzuki GT750
The Suzuki GT750 is a water-cooled three-cylinder two-stroke motorcycle made by Suzuki from 1971 to 1977. It is the first Japanese motorcycle with a liquid-cooled engine. The Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan includes the 1971 Suzuki GT750 as one of their ''240 Landmarks of Japanese Automotive Technology''. Introduction The prototype Suzuki GT750 was shown at the 17th Tokyo Motor Show in October 1970 and launched in Japan in September 1971 as a sports tourer (GT standing for Grand Tourismo) and was developed from the Suzuki T500 with an extra cylinder and liquid cooling. Marketed as the ''Le Mans'' in the US and Canada, it was nicknamed the "Kettle" in Britain, the "Water Bottle" in Australia, and the "Water Buffalo" in the United States. The GT750 was heavy at 550 lbs, with a 739 cc two-stroke three-cylinder engine with 70 mm bore and 64 mm stroke. It had a five-speed gearbox and three-into-four exhaust. 1972 model The first model year (1972), the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
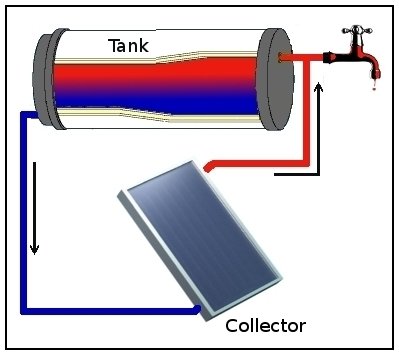
Thermosiphon
Thermosiphon (or thermosyphon) is a method of passive heat exchange, based on natural convection, which circulates a fluid without the necessity of a mechanical pump. Thermosiphoning is used for circulation of liquids and volatile gases in heating and cooling applications such as heat pumps, water heaters, boilers and furnaces. Thermosiphoning also occurs across air temperature gradients such as those utilized in a wood fire chimney or solar chimney. This circulation can either be open-loop, as when the substance in a holding tank is passed in one direction via a heated transfer tube mounted at the bottom of the tank to a distribution point—even one mounted above the originating tank—or it can be a vertical closed-loop circuit with return to the original container. Its purpose is to simplify the transfer of liquid or gas while avoiding the cost and complexity of a conventional pump. Simple thermosiphon Natural convection of the liquid starts when heat transfer to the liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coolant
A coolant is a substance, typically liquid, that is used to reduce or regulate the temperature of a system. An ideal coolant has high thermal capacity, low viscosity, is low-cost, non-toxic, chemically inert and neither causes nor promotes corrosion of the cooling system. Some applications also require the coolant to be an electrical insulator. While the term "coolant" is commonly used in automotive and HVAC applications, in industrial processing heat-transfer fluid is one technical term more often used in high temperature as well as low-temperature manufacturing applications. The term also covers cutting fluids. Industrial cutting fluid has broadly been classified as water-soluble coolant and neat cutting fluid. Water-soluble coolant is oil in water emulsion. It has varying oil content from nil oil (synthetic coolant). This coolant can either keep its phase and stay liquid or gaseous, or can undergo a phase transition, with the latent heat adding to the cooling efficiency. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |