|
Silicates
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate .Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In all silicates, silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedron whose corner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicate Minerals
Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust. In mineralogy, silica (silicon dioxide, ) is usually considered a silicate mineral. Silica is found in nature as the mineral quartz, and its polymorphs. On Earth, a wide variety of silicate minerals occur in an even wider range of combinations as a result of the processes that have been forming and re-working the crust for billions of years. These processes include partial melting, crystallization, fractionation, metamorphism, weathering, and diagenesis. Living organisms also contribute to this geologic cycle. For example, a type of plankton known as diatoms construct their exoskeletons ("frustules") from silica extracted from seawater. The frustules of dead diatoms are a major constituent of deep ocean sediment, and of diatomaceous earth. General structure A silicate mineral is general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inosilicate
Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust. In mineralogy, silica (silicon dioxide, ) is usually considered a silicate mineral. Silica is found in nature as the mineral quartz, and its polymorphism (materials science), polymorphs. On Earth, a wide variety of silicate minerals occur in an even wider range of combinations as a result of the processes that have been forming and re-working the crust for billions of years. These processes include partial melting, crystallization, fractionation, metamorphism, weathering, and diagenesis. Living organisms also contribute to this carbonate–silicate cycle, geologic cycle. For example, a type of plankton known as diatoms construct their exoskeletons ("frustules") from silica extracted from seawater. The frustules of dead diatoms are a major constituent of deep ocean sediment, and of diatomaceous e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive. Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to prepare it and characterize it in pure form. Its oxides form a family of anions known as silicates. Its melting and boiling points of 1414 °C and 3265 °C, respectively, are the second highest among all the metalloids and nonmetals, being surpassed only by boron. Silicon is the eighth most common element in the universe by mass, but very rarely occurs as the pure element in the Earth's crust. It is widely distributed in space in cosmic dusts, planetoids, and planets as various forms of silicon dioxide ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
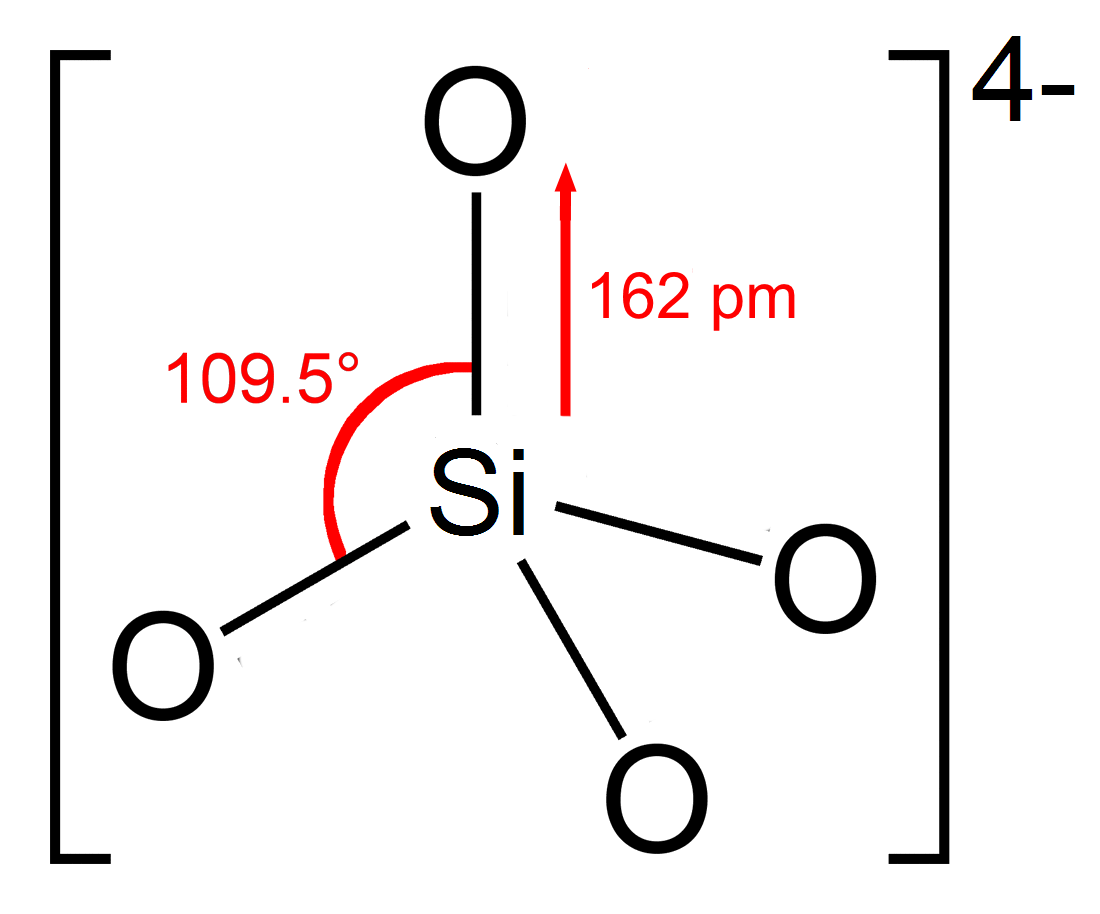
Orthosilicate
In chemistry, orthosilicate is the anion , or any of its salts and esters. It is one of the silicate anions. It is occasionally called the silicon tetroxide anion or group.C. A. Kumins, and A. E. Gessler (1953), "Short-Cycle Syntheses of Ultramarine Blue". ''Indunstrial & Engineering Chemistry'', volume 45, issue 3, pages 567–572. Orthosilicate salts, like sodium orthosilicate, are stable, and occur widely in nature as silicate minerals, being the defining feature of the nesosilicates. Olivine, a magnesium or iron(II) orthosilicate, is the most abundant mineral in the upper mantle. The orthosilicate anion is a strong base, the conjugate base of the extremely weak orthosilicic acid (p''K''a2 = 13.2 at 25 °C). This equilibrium is difficult to study since the acid tends to decompose into a hydrated silica condensate. Structure The orthosilicate ion or group has tetrahedral shape, with one silicon atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms. In the anion, each oxygen carries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covalent Bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding. Covalent bonding also includes many kinds of interactions, including σ-bonding, π-bonding, metal-to-metal bonding, agostic interactions, bent bonds, three-center two-electron bonds and three-center four-electron bonds. The term ''covalent bond'' dates from 1939. The prefix ''co-'' means ''jointly, associated in action, partnered to a lesser degree, '' etc.; thus a "co-valent bond", in essence, means that the atoms share " valence", such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of the molten form; some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring. The most familiar, and historically the oldest, types of manufactured glass are "silicate glasses" based on the chemical compound silica (silicon dioxide, or quartz), the primary constituent of sand. Soda–lime glass, containing around 70% silica, accounts for around 90% of manufactured glass. The term ''glass'', in popular usage, is often used to refer only to this type of material, although silica-free glasses often have desirable properties for applications in modern communications technology. Some objects, such as drinking glasses and eyeglasses, are so commonly made of silicate-based glass that they are simply called by the name of the material. Despite bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polyhedra and the only one that has fewer than 5 faces. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called the circumsphere) on which all four vertices lie, and another sphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octet Rule
The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that reflects the theory that main-group elements tend to bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its valence shell, giving it the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The rule is especially applicable to carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and the halogens; although more generally the rule is applicable for the s-block and p-block of the periodic table. Other rules exist for other elements, such as the duplet rule for hydrogen and helium, or the 18-electron rule for transition metals. The valence electrons can be counted using a Lewis electron dot diagram as shown at the right for carbon dioxide. The electrons shared by the two atoms in a covalent bond are counted twice, once for each atom. In carbon dioxide each oxygen shares four electrons with the central carbon, two (shown in red) from the oxygen itself and two (shown in black) from the carbon. All four of these electrons are counted in both the carbon octet and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickly on the surface. For this reason, olivine has been proposed as a good candidate for accelerated weathering to sequester carbon dioxide from the Earth's oceans and atmosphere, as part of climate change mitigation. Olivine also has many other historical uses, such as the gemstone peridot (or chrysolite), as well as industrial applications like metalworking processes. The ratio of magnesium to iron varies between the two endmembers of the solid solution series: forsterite (Mg-endmember: ) and fayalite (Fe-endmember: ). Compositions of olivine are commonly expressed as molar percentages of forsterite (Fo) and fayalite (Fa) (''e.g.'', Fo70Fa30). Forsterite's melting temperature is unusually high at atmospheric pressure, almost , while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

