|
Silhouette (boat)
The Silhouette also called the Silhouette 17, is a British trailerable sailboat that was designed by Robert Tucker as a pocket cruiser and first built in 1954.Henkel, Steve: ''The Sailor's Book of Small Cruising Sailboats'', page XX. International Marine/McGraw-Hill, 2010. The basic Silhouette 17 design was developed through five marks and produced for more than 30 years. Production Originally made available as a kit for amateur construction from plywood, later kits and finished boats were supplied by Hurley Marine in Plymouth, United Kingdom and later by Varne Marine, among other builders. Production ran between 1954 and 1986, with about 3,000 boats of all marks completed. After drawings were published in ''The Rudder'' magazine in April 1955, some readers noted the boat's outline shape or silhouette and the boat got its name. Design The Silhouette 17 is a recreational keelboat, with the early models built predominantly of plywood and later ones from glassfibre, with wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Tucker (boat Designer)
Robert Tucker (died 1998) was a sailor and boat designer from the United Kingdom. His designs covered a wide range of yachts, but he is principally known for smaller models, of which one source names 18 varieties dating from 1954 to 1972. He is notable for having designed one of the first trailer sailers, the Silhouette A silhouette ( , ) is the image of a person, animal, object or scene represented as a solid shape of a single colour, usually black, with its edges matching the outline of the subject. The interior of a silhouette is featureless, and the silhou .... Boat designs * Matilda 20 * Silhouette (boat) References Year of birth missing 1998 deaths Boat and ship designers {{designer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homebuilt Machines
Homebuilt machines are machines built outside of specialised workshops or factories. This can include different things such as kit cars or homebuilt computers, but normally it pertains to homebuilt aircraft, also known as amateur-built aircraft or kit planes. Homebuilt aircraft or kit cars are constructed by amateurs. Homebuilt computers have been built at home for a long time, starting with the Victorian era pioneer Charles Babbage in the 1820s. A century later, Konrad Zuse built his own machine when electromechanical relay technology was widely available. The hobby took off with the early development of microprocessors and, since then, many enthusiasts have constructed their own computers. A homebuilt vehicle is a wider concept than a kit car. A homebuilt vehicle is a motor vehicle (car, truck or motorcycle) built by an individual instead of a manufacturer. These machines may be constructed "from scratch", from plans, or from assembly kits. Outside of the United States (for exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunter Rig
Gunter rig is a configuration of sail and spars used in sailing. It is a fore and aft sail set abaft (behind) the mast. The lower half of the luff (front) of the sail is attached to the mast, and the upper half is fastened to a spar which is approximately vertical and reaches above the top of the mast. This spar is called a "yard", but it is common for some to confuse it with a "gaff" (as in gaff rig). The overall shape of a gunter sail is roughly triangular, so having a superficial resemblance to Bermuda rig. A gunter sail may also be called a "gunter lug" - a name which suggests developmental origins from increasing the angle of a high peaked standing lug. Gunter sails are sometimes described as "sliding gunter". Gunter rig is generally used in small sailing craft. One important advantage is that the shorter mast used with this rig usually fits within the hull when unstepped, together with the boom and yard. This is helpful for a dinghy that is towed behind a car, stored in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hull Speed
Hull speed or displacement speed is the speed at which the wavelength of a vessel's bow wave is equal to the waterline length of the vessel. As boat speed increases from rest, the wavelength of the bow wave increases, and usually its crest-to-trough dimension (height) increases as well. When hull speed is exceeded, a vessel in displacement mode will appear to be climbing up the back of its bow wave. From a technical perspective, at hull speed the bow and stern waves interfere constructively, creating relatively large waves, and thus a relatively large value of wave drag. Ship drag for a displacement hull increases smoothly with speed as hull speed is approached and exceeded, often with no noticeable inflection at hull speed. The concept of hull speed is not used in modern naval architecture, where considerations of speed/length ratio or Froude number are considered more helpful. Background As a ship moves in the water, it creates standing waves that oppose its movement. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inboard Engine
Marine propulsion is the mechanism or system used to generate thrust to move a watercraft through water. While paddles and sails are still used on some smaller boats, most modern ships are propelled by mechanical systems consisting of an electric motor or internal combustion engine driving a propeller, or less frequently, in pump-jets, an impeller. Marine engineering is the discipline concerned with the engineering design process of marine propulsion systems. Human-powered paddles and oars, and later, sails were the first forms of marine propulsion. Rowed galleys, some equipped with sail, played an important early role in early human seafaring and warfares. The first advanced mechanical means of marine propulsion was the marine steam engine, introduced in the early 19th century. During the 20th century it was replaced by two-stroke or four-stroke diesel engines, outboard motors, and gas turbine engines on faster ships. Marine nuclear reactors, which appeared in the 1950s, produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
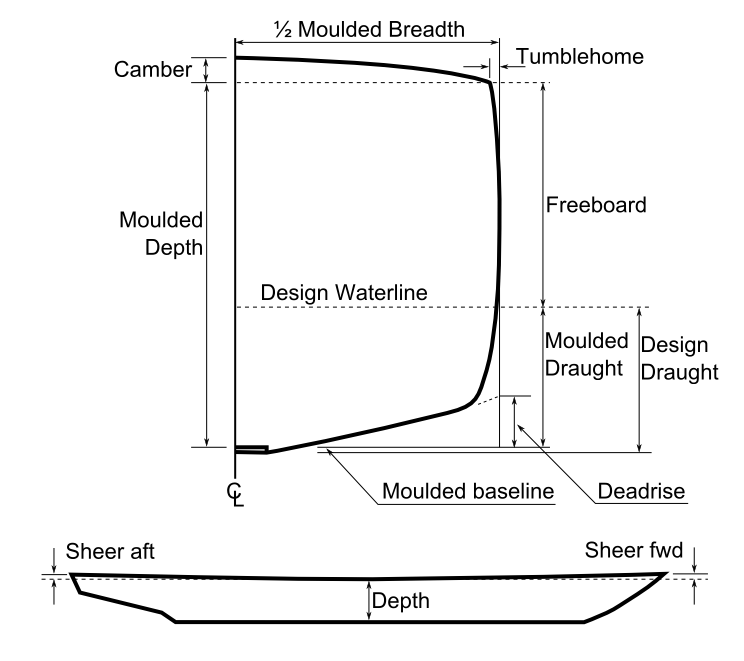
Sheer (ship)
The sheer is a measure of longitudinal main deck curvature, in naval architecture. The sheer forward is usually twice that of sheer aft. Increases in the rise of the sheer forward and aft build volume into the hull, and in turn increase its buoyancy forward and aft, thereby keeping the ends from diving into an oncoming wave and slowing the ship. In the early days of sail, one discussed a hull's sheer in terms of how much "hang" it had. William Sutherland's ''The Ship-builders Assistant'' (1711) covers this information in more detail. The practice of building sheer into a ship dates back to the era of small sailing ships. These vessels were built with the decks curving upwards at the bow and stern in order to increase stability by preventing the ship from pitching up and down. Sheer on exposed decks also makes a ship more seaworthy by raising the deck at fore and aft ends further from the water and by reducing the volume of water coming on deck. See also *Camber (ship) The camb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in British and American shipbuilding traditions the construction is dated from this event. Etymology The word "keel" comes from Old English , Old Norse , = "ship" or "keel". It has the distinction of being regarded by some scholars as the first word in the English language recorded in writing, having been recorded by Gildas in his 6th century Latin work ''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'', under the spelling ''cyulae'' (he was referring to the three ships that the Saxons first arrived in). is the Latin word for "keel" and is the origin of the term careen (to clean a keel and the hull in general, often by rolling the ship on its side). An example of this use is Careening Cove, a suburb of Sydney, Australia, where careening was carried out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiller
A tiller or till is a lever used to steer a vehicle. The mechanism is primarily used in watercraft, where it is attached to an outboard motor, rudder post or stock to provide leverage in the form of torque for the helmsman to turn the rudder. A tiller may also be used in vehicles outside of water, and was seen in early automobiles. On vessels, a tiller can be used by the helmsman directly pulling or pushing it, but it may also be moved remotely using tiller lines or a ship's wheel. Rapid or excessive movement of the tiller results in an increase in drag and will result in braking or slowing the boat. Description A tiller is a lever used to steer a vehicle. It provides leverage in the form of torque to turn the device that changes the direction of the vehicle, such as a rudder on a watercraft or the surface wheels on a wheeled vehicle. A tiller can be used by directly pulling or pushing it, but it may also be moved remotely using tiller lines or a ship's wheel; some kayaks wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally aircraft, air or watercraft, water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw and p-factor and is not the primary control used to turn the airplane. A rudder operates by redirecting the fluid past the hull (watercraft), hull or fuselage, thus imparting a turning or yaw (rotation), yawing motion to the craft. In basic form, a rudder is a flat plane or sheet of material attached with hinges to the craft's stern, tail, or after end. Often rudders are shaped so as to minimize Drag (physics), hydrodynamic or aerodynamic drag. On simple watercraft, a tiller—essentially, a stick or pole acting as a lever arm—may be attached to the top of the rudder to allow it to be turned by a helmsman. In larger vessels, cables, pushrods, or hydraulics may be used to link rudders to steering wheels. In typical air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transom (nautical)
A transom is the vertical reinforcement which strengthens the stern of a boat. This flat termination of the stern is typically above the waterline. The term was used as far back as Middle English in the 1300s, having come from Latin ''transversus'' (transverse) via Old French ''traversain'' (set crosswise). The stern of a boat is typically vertical. It can be raked such that there is an overhang above the water, as at the bow. A reverse transom is angled from the waterline forwards. Transoms can be used to support a rudder, outboard motor, or as a swimming and access platform. Gallery File:The Bermuda cedar (Juniperus bermudiana) transom of Spirit of Bermuda, 2016.jpg, The Bermuda cedar transom of the Spirit of Bermuda File:Sea Scooter transom.jpg, Flat transom on a dinghy with mount points for a rudder. File:Coble on shore at Boulmer (2) - geograph.org.uk - 1381157.jpg, Raked transom with rudder mount points. File:CS 30 Sailboat Kelsea 0297.jpg, Reverse transom with rudder m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raked Stem
The stem is the most forward part of a boat or ship's bow and is an extension of the keel itself. It is often found on wooden boats or ships, but not exclusively. Description The stem is the curved edge stretching from the keel below, up to the gunwale of the boat. It is part of the physical structure of a wooden boat or ship that gives it strength at the critical section of the structure, bringing together the port and starboard side planks of the hull. Plumb and raked stem There are two styles of stems: ''plumb'' and ''raked''. When the stem comes up from the water, if it is perpendicular to the waterline it is "plumb". If it is inclined at an angle to the waterline it is "raked". (For example, "The hull is single decked and characterized by a plumb stem, full bows, straight keel, moderate deadrise, and an easy turn of bilge.") Stemhead Because the stem is very sturdy, the top end of it may have something attached, either ornamental or functional in nature. On small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masthead Sloop
A masthead rig on a sailing vessel consists of a forestay and backstay both attached at the top of the mast. The Bermuda rig can be split into two groups: the masthead rig and the fractional rig. The masthead rig has larger and more headsails, and a smaller mainsail, compared to the fractional rig. The major advantage a masthead sloop has over a fractional one, is that the jib is larger. Since the jib has no mast in front of it to cause turbulent airflow over it, it is considered much more efficient than the main, especially for sailing up wind. Also, since the fore stay is attached to the top of the mast, it pulls directly against the back stay. Tightening the back stay, then, increases the tension on the fore stay. This is useful because the jib needs considerable fore stay tension to set well. This need increases in direct proportion to the wind speed and jib size. Increasing the tension on the back stay does not tend to bend the mast, as it would on a fractional sloop. It put ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)