|
Sileo (electricity Bus)
Dexmedetomidine, sold under the trade name Precedex among others, is a drug used in humans for sedation. Veterinarians use dexmedetomidine for similar purposes in treating cats, dogs, and horses. It is also used in humans to treat acute agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I or II disorder. Similar to clonidine, it is a sympatholytic drug that acts as an agonist of α2-adrenergic receptors in certain parts of the brain. It was developed by Orion Pharma. Medical uses Intensive care unit sedation Studies suggest dexmedetomidine for sedation in mechanically ventilated adults may reduce time to extubation and ICU stay. Compared with other sedatives, some studies suggest dexmedetomidine may be associated with less delirium. However, this finding is not consistent across multiple studies. At the very least, when aggregating many study results together, use of dexmedetomidine appears to be associated with less neurocognitive dysfunction compared to other sedatives. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Therapy
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium), was discovered accidentally by Leo Sternbach in 1955 and was made available in 1960 by Hoffmann–La Roche, who soon followed with diazepam (Valium) in 1963. By 1977, benzodiazepines were the most prescribed medications globally; the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), among other factors, decreased rates of prescription, but they remain frequently used worldwide. Benzodiazepines are depressants that enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the GABAA receptor, resulting in sedative, hypnotic ( sleep-inducing), anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant properties. High doses o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventrolateral Preoptic Nucleus
The ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO), also known as the intermediate nucleus of the preoptic area (IPA), is a small cluster of neurons situated in the anterior hypothalamus, sitting just above and to the side of the optic chiasm in the brain of humans and other animals. The brain's sleep-promoting nuclei (e.g., the VLPO, parafacial zone, nucleus accumbens core, and lateral hypothalamic MCH neurons), together with the ascending arousal system which includes components in the brainstem, hypothalamus and basal forebrain, are the interconnected neural systems which control states of arousal, sleep, and transitions between these two states. The VLPO is active during sleep, particularly during non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREM sleep), and releases inhibitory neurotransmitters, mainly GABA and galanin, which inhibit neurons of the ascending arousal system that are involved in wakefulness and arousal. The VLPO is in turn innervated by neurons from several components of the ascen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem. The brainstem is very small, making up around only 2.6 percent of the brain's total weight. It has the critical roles of regulating cardiac, and respiratory function, helping to control heart rate and breathing rate. It also provides the main motor and sensory nerve supply to the face and neck via the cranial nerves. Ten pairs of cranial nerves come from the brainstem. Other roles include the regulation of the central nervous system and the body's sleep cycle. It is also of prime importance in the conveyance of motor and sensory pathways from the rest of the brain to the body, and from the body back to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
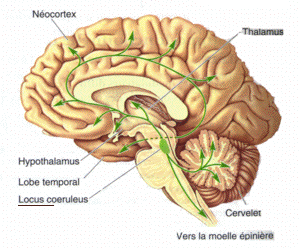
Locus Coeruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system. The locus coeruleus, which in Latin means "blue spot", is the principal site for brain synthesis of norepinephrine (noradrenaline). The locus coeruleus and the areas of the body affected by the norepinephrine it produces are described collectively as the locus coeruleus-noradrenergic system or LC-NA system. Norepinephrine may also be released directly into the blood from the adrenal medulla. Anatomy The locus coeruleus (LC) is located in the posterior area of the rostral pons in the lateral floor of the fourth ventricle. It is composed of mostly medium-size neurons. Melanin granules inside the neurons of the LC contribute to its blue colour. Thus, it is also known as the nucleus pigmentosus pontis, meaning "heavily pigmented nucleus of the pons." The n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage cardiac arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second myocardial infarction, heart attack after a first heart attack (preventative healthcare, secondary prevention). They are also widely used to treat hypertension, high blood pressure, although they are no longer the first choice for initial treatment of most patients. Beta blockers are competitive antagonists that block the receptor sites for the endogenous catecholamines Adrenaline, epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) on beta receptor, adrenergic beta receptors, of the sympathetic nervous system, which mediates the fight-or-flight response. Some block activation of all types of β-adrenergic receptors and others are selective for one of the three known types of beta receptors, designated β1, β2 and β3 receptors. Beta-1 adrenergic receptor, β1-adrenergic receptors are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrioventricular Block
Atrioventricular block (AV block) is a type of heart block that occurs when the electrical signal traveling from the atria, or the upper chambers of the heart, to ventricles, or the lower chambers of the heart, is impaired. Normally, the sinoatrial node (SA node) produces an electrical signal to control the heart rate. The signal travels from the SA node to the ventricles through the atrioventricular node (AV node). In an AV block, this electrical signal is either delayed or completely blocked. When the signal is completely blocked, the ventricles produce their own electrical signal to control the heart rate. The heart rate produced by the ventricles is much slower than that produced by the SA node. Some AV blocks are benign, or normal, in certain people, such as in athletes or children. Other blocks are pathologic, or abnormal, and have several causes, including ischemia, infarction, fibrosis, and drugs. __TOC__ Classification There are three types, or degrees, of AV block: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Anesthetic Nerve Block
Local anesthetic nerve block (local anesthetic regional nerve blockade, or often simply nerve block) is a short-term nerve block involving the injection (medicine), injection of local anesthetic as close to the nerve as possible for analgesia, pain relief. The local anesthetic bathes the nerve and numbs the area of the body that is supplied by that nerve. The goal of the nerve block is to prevent pain by blocking the transmission of pain signals from the affected area. Nerve blocks have a number of uses including treating headache disorders and providing anesthesia during surgery. The analgesia, pain relief provided by the block is present during the surgery and continues to last after the procedure. This can lead to a reduction in the amount of opiates needed for pain control. The advantages of nerve blocks over General anaesthesia, general anesthesia include faster recovery, Anesthesia awareness#Conscious sedation and monitored anesthesia care, monitored anesthesia care vs. Trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overdose
A drug overdose (overdose or OD) is the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities much greater than are recommended.Definitions Retrieved on 20 September 2014."Stairway to Recovery: Glossary of Terms" . Retrieved on 19 March 2021 Typically it is used for cases when a risk to health will potentially result. An overdose may result in a toxic state or . Classification [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocaine Intoxication
Cocaine intoxication refers to the subjective, desired and adverse effects of cocaine on the mind and behavior of users. Both self-induced and involuntary cocaine intoxication have medical and legal implications (even in absence of relevant adverse effects). Adverse effects can develop over time due to repeated use and so become chronic conditions. However, even a one-time intake of the substance can result in severe acute intoxication. Recurrent cocaine use and dependence to the drug inevitably leads to the reduction of the desired effects perceived by the users, while the occurrence of adverse effects of intoxication increase. The last can sometimes be completely reversed without bearing consequences but they can also potentially kill the users (e.g., in cases of untreated or non-manageable overdoses). Signs and symptoms Cocaine increases alertness, feelings of well-being, euphoria, energy, sociability, and sexuality. The former are some of the desired effects of cocaine int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechuan languages, Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly recreational drug use, used recreationally for its euphoria, euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South America, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense''. After extraction from coca leaves and further processing into cocaine hydrochloride (powdered cocaine), the drug is often Insufflation (medicine), snorted, applied topical administration, topically to the mouth, or dissolved and injection (medicine), injected into a vein. It can also then be turned into free base form (crack cocaine), in which it can be heated until sublimated and then the vapours can be smoking, inhaled. Cocaine stimulates the mesolimbic pathway, reward pathway in the brain. Mental effects may include an euphoria, intense feeling of happiness, sexual arousal, psychosis, loss of contact with reality, or psychomo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |