|
Sikkimese Language
The Sikkimese language, also called Sikkimese, Bhutia, or Drenjongké (, "Rice Valley language"),"Lost Syllables and Tone Contour in Dzongkha (Bhutan)" ''in'' David Bradley, Eguénie J.A. Henderson and Martine Mazaudon, eds, Prosodic analysis and Asian linguistics: to honour R. K. Sprigg, 115-136; Pacific Linguistics, C-104, 1988 ''Dranjoke'', ''Denjongka'', ''Denzongpeke'' and ''Denzongke'', belongs to the Tibeto-Burman languages. It is spoken by the Bhutia in Sikkim, India and in parts of Province No. 1, Nepal. The Sikkimese people refer to their own language as Drendzongké and their homeland as Drendzong (, "Rice Valley"). Up until 1975 Sikkimese did not have a written language. After gaining Indian Statehood the language was introduced as a school subject in Sikkim and the written language was developed. Script Sikkimese is written using Sambhota script and Zhang Yeshe De Script, which it inherited from Classical Tibetan. Sikkimese phonology and lexicon differ markedly f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
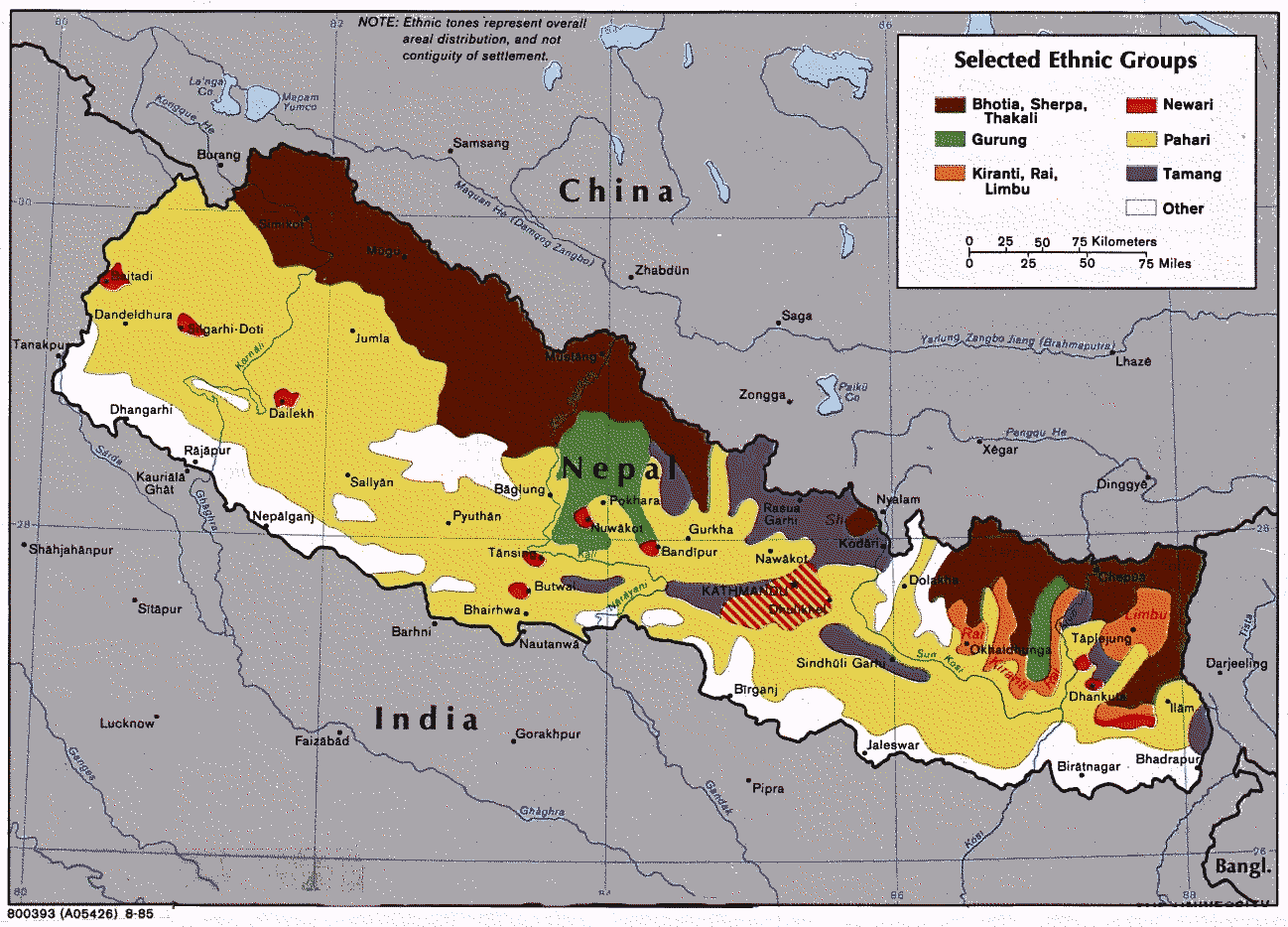
Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Siliguri Corridor, which borders Bangladesh. Sikkim is the least populous and second smallest among the Indian states. Situated in the Eastern Himalaya, Sikkim is notable for its biodiversity, including alpine and subtropical climates, as well as being a host to Kangchenjunga, the highest peak in India and third highest on Earth. Sikkim's capital and largest city is Gangtok. Almost 35% of the state is covered by Khangchendzonga National Park – a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The Kingdom of Sikkim was founded by the Namgyal dynasty in the 17th century. It was ruled by Buddhist priest-kings known as the Chogyal. It became a princely state of British India in 1890. Following Indian independence, Sikkim continued its protectorate stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIL International
SIL International (formerly known as the Summer Institute of Linguistics) is an evangelical Christian non-profit organization whose main purpose is to study, develop and document languages, especially those that are lesser-known, in order to expand linguistic knowledge, promote literacy, translate the Christian Bible into local languages, and aid minority language development. Based on its language documentation work, SIL publishes a database, '' Ethnologue'', of its research into the world's languages, and develops and publishes software programs for language documentation, such as FieldWorks Language Explorer (FLEx) and Lexique Pro. Its main offices in the United States are located at the International Linguistics Center in Dallas, Texas. History William Cameron Townsend, a Presbyterian minister, founded the organization in 1934, after undertaking a Christian mission with the Disciples of Christ among the Kaqchikel Maya people in Guatemala in the early 1930s.George Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolar Consonant
Alveolar (; UK also ) consonants are place of articulation, articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the Dental alveolus, alveoli (the sockets) of the upper teeth. Alveolar consonants may be articulated with the tip of the tongue (the apical consonants), as in English, or with the flat of the tongue just above the tip (the "blade" of the tongue; called laminal consonants), as in French and Spanish. The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) does not have separate symbols for the alveolar consonants. Rather, the same symbol is used for all Coronal consonant, coronal places of articulation that are not Palatalization (phonetics), palatalized like English Palato-alveolar consonant, palato-alveolar ''sh'', or retroflex. To disambiguate, the ''bridge'' (, ''etc.'') may be used for a dental consonant, or the retracted (phonetics), under-bar (, ''etc.'') may be used for the postalveolar consonant, postalveolars. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Consonant
A dental consonant is a consonant articulated with the tongue against the upper teeth, such as , . In some languages, dentals are distinguished from other groups, such as alveolar consonants, in which the tongue contacts the gum ridge. Dental consonants share acoustic similarity and in Latin script are generally written with consistent symbols (e.g. ''t'', ''d'', ''n''). In the International Phonetic Alphabet, the diacritic for dental consonant is . When there is no room under the letter, it may be placed above, using the character , such as in / p͆/. Cross-linguistically For many languages, such as Albanian, Irish and Russian, velarization is generally associated with more dental articulations of coronal consonants. Thus, velarized consonants, such as Albanian , tend to be dental or denti-alveolar, and non-velarized consonants tend to be retracted to an alveolar position. Sanskrit, Hindustani and all other Indo-Aryan languages have an entire set of dental stops that o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labial Consonant
Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. The two common labial articulations are bilabials, articulated using both lips, and labiodentals, articulated with the lower lip against the upper teeth, both of which are present in English. A third labial articulation is dentolabials, articulated with the upper lip against the lower teeth (the reverse of labiodental), normally only found in pathological speech. Generally precluded are linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue contacts the posterior side of the upper lip, making them coronals, though sometimes, they behave as labial consonants. The most common distribution between bilabials and labiodentals is the English one, in which the nasal and the stops, , , and , are bilabial and the fricatives, , and , are labiodental. The voiceless bilabial fricative, voiced bilabial fricative, and the bilabial approximant do not exist as the primary realizations of any sounds in Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Helsinki
The University of Helsinki ( fi, Helsingin yliopisto, sv, Helsingfors universitet, abbreviated UH) is a public research university located in Helsinki, Finland since 1829, but founded in the city of Turku (in Swedish ''Åbo'') in 1640 as the Royal Academy of Åbo, at that time part of the Swedish Empire. It is the oldest and largest university in Finland with the widest range of disciplines available. In 2020, around 31,600 students were enrolled in the degree programs of the university spread across 11 faculties and 11 research institutes. As of 1 August 2005, the university complies with the harmonized structure of the Europe-wide Bologna Process and offers bachelor, master, licenciate, and doctoral degrees. Admission to degree programmes is usually determined by entrance examinations, in the case of bachelor's degrees, and by prior degree results, in the case of master and postgraduate degrees. Entrance is particularly selective (circa 15% of the yearly applicants are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honorifics (linguistics)
In linguistics, an honorific (abbreviated ) is a grammatical or morphosyntactic form that encodes the relative social status of the participants of the conversation. Distinct from honorific titles, linguistic honorifics convey formality , social distance, politeness , humility , deference, or respect through the choice of an alternate form such as an affix, clitic, grammatical case, change in person or number, or an entirely different lexical item. A key feature of an honorific system is that one can convey the same message in both honorific and familiar forms—i.e., it is possible to say something like (as in an oft-cited example from Brown and Levinson) "The soup is hot" in a way that confers honor or deference on one of the participants of the conversation. Honorific speech is a type of social deixis, as an understanding of the context—in this case, the social status of the speaker relative to the other participants or bystanders—is crucial to its use. There are three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Intelligibility
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. It is sometimes used as an important criterion for distinguishing languages from dialects, although sociolinguistic factors are often also used. Intelligibility between languages can be asymmetric, with speakers of one understanding more of the other than speakers of the other understanding the first. When it is relatively symmetric, it is characterized as "mutual". It exists in differing degrees among many related or geographically proximate languages of the world, often in the context of a dialect continuum. Intelligibility Factors An individual's achievement of moderate proficiency or understanding in a language (called L2) other than their first language (L1) typically requires considerable time and effort through study and practical application if the two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepali Language
Nepali (; , ) is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Himalayas region of South Asia. It is the official, and most widely spoken, language of Nepal, where it also serves as a '' lingua franca''. Nepali has official status in the Indian state of Sikkim and in the Gorkhaland Territorial Administration of West Bengal. It is spoken by about a quarter of Bhutan's population. Nepali also has a significant number of speakers in the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Uttarakhand. In Myanmar it is spoken by the Burmese Gurkhas. The Nepali diaspora in the Middle East, Brunei, Australia and worldwide also use the language. Nepali is spoken by approximately 16 million native speakers and another 9 million as a second language. Nepali is commonly classified within the Eastern Pahari group of the Northern zone of Indo-Aryan. The language originated from the Sinja Valley, Karnali Province then the capital city of the Khasa Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gangtok
Gangtok is a city, municipality, the capital and the largest populated place of the Indian state of Sikkim. It is also the headquarters of the Gangtok District. Gangtok is in the eastern Himalayan range, at an elevation of . The city's population of 100,000 are from different ethnicities of Sikkimese people such as Indian Gorkhas, Bhutia and Lepchas. Within the higher peaks of the Himalayas and with a year-round mild temperate climate, Gangtok is at the centre of Sikkim's tourism industry. Gangtok rose to prominence as a popular Buddhist pilgrimage site after the construction of the Enchey Monastery in 1840. In 1894, the ruling Sikkimese Chogyal, Thutob Namgyal, transferred the capital to Gangtok. In the early 20th century, Gangtok became a major stopover on the trade route between Lhasa in Tibet and cities such as Kolkata (then Calcutta) in British India. After India won its independence from the British Empire in 1947, Sikkim chose to remain an independent monarchy, with Gan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamang Language
Tamang (Devanagari: तामाङ; ''tāmāng'') is a term used to collectively refer to a dialect cluster spoken mainly in Nepal, Sikkim, West Bengal ( Darjeeling) and North-Eastern India. It comprises Eastern Tamang, Northwestern Tamang, Southwestern Tamang, Eastern Gorkha Tamang, and Western Tamang. Lexical similarity between Eastern Tamang (which is regarded as the most prominent) and other Tamang languages varies between 81% to 63%. For comparison, lexical similarity between Spanish and Portuguese, is estimated at 89%. Ethnologue report for Spanish Dialects '' Ethnologue'' divides Tamang into the following varieties due to mutual unintelligibility. *Eastern Tamang: 759,000 in Nepal (2000 WCD). Population total all countries: 773,000. Sub-dialects are as follows. **Outer-Eastern Tamang (Sailung Tamang) **Central-Eastern Tamang (Temal Tamang) **Southwestern Tamang (Kath-Bhotiya, Lama Bhote, Murmi, Rongba, Sain, Tamang Gyoi, Tamang Gyot, Tamang Lengmo, Tamang Tam) *We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yolmo Language
Yolmo (Hyolmo) or Helambu Sherpa, is a Tibeto-Burman language of the Hyolmo people of Nepal (ISO 639-3: scp, GlottoCodeyolm1234. Yolmo is spoken predominantly in the Helambu and Melamchi valleys in northern Nuwakot District and northwestern Sindhupalchowk District. Dialects are also spoken by smaller populations in Lamjung District and Ilam District and also in Ramecchap District (where it is known as Syuba). It is very similar to Kyirong Tibetan and less similar to Standard Tibetan and Sherpa. There are approximately 10,000 Yolmo speakers, although some dialects have larger populations than others. Language name Yolmo is both the name of the language (glottonym), and the ethnic group of people who speak the language ( ethnonym). Yolmo is also written ''Hyolmo, Yholmo'' or ''Yohlmo''. The 'h' in all of these spellings marks that the word has low tone. Sometimes the language is referred to as ''Yolmo Tam'', ''tam'' is the Yolmo word for 'language'. The language is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)