|
Sierra Ancha
The Sierra Ancha ("broad range" in Spanish, in Western Apache: Dził Nteel - "Wide Flat Mountain") is a mountain range in Gila County, in central Arizona. It lies between Roosevelt Lake to the south, the Tonto Basin to the west, Cherry Creek to the east, and Pleasant Valley to the north. The range is one of several, including the Bradshaw Mountains, Mingus Mountain of the Black Hills, and the Mazatzal Mountains, which form a ''transitional zone'' between the lowland deserts of southern Arizona and the Colorado Plateau of northeastern Arizona. The highest point in the range is Aztec Peak, at an elevation of 2345 m (7694 ft). The Sierra Ancha is penetrated by few improved roads, and the range is cut by numerous deep, spectacular canyons, particularly on its eastern flank. Little agricultural, commercial, or residential development has taken place, though in the past asbestos mining was carried out at a mine between Asbestos and Zimmerman Points. Cattle ranching is st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonto Basin, Arizona
Tonto Basin is a census-designated place (CDP) in Gila County, Arizona, United States. The population was 1,424 at the 2010 United States Census, up from 840 in 2000. Within Tonto Basin is located the unincorporated community of Punkin Center. History The Pleasant Valley War (also sometimes called the Tonto Basin War or Feud) was an 1886 Arizona range war between two feuding families, the cattle-herding Grahams and the sheep-herding Tewksburys. Geography Tonto Basin is located in western Gila County at (33.839953, -111.284734), in the valley of Tonto Creek, a south-flowing tributary of the Salt River. Arizona State Route 188 passes through the community, leading southeast to Globe, the county seat, and north to Payson. According to the United States Census Bureau, the Tonto Basin CDP has a total area of , all land. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 840 people, 439 households, and 262 families residing in the CDP. The population density was . There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mogollon Culture
Mogollon culture () is an archaeological culture of Native American peoples from Southern New Mexico and Arizona, Northern Sonora and Chihuahua, and Western Texas. The northern part of this region is Oasisamerica, while the southern span of the Mogollon culture is known as Aridoamerica. The Mogollon culture is one of the major prehistoric Southwestern cultural divisions of the Southwestern United States and Northern Mexico. The culture flourished from the archaic period, , to either 1450 or 1540 CE, when the Spanish arrived. Etymology The name ''Mogollon'' comes from the Mogollon Mountains, which were named after Don Juan Ignacio Flores Mogollón, Spanish Governor of New Spain (including what is now New Mexico) from 1712 to 1715. The name was chosen and defined in 1936 by archaeologist Emil W. Haury. Cultural traits The distinct facets of Mogollon culture were recorded by Emil Haury, based on his excavations in 1931, 1933, and 1934 at the Harris Village in Mimbres, New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salado Culture
Salado culture, or Salado Horizon, Todd Bostwick of Pueblo Grande Museum, "Salado Summary". was a human culture in the upper Salt River () of the Tonto Basin in southeastern Arizona from approximately 1150 CE through the 15th century. Distinguishing characteristics of the Salado include distinctive Salado Polychrome pottery, communities within walled adobe compounds, and burial of the dead (rather than cremation). The Salado were farmers, using simple irrigation techniques to water fields of maize, beans, pumpkins, amaranth, and cotton. They also hunted local game and gathered buds, leaves, and roots to supplement their diet. The Salado: People of the Salt River" by National Park Service. They traded with other cultures, as indicated by archaeological finds of seashells from the |
Cliff-dwelling
In archaeology, cliff dwellings are dwellings formed by using niches or caves in high cliffs, and sometimes with excavation or additions in the way of masonry. Two special types of cliff dwelling are distinguished by archaeologists: the cliff-house, which is actually built on levels in the cliff, and the cavate, which is dug out, by using natural recesses or openings. Rock-cut architecture generally refers to rather grander temples, but also tombs, cut into living rock, although for example the Ajanta Caves in India, of the 2nd century BCE to 5th century CE, probably housed several hundred Buddhist monks and are cut into a cliff, as are the Mogao Caves in China. Famous cliff dwellings are found around the world. In China, the Guyaju Caves located near Dongmenying, Yanqing District, Beijing are a cave complex of many rock hewn dwellings that form a community. In the United States and Mexico, among the canyons of the southwest, in Arizona, New Mexico, Utah, Colorado, and C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the ''drainage divide'', made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern. Other terms for a drainage basin are catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, water basin, and impluvium. In North America, they are commonly called a watershed, though in other English-speaking places, "watershed" is used only in its original sense, that of a drainage divide. In a closed drainage basin, or endorheic basin, the water converges to a single point inside the basin, known as a sink, which may be a permanent lake, a dry lake, or a point where surface water is lost underground. Drainage basins are similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Nevada, Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah. The largest cities by List of metropolitan statistical areas, metropolitan area are Phoenix, Arizona, Phoenix, Las Vegas, El Paso, Texas, El Paso, Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque, and Tucson, Arizona, Tucson. Prior to 1848, in the historical region of Santa Fe de Nuevo México as well as parts of Alta California and Coahuila y Tejas, settlement was almost non-existent outside of Nuevo México's Pueblos and Santa Fe de Nuevo México#Regions and municipalities, Spanish or Mexican municipalities. Much of the area had been a part of New Spain and Mexico until the United States acquired the area through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 and the smaller Gadsden Purchase in 1854. While the region's bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierra Ancha Wilderness
The Sierra Ancha Wilderness The Sierra Ancha Wilderness is located about 100 miles east of Phoenix, between Globe and Young. Though fairly small at 32 square miles, it contains some of the most rugged and inaccessible terrain in Arizona. Most of the Sierra Ancha Wilderness lies at an elevation of about 7000 feet. But along the eastern border, is a U.S. wilderness area on the Tonto National Forest in the state of Arizona. The terrain varies from box canyons to high cliffs and pine-covered mountains. Elevations range from lows of about to a high of at Aztec Peak. It is one of two wilderness areas within the Sierra Ancha mountain range. Cherry Creek has cut a substantial valley down to an elevation of 3000 to 3500 feet. The four thousand foot elevation change from the mesa top to the river results in a series of vertical-walled canyons cutting back into the mesa towards the west. Within these canyons, virtually any south-facing location with a protective overhang and sufficient b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salome Creek
Salome Creek is a watercourse in the Salome Wilderness in central Arizona, United States. Natural history The oldest exposed rock forms in the watershed are graphic granite, which dates to 1400 million years before present. The watershed holds a diverse flora and fauna. Within this part of the Sierra Ancha range there are notable disjunctive populations of Coastal woodfern, ''Dryopteris arguta'';C. Michael Hogan. 2008 this fern is otherwise common in areas nearer the Pacific coast. See also * Workman Creek Workman Creek is a watercourse in the Salome Wilderness in central Arizona, United States. Natural history The oldest exposed rock forms in the general area are Runite granite, which dates to 1400 million years before present. The watershed holds ... References :;Citations * Ivo Lucchitta. 2001. ''Hiking Arizona's Geology'', Published by The Mountaineers Books, * Tom Dollar and Jerry Sieve. 1999. ''Guide to Arizona's Wilderness Areas'', Big Earth Publishing, * C. Michael ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salome Wilderness
The Salome Wilderness of Tonto National Forest is a protected area in the rim country of the southwestern US. The Salome Wilderness lies within the Sierra Ancha mountain range in Gila County, Arizona. Ecology Prominent perennial streams within this wilderness area are Workman Creek and Salome Creek. The region has a diverse flora and fauna. Within this part of the Sierra Ancha Range there are notable disjunctive populations of Coastal woodfern, ''Dryopteris arguta ''Dryopteris arguta'', with the common name coastal woodfern, is a species of wood fern. It is native to the west coast and western interior mountain ranges of North America, from British Columbia, throughout California, and into Arizona. It g ...'';C. Michael Hogan. 2008 this fern is otherwise common in areas nearer the Pacific coast. References * Tom Dollar and Jerry Sieve. 1999. ''Guide to Arizona's Wilderness Areas'', Big Earth Publishing, , 304 pages * C. Michael Hogan. 2008''Coastal Woodfern (Dryopteris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
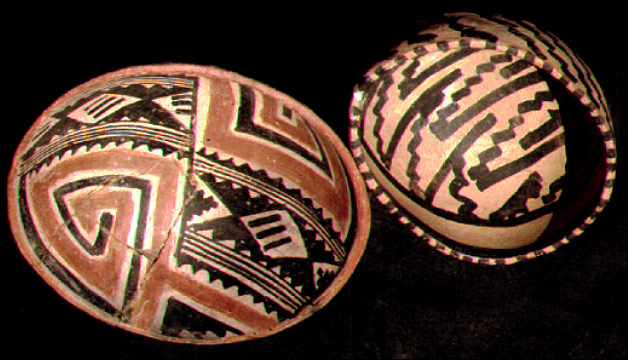
%2C_Arizona.jpg)
.jpg)