|
Siege Of Euripos
The siege of Euripos (modern Chalcis) occurred in the mid-880s, when an Abbasid fleet, led by the emir of Tarsos, Yazaman al-Khadim, laid siege to the city. The local Byzantine commander, Oiniates, successfully defended the city and destroyed a large part of the besieging force. Background In the 820s, two events, the beginning of the Muslim conquest of Sicily and the establishment of the Emirate of Crete, altered the balance of power between the Byzantine Empire and the Arabs in the Mediterranean. The former soon led to the establishment of Muslim bases on the Italian peninsula, while the loss of Crete was particularly important, as it opened the Aegean Sea to constant Muslim raiding. Apart from the raids of the Cretan Saracens, the Abbasid caliphs also took care to strengthen their forces in the Cilician frontier districts, and Tarsos became a major base for land and seaborne attacks against Byzantine territory. This was especially the case during the tenure of Yazaman al-Khadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab–Byzantine Wars
The Arab–Byzantine wars were a series of wars between a number of Muslim Arab dynasties and the Byzantine Empire between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. Conflict started during the initial Muslim conquests, under the expansionist Rashidun and Umayyad caliphs, in the 7th century and continued by their successors until the mid-11th century. The emergence of Muslim Arabs from Arabia in the 630s resulted in the rapid loss of Byzantium's southern provinces ( Syria and Egypt) to the Arab Caliphate. Over the next fifty years, under the Umayyad caliphs, the Arabs would launch repeated raids into still-Byzantine Asia Minor, twice besiege the Byzantine capital of Constantinople, and conquer the Byzantine Exarchate of Africa. The situation did not stabilize until after the failure of the Second Arab Siege of Constantinople in 718, when the Taurus Mountains on the eastern rim of Asia Minor became established as the mutual, heavily fortified and largely depopulated frontier. Under the Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Skylitzes
John Skylitzes, commonly Latinized as Ioannes, la, Johannes, label=none, la, Iōannēs, label=none Scylitzes ( el, Ἰωάννης Σκυλίτζης, ''Iōánnēs Skylítzēs'', or el, Σκυλίτση, ''Skylítsē'', label=none ; la, Ioannes Scyllitzes, , la, Scylitza, label=none , or la, Schillizzi, label=none ; early 1040s – after 1101), was a Byzantine historian of the late 11th century. Life Very little is known about his life. The title of his work records him as a ''kouropalatēs'' and a former ''droungarios'' of the ''Vigla'', whereby he is usually identified with a certain John Thrakesios. His major work is the ''Synopsis of Histories'' ( el, Σύνοψις Ἱστοριῶν ), which covers the reigns of the Byzantine emperors from the death of Nikephoros I in 811 to the deposition of Michael VI in 1057; it continues the chronicle of Theophanes the Confessor. There is a continuation of this work, known as ''Scylitzes Continuatus'', covering 1057 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
880s In The Byzantine Empire
88 may refer to: * 88 (number) * one of the years 88 BC, AD 88, 1888 CE, 1988 CE, 2088 CE, etc. * "88", a song by Sum 41 from '' Chuck'' * "88", a song by The Cool Kids from ''The Bake Sale'' * The 88, an American indie rock band * ''The 88'' (album), the 2003 debut album by New Zealand band Minuit * Highway 88, see List of highways numbered 88 * The 88 (San Jose), a residential skyscraper in San Jose, California, USA * The 88, a nickname for the piano derived from the number of keys it typically has * A Morse code abbreviation meaning "Love and kisses" * 88 Generation Students Group, a Burmese pro-democracy movement * 8.8 cm Flak 18/36/37/41, known as ''the eighty-eight'', a German anti-tank and anti-aircraft gun from World War II * ''88'' (film), a 2015 film directed by April Mullen, starring Katharine Isabelle * Atomic number 88: radium * The butterfly genus ''Diaethria'', which has an 88-like pattern on its wings * The butterfly genus ''Callicore'', which has an 88-like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros Phokas
Nikephoros II Phokas (; – 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless included brilliant military exploits which contributed to the resurgence of the Byzantine Empire during the 10th century. In the east, Nikephoros completed the conquest of Cilicia and even retook the islands of Crete and Cyprus, thus opening the path for subsequent Byzantine incursions reaching as far as Upper Mesopotamia and the Levant; these campaigns earned him the sobriquet "pale death of the Saracens". Meanwhile in the west, he inflamed conflict with the Bulgarians and saw Sicily completely turn over to the Muslims, while he failed to make any serious gains in Italy following the incursions of Otto I. At home, Nikephoros' administrative policies caused controversy. He financed his wars with increased taxes both on the people and on the church, while maintaining unpopular th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geographically in Western Asia, its cultural ties and geopolitics are overwhelmingly Southern European. Cyprus is the third-largest and third-most populous island in the Mediterranean. It is located north of Egypt, east of Greece, south of Turkey, and west of Lebanon and Syria. Its capital and largest city is Nicosia. The northeast portion of the island is ''de facto'' governed by the self-declared Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, which was established after the 1974 invasion and which is recognised as a country only by Turkey. The earliest known human activity on the island dates to around the 10th millennium BC. Archaeological remains include the well-preserved ruins from the Hellenistic period such as Salamis and Kourion, and Cypr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sack Of Thessalonica (904)
The Sack of Thessalonica refers to the capture, and subsequent sack, of the Byzantine city of Thessalonica by the Abbasid Caliphate in the year 904, led by Leo of Tripoli, a privateer and Muslim convert. Background The city, which is now in modern-day Greece, was in 904 A.D. a part of the Byzantine Empire, and was considered the greatest city in the empire, second only to Constantinople. Following the weakening of centralized power in the Abbasid Caliphate due to the Fourth Fitna and the Anarchy at Samarra, many areas of the vast Abbasid Caliphate began to breakaway from the Caliph's control and while still paying religious lip service, acted independently on military and state matters. The attention of these largely autonomous Muslim dynasties was subsequently turned to the Mediterranean sea. In 860 the Muslim dynasties attempted to reassert their dominance over the Mediterranean seaway and built naval bases at Tripoli and Tarsus. In 898, the eunuch admiral Raghib, a former ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damian Of Tarsus
Damian of Tarsus (Greek: Δαμιανός ό Ταρσεύς, ; died 924), surnamed Ghulam Yazman (" slave/page of Yazman"), was a Byzantine Greek convert to Islam, governor of Tarsus in 896–897 and one of the main leaders of naval raids against the Eastern Roman Empire in the early 10th century. Biography Damian was a convert servant of the eunuch governor of Tarsus Yazman al-Khadim (died 891), who had recognized the overlordship of the Tulunids of Egypt under Ibn Tulun's son Khumarawaih. In October 896, Damian was named governor of Tarsus by the then-governor Ahmad ibn Tughan. Yusuf al-Baghmardi was his deputy and commander of the military forces of the region. Damian and al-Baghmardi, however, were ousted from Tarsus in March/April 897 by a revolt of the pro-Abbasid faction of the city under Raghib, a former ''mawla'' of al-Muwaffaq. In 900, al-Tabari reports that Damian urged the Caliph al-Mu'tadid to burn the fleet of Tarsus, of over 50 large ships, as a revenge for hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Of Tripoli
Leo of Tripoli ( el, Λέων ὸ Τριπολίτης), known in Arabic as Rashīq al-Wardāmī (), and Ghulām Zurāfa (), was a Greek renegade and fleet commander for the Abbasid Caliphate in the early tenth century. He is most notable for his sack of Thessalonica, the Byzantine Empire's second city, in 904. Life Nothing is known of Leo's early life except that he was born in or near Attaleia, the capital of the maritime Cibyrrhaeot Theme, and was captured in an Arab raid and brought to Tripoli. In captivity, he converted to Islam, and entered the service of his captors as a seaman and commander. In Arabic sources he is called Lāwī Abū'l-Ḥārith and given the sobriquet ghulām Zurāfa, "servant/page of Zurafa", probably reflecting the name of his first Muslim master. He is also referred to as Rashīq al-Wardāmī. Alexander Vasiliev interpreted the element ''Wardāmī'' in his second Arabic name to mean that Leo was a Mardaite. The details of Leo's early career in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Tabari
( ar, أبو جعفر محمد بن جرير بن يزيد الطبري), more commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (), was a Muslim historian and scholar from Amol, Tabaristan. Among the most prominent figures of the Islamic Golden Age, al-Tabari is known for his historical works and his expertise in Qur'anic exegesis (), but he has also been described as "an impressively prolific polymath".Lindsay Jones (ed.), ''Encyclopedia of religion'', volume 13, Macmillan Reference USA, 2005, p. 8943 He wrote works on a diverse range of subjects, including world history, poetry, lexicography, grammar, ethics, mathematics, and medicine. His most influential and best known works are his Quranic commentary, known in Arabic as , and his historical chronicle called ''History of the Prophets and Kings'' (), often referred to as ("al-Tabari's History"). Al-Tabari followed the Shafi'i madhhab for nearly a decade before he developed his own interpretation of Islamic jurisprudence. His understanding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Fire
Greek fire was an incendiary weapon used by the Eastern Roman Empire beginning . Used to set fire to enemy ships, it consisted of a combustible compound emitted by a flame-throwing weapon. Some historians believe it could be ignited on contact with water, and was probably based on naphtha and quicklime. The Byzantines typically used it in naval battles to great effect, as it could continue burning while floating on water. The technological advantage it provided was responsible for many key Byzantine military victories, most notably the salvation of Constantinople from the first and second Arab sieges, thus securing the empire's survival. The impression made by Greek fire on the western European Crusaders was such that the name was applied to any sort of incendiary weapon, including those used by Arabs, the Chinese, and the Mongols. However, these mixtures used formulas different from that of Byzantine Greek fire, which was a closely guarded state secret. Byzantines also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
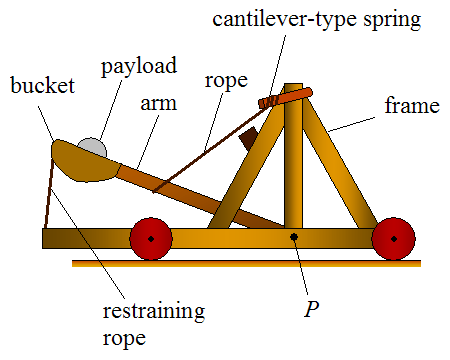
Catapults
A catapult is a ballistic device used to launch a projectile a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of stored potential energy to propel its payload. Most convert tension or torsion energy that was more slowly and manually built up within the device before release, via springs, bows, twisted rope, elastic, or any of numerous other materials and mechanisms. In use since ancient times, the catapult has proven to be one of the most persistently effective mechanisms in warfare. In modern times the term can apply to devices ranging from a simple hand-held implement (also called a "slingshot") to a mechanism for launching aircraft from a ship. The earliest catapults date to at least the 7th century BC, with King Uzziah, of Judah, recorded as equipping the walls of Jerusalem with machines that shot "great stones". Catapults are mentioned in Yajurveda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theme Of Hellas
The Theme of Hellas ( el, , ''Thema Hellados'') was a Byzantine military-civilian province (''thema'', theme) located in southern Greece. The theme encompassed parts of Central Greece, Thessaly and, until , the Peloponnese peninsula. It was established in the late 7th century, and survived until the late 11th/12th century, when it was broken up into smaller districts. History 7th–8th centuries The ancient term "Hellas" was already in use in the 6th century to designate southern Greece in an administrative context, being employed in the ''Synekdemos'' as an alternative name for the Roman province of Achaea. During the late 6th and early 7th centuries, the collapse of the Byzantine Empire's Danube frontier allowed large-scale Slavic invasions and settlements to occur all over the Balkan peninsula. From 578, Slavic raids reached Thessaly and southern Greece. Aided by the Byzantine Empire's preoccupation with the long and bloody wars with Sassanid Persia in the east, and with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |