|
Siege Of Besançon
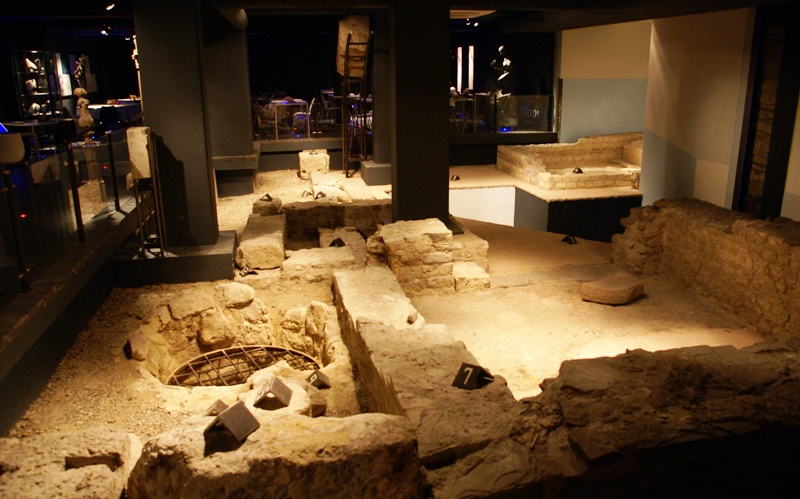
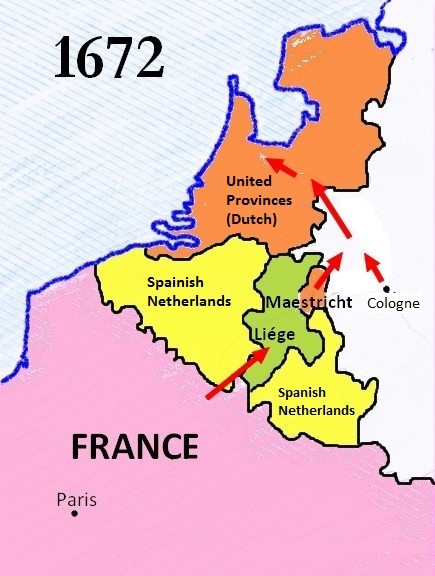
The siege of Besançon took place from 25 April to 22 May 1674 during the Franco-Dutch War, when French forces nominally led by Louis XIV of France invaded Franche-Comté, then part of the Spanish Empire. Siege works were supervised by the duc d'Enghien, eldest son of le Grand Condé, and French military engineer Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban. The defenders were commanded by Vaudémont but the town's isolated position meant they could only delay capture. The bulk of French casualties were caused by a botched assault, allegedly launched to impress Louis, before the garrison surrendered and were allowed free passage to the Spanish Netherlands. Under the 1678 Treaties of Nijmegen, the province was annexed by France and Besançon replaced Dole as the regional capital. Background In the 1667–1668 War of Devolution, France captured most of the Spanish Netherlands and Franche-Comté before a Dutch-led coalition forced Louis XIV to return most of their gains in the Treaty of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Norway. In its early stages, France was allied with Münster and Cologne, as well as England. The 1672 to 1674 Third Anglo-Dutch War and 1675 to 1679 Scanian War are considered related conflicts. The war began in May 1672 when France nearly overran the Dutch Republic, an event still known as the ''Rampjaar'' or "Disaster Year". Their advance was halted by the Dutch Water Line in June and by late July the Dutch position had stabilised. Concern over French gains led to a formal alliance in August 1673 between the Dutch, Emperor Leopold I, Spain and Brandenburg-Prussia. They were joined by Lorraine and Denmark, while England made peace in February 1674. Now facing a war on multiple fronts, the French withdrew from the Dutch Republic, retaining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick William, Elector Of Brandenburg
Frederick William (german: Friedrich Wilhelm; 16 February 1620 – 29 April 1688) was Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia, thus ruler of Brandenburg-Prussia, from 1640 until his death in 1688. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, he is popularly known as "the Great Elector" (') because of his military and political achievements. Frederick William was a staunch pillar of the Calvinist faith, associated with the rising commercial class. He saw the importance of trade and promoted it vigorously. His shrewd domestic reforms gave Prussia a strong position in the post-Westphalian political order of north-central Europe, setting Prussia up for elevation from duchy to kingdom, achieved under his son and successor. Biography Elector Frederick William was born in Berlin to George William, Elector of Brandenburg, and Elisabeth Charlotte of the Palatinate. His inheritance consisted of the Margraviate of Brandenburg, the Duchy of Cleves, the County of Mark, and the Duchy of Pru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. From the accession of Otto I in 962 until the twelfth century, the Empire was the most powerful monarchy in Europe. Andrew Holt characterizes it as "perhaps the most powerful European state of the Middle Ages". The functioning of government depended on the harmonic cooperation (dubbed ''consensual rulership'' by Bernd Schneidmüller) between monarch and vassals but this harmony was disturbed during the Salian Dynasty, Salian period. The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power under the House of Hohenstaufen in the mid-thirteenth century, but overextending led to partial collapse. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the List of Frankish kings, Frankish king Charlemagne as Carolingi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Imperial City
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that had a certain amount of autonomy and was represented in the Imperial Diet. An imperial city held the status of Imperial immediacy, and as such, was subordinate only to the Holy Roman Emperor, as opposed to a territorial city or town (') which was subordinate to a territorial princebe it an ecclesiastical lord ( prince-bishop, prince-abbot) or a secular prince (duke ('), margrave, count ('), etc.). Origin The evolution of some German cities into self-ruling constitutional entities of the Empire was slower than that of the secular and ecclesiastical princes. In the course of the 13th and 14th centuries, some cities were promoted by the emperor to the status of Imperial Cities ('; '), essentially for fiscal reasons. Those cities, which had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salins-les-Bains
Salins-les-Bains (), commonly referred to simply as Salins, is a commune in the Jura department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in Eastern France. It is located on the departmental border with Doubs, 34.8 km (21.6 mi) to the south-southwest of Besançon. In 2018, Salins-les-Bains had a population of 2,567. The town owes its name to its saline waters which shaped its history for centuries; they continue to attract visitors today, for the town's bedrock contains salt and gypsum deposits. In 2009 the historic saltworks were added to the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites as an addition to the Royal Saltworks at Arc-et-Senans site, which was inscribed in 1982. Geography Salins is situated in the narrow Valley of the Furieuse, between two fortified hills, Fort Belin and Fort Saint-André, while to the north rises Mont Poupet (851 m or 2,791 ft). History Salins was an important city in Celtic times and was an oppidum of Ancient Rome. The territory of Salins, which was en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François-Michel Le Tellier, Marquis De Louvois
François Michel Le Tellier, Marquis of Louvois (18 January 1641 – 16 July 1691) was the French Secretary of State for War during a significant part of the reign of Louis XIV. Together with his father, Michel le Tellier Michel Le Tellier, marquis de Barbezieux, seigneur de Chaville et de Viroflay (19 April 1603 – 30 October 1685) was a French statesman. Biography Le Tellier was born in Paris to a Parisian magistrate, Michel III Le Tellier, and his wife, Clau ..., the French Army would eventually be increased to 340,000 soldiers – an army that would fight four wars between 1667 and 1713. He is commonly referred to as "Louvois". Early life Louvois was born in Paris on 18 January 1641, to Michel Le Tellier, and Élisabeth Turpin. Louvois received instructions from his father in the management of state affairs. The young man won the king's confidence, and in 1666 he succeeded his father as war minister. His talents were perceived by Henri de la Tour d'Auvergne, Vicomte de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesoul
Vesoul () is a commune in the Haute-Saône department in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté located in eastern France. It is the most populated municipality of the department with inhabitants in 2014. The same year, the Communauté d'agglomération de Vesoul which covers 20 municipalities together had inhabitants while the Urban area of Vesoul which includes 78 municipalities, had inhabitants. Its inhabitants are known in French as ''Vésuliens''. Built on top of the hill of La Motte in the first millennium under the name of ''Castrum Vesulium'', the city gradually evolved into a European commercial and economic center. At the end of the Middle Ages, the city experienced a challenging period beset with plagues, epidemics, and localized conflict. Main urban center of the department, Vesoul is also home to a major PSA parts manufacturing plant and to the Vesoul International Film Festival of Asian Cinema. It was immortalized by Jacques Brel in his 1968 song "Vesoul". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray, Haute-Saône
Gray () is a commune in the Haute-Saône department, region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté, eastern France. It has a population of 5,553 inhabitants (2019).Téléchargement du fichier d'ensemble des populations légales en 2019 INSEE Geography Gray is situated on the banks of the river . It is the last major town in Haute-Saône before the Saône flows into |
Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; li, Mestreech ; french: Maestricht ; es, Mastrique ) is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the Meuse ( nl, Maas), at the point where the Jeker joins it. Mount Saint Peter (''Sint-Pietersberg'') is largely situated within the city's municipal borders. Maastricht is about 175 km south east of the capital Amsterdam and 65 km from Eindhoven; it is adjacent to the border with Belgium and is part of the Meuse-Rhine Euroregion, an international metropolis with a population of about 3.9 million, which includes the nearby German and Belgian cities of Aachen, Liège and Hasselt. Maastricht developed from a Roman settlement (''Trajectum ad Mosam'') to a medieval religious centre. In the 16th century it became a garrison town and in the 19th century an early industrial centre. Today, the city is a thriving cultural and regional hub. It beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grave, Netherlands
Grave (; formerly ''De Graaf'') is a city and former municipality in the Dutch province of North Brabant. The former municipality had a population of in . Grave is a member of the Dutch Association of Fortified Cities. The former municipality included the following towns : Grave (capital), Velp, Escharen and Gassel. Grave, Boxmeer, Cuijk, Mill en Sint Hubert, and Sint Anthonis merged into the new municipality of Land van Cuijk on 1 January 2022. History Grave received city rights in 1233. The former municipality of Grave was formed in the Napoleonic era (1810) and coincided with the fortified Grave and immediate surroundings. The history of the town was thus linked to that of the place. This changed in 1942. Then there was a reclassification place where the municipality Grave was expanded with the previously independent municipalities Velp and Escharen. Moreover, in 1994 the neighboring municipality of Beers was abolished and a part thereof, the parish Gassel, wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section. Term Historically, the Rhinelands refers (physically speaking) to a loosely defined region embracing the land on the banks of the Rhine in Central Europe, which were settled by Ripuarian and Salian Franks and became part of Frankish Austrasia. In the High Middle Ages, numerous Imperial States along the river emerged from the former stem duchy of Lotharingia, without developing any common political or cultural identity. A "Rhineland" conceptualization can be traced to the period of the Holy Roman Empire from the sixteenth until the eighteenth centuries when the Empire's Imperial Estates (territories) were grouped into regional districts in charge of defence and judicial execution, known as Imperial Circles. Three of the ten circles through which the Rhine flowed referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Westminster (1674)
The Treaty of Westminster of 1674 was the peace treaty that ended the Third Anglo-Dutch War. Signed by the Dutch Republic and the Kingdom of England, the treaty provided for the return of the colony of New Netherland (now New York) to England and renewed the Treaty of Breda of 1667. The treaty also provided for a mixed commission for the regulation of commerce, particularly in the East Indies. It was signed on 19 February 1674 Old Style (9 February 1674 New Style) by Charles II of England and ratified by the States General of the Netherlands on 5 March 1674. England was forced to sign the treaty since Parliament would not allow more money to be spent on the war and had become aware of the secret Treaty of Dover in which Charles had promised Louis XIV of France to convert to Catholicism at an opportune moment. The English were dismayed by the unexpected fact that Dutch raiders had managed to capture more English ships than vice versa and that New Amsterdam had been retaken by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |