|
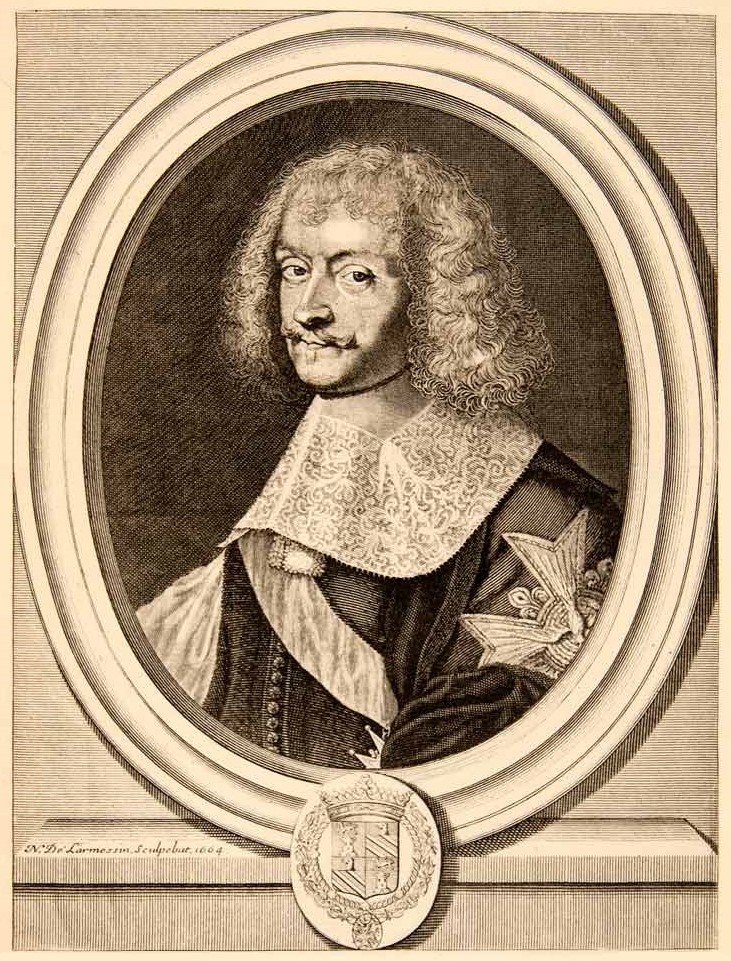
François-Michel Le Tellier, Marquis De Louvois
François Michel Le Tellier, Marquis of Louvois (18 January 1641 – 16 July 1691) was the French Secretary of State for War during a significant part of the reign of Louis XIV. Together with his father, Michel le Tellier, the French Army would eventually be increased to 340,000 soldiers – an army that would fight four wars between 1667 and 1713. He is commonly referred to as "Louvois". Early life Louvois was born in Paris on 18 January 1641, to Michel Le Tellier, and Élisabeth Turpin. Louvois received instructions from his father in the management of state affairs. The young man won the king's confidence, and in 1666 he succeeded his father as war minister. His talents were perceived by Turenne in the War of Devolution (1667–68), who gave him instruction in the art of providing armies. After the peace of Aix-la-Chapelle, Louvois devoted himself to organising the French army. The years between 1668 and 1672, says Camille Rousset, "were years of preparation, when Lionne was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquis
A marquess (; french: marquis ), es, marqués, pt, marquês. is a nobleman of high hereditary rank in various European peerages and in those of some of their former colonies. The German language equivalent is Markgraf (margrave). A woman with the rank of a marquess or the wife (or widow) of a marquess is a marchioness or marquise. These titles are also used to translate equivalent Asian styles, as in Imperial China and Imperial Japan. Etymology The word ''marquess'' entered the English language from the Old French ("ruler of a border area") in the late 13th or early 14th century. The French word was derived from ("frontier"), itself descended from the Middle Latin ("frontier"), from which the modern English word '' march'' also descends. The distinction between governors of frontier territories and interior territories was made as early as the founding of the Roman Empire when some provinces were set aside for administration by the senate and more unpacified or vuln ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin. Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Françoise D'Aubigné, Marquise De Maintenon
Françoise d'Aubigné (27 November 1635 – 15 April 1719), known first as Madame Scarron and subsequently as Madame de Maintenon (), was a French noblewoman who secretly married King Louis XIV. Although she was never considered queen of France, she was one of the King's closest advisers and the royal children's governess. In 1686, she founded the Maison royale de Saint-Louis, a school for girls from poorer noble families. Childhood Birth at Niort Françoise d'Aubigné was born on 27 November 1635, in Niort, France. A plaque suggests her birthplace was at the Hotel du Chaumont, but some sources indicate she was born in or just outside the local prison, where her Huguenot father Constant d'Aubigné was incarcerated for conspiring against King Louis XIII's powerful chief minister, Cardinal Richelieu. Her mother, Jeanne de Cardilhac, was the daughter of the prison director and was probably seduced by the incarcerated Constant. She was a fervent Catholic and had her child bapti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaties Of Nijmegen
The Treaties of Peace of Nijmegen ('; german: Friede von Nimwegen) were a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Nijmegen between August 1678 and October 1679. The treaties ended various interconnected wars among France, the Dutch Republic, Spain, Brandenburg, Sweden, Denmark-Norway, the Prince-Bishopric of Münster, and the Holy Roman Empire. The most significant of the treaties was the first, which established peace between France and the Dutch Republic and placed the northern border of France very near its modern position. Background The Franco-Dutch War of 1672–78 was the source of all the other wars that were ended formally at Nijmegen. Separate peace treaties were arranged for conflicts like the Third Anglo-Dutch War and the Scanian War, but all of them had been directly caused by and form part of the Franco-Dutch War. England initially participated in the war on the French side but withdrew in 1674, after the Treaty of Westminster. The Electorate of Cologn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
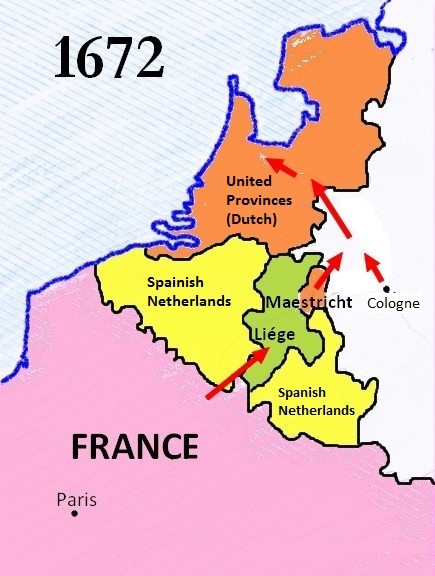
Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Norway. In its early stages, France was allied with Münster and Cologne, as well as England. The 1672 to 1674 Third Anglo-Dutch War and 1675 to 1679 Scanian War are considered related conflicts. The war began in May 1672 when France nearly overran the Dutch Republic, an event still known as the '' Rampjaar'' or "Disaster Year". Their advance was halted by the Dutch Water Line in June and by late July the Dutch position had stabilised. Concern over French gains led to a formal alliance in August 1673 between the Dutch, Emperor Leopold I, Spain and Brandenburg-Prussia. They were joined by Lorraine and Denmark, while England made peace in February 1674. Now facing a war on multiple fronts, the French withdrew from the Dutch Republic, ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portrait Of The Marquis De Louvois, Engraved By Robert Nanteuil – Gallica Btv1b550039669
A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face and its expressions are predominant. The intent is to display the likeness, personality, and even the mood of the person. For this reason, in photography a portrait is generally not a snapshot, but a composed image of a person in a still position. A portrait often shows a person looking directly at the painter or photographer, in order to most successfully engage the subject with the viewer. History Prehistorical portraiture Plastered human skulls were reconstructed human skulls that were made in the ancient Levant between 9000 and 6000 BC in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B period. They represent some of the oldest forms of art in the Middle East and demonstrate that the prehistoric population took great care in burying their ancestors below their homes. The skulls denote some of the earliest sculptural examples of portraiture in the history of art. Historical portraitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Man In The Iron Mask
The Man in the Iron Mask ( French ; died 19 November 1703) was an unidentified prisoner of state during the reign of King Louis XIV of France (1643–1715). Warranted for arrest on 28 July 1669 under the pseudonym of "Eustache Dauger", he was incarcerated on 24 August and held for 34 years in the custody of the same jailer, , in four successive French prisons, including the Bastille. When he died there on 19 November 1703, his inhumation certificate bore the pseudonym of "Marchioly", leading several 19th century historians to conclude the prisoner was Italian diplomat Ercole Antonio Mattioli. His true identity remains a mystery, even though it has been extensively debated by historians, and various theories have been expounded in numerous books, articles, poems, plays, and films. Among the oldest theories is one proposed by the French philosopher and writer Voltaire, who claimed in the second edition of his (1771) that the prisoner was an older, illegitimate brother of Lou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugues De Lionne
Hugues de Lionne (11 October 1611 – 1 September 1671) was a French statesman. He was born in Grenoble, of an old family of Dauphiné. Early trained for diplomacy, he fell into disgrace under Cardinal Richelieu, but his remarkable abilities attracted the notice of Cardinal Mazarin, who sent him as secretary of the French embassy to the congress of Munster, and, in 1642, on a mission to the pope. In 1646 he became secretary to the queen regent Anne of Austria; in 1653 obtained high office in the kings household; and in 1654 was ambassador extraordinary at the election of Pope Alexander VII. On the death of Ferdinand III, Hugues co-led the French effort to select an Emperor outside the Habsburg family. He and the Cardinal cultivated relationships with German nobility, including Franz Egon of Fürstenberg, prime minister of Cologne, and his brother Wilhelm. With their help, Hugues was instrumental in forming the league of the Rhine, by which Austria was cut off from the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aix-la-Chapelle
Aachen ( ; ; Aachen dialect: ''Oche'' ; French and traditional English: Aix-la-Chapelle; or ''Aquisgranum''; nl, Aken ; Polish: Akwizgran) is, with around 249,000 inhabitants, the 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, and the 28th-largest city of Germany. It is the westernmost city in Germany, and borders Belgium and the Netherlands to the west, the triborder area. It is located between Maastricht (NL) and Liège (BE) in the west, and Bonn and Cologne in the east. The Wurm River flows through the city, and together with Mönchengladbach, Aachen is the only larger German city in the drainage basin of the Meuse. Aachen is the seat of the City Region Aachen (german: link=yes, Städteregion Aachen). Aachen developed from a Roman settlement and (bath complex), subsequently becoming the preferred medieval Imperial residence of Emperor Charlemagne of the Frankish Empire, and, from 936 to 1531, the place where 31 Holy Roman Emperors were crowned Kings of the Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of Devolution
In the 1667 to 1668 War of Devolution (, ), France occupied large parts of the Spanish Netherlands and Franche-Comté, both then provinces of the Holy Roman Empire (and properties of the King of Spain). The name derives from an obscure law known as the ''Jus Devolutionis'', used by Louis XIV of France to claim that these territories had "devolved" to him by right of marriage to Maria Theresa of Spain. In the fighting, the French encountered minimal resistance; however, Louis was more concerned with asserting his inheritance rights in the Spanish Empire, and consequently returned much of his gains in the May 1668 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle. The terms were agreed by Emperor Leopold I in January 1668, reinforced by the Triple Alliance of England, Sweden and the Dutch Republic. The conflict marked the end of the long-standing Franco-Dutch alliance, and was the first of the French wars of expansion that dominated Europe for the next 50 years. Background As part of the 1659 Treaty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri De La Tour D'Auvergne, Vicomte De Turenne
Henri de La Tour d'Auvergne, vicomte de Turenne (11 September 161127 July 1675), commonly known as Turenne , was a French general and one of only six Marshals to have been promoted Marshal General of France. The most illustrious member of the La Tour d'Auvergne family, his military exploits over his five-decade career earned him a reputation as one of the greatest military commanders in history. Born to a Huguenot family, the son of a Marshal of France, he was introduced to the art of war at a young age. He first served as a volunteer in the Dutch States Army under the orders of his maternal uncles Maurice of Nassau and Frederick Henry but later chose to continue his career in the service of France, where his noble origins and proven qualities soon saw him rise to the top of the military hierarchy. He rose to prominence during the Thirty Years' War by capturing the fortress of Breisach in 1638. Promoted Marshal of France in 1643, he struck against Bavaria the followin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soldier
A soldier is a person who is a member of an army. A soldier can be a conscripted or volunteer enlisted person, a non-commissioned officer, or an officer. Etymology The word ''soldier'' derives from the Middle English word , from Old French or , meaning mercenary, from , meaning shilling's worth or wage, from or , shilling. The word is also related to the Medieval Latin , meaning soldier (literally, "one having pay"). These words ultimately derive from the Late Latin word , referring to an Ancient Roman coin used in the Byzantine Empire. Occupational designations In most armies use of the word "soldier" has taken on a more general meaning due to the increasing specialization of military occupations that require different areas of knowledge and skill-sets. As a result, "soldiers" are referred to by names or ranks which reflect an individual's military occupation specialty arm, service, or branch of military employment, their type of unit, or operational employment or techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)