|
Siege Of Fort Stanwix
The siege of Fort Stanwix (also known at the time as Fort Schuyler) in 1777 began on August 2 and ended August 22. Fort Stanwix, in the western part of the Mohawk River Valley, was then the primary defense point for the Continental Army against British and Indian forces aligned against them in the American Revolutionary War. The fort was occupied by Continental Army forces from New York and Massachusetts under the command of Colonel Peter Gansevoort. The besieging force was composed of British regulars, American Loyalists, Hessian soldiers from Hesse-Hanau, and Indians, under the command of British Brigadier General Barry St. Leger and the Iroquois leader Joseph Brant. St. Leger's expedition was a diversion in support of General John Burgoyne's campaign to gain control of the Hudson River Valley to the east. One attempt at relief was thwarted early in the siege when a force of New York militia under Nicholas Herkimer was stopped in the August 6 Battle of Oriskany by a detac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of the United States, fighting began on April 19, 1775, followed by the Lee Resolution on July 2, 1776, and the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The American Patriots were supported by the Kingdom of France and, to a lesser extent, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Empire, in a conflict taking place in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. Established by royal charter in the 17th and 18th centuries, the American colonies were largely autonomous in domestic affairs and commercially prosperous, trading with Britain and its Caribbean colonies, as well as other European powers via their Caribbean entrepôts. After British victory over the French in the Seven Years' War in 1763, tensions between the motherla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was established by a resolution of Congress on June 14, 1775. The Continental Army was created to coordinate military efforts of the Colonies in their war for independence against the British, who sought to keep their American lands under control. General George Washington was the commander-in-chief of the army throughout the war. The Continental Army was supplemented by local militias and volunteer troops that were either loyal to individual states or otherwise independent. Most of the Continental Army was disbanded in 1783 after the Treaty of Paris formally ended the fighting. The 1st and 2nd Regiments of the Army went on to form what was to become the Legion of the United States in 1792. This became the foundation of what is now the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
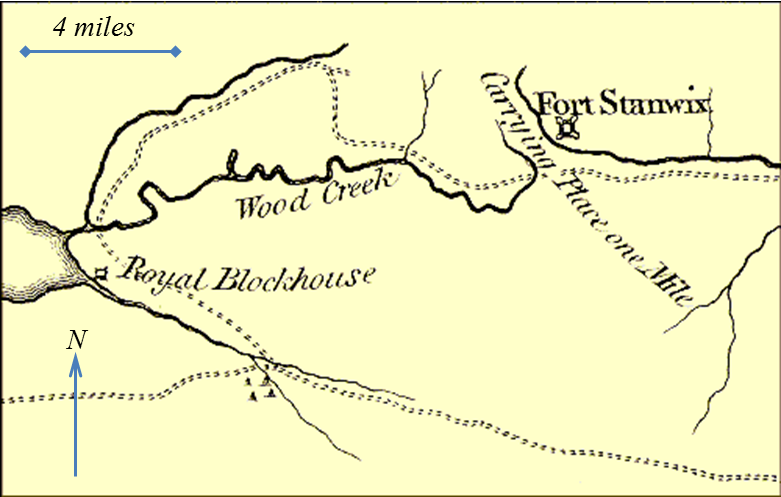
Oneida Carry
The Oneida Carry was an important link in the main 18th century trade route between the Atlantic seaboard of North America and interior of the continent. From Schenectady, near Albany, New York on the Hudson River, cargo would be carried upstream along the Mohawk River using boats known as '' bateaux''. At the location at modern-day Rome, New York, the cargo and boats would be portaged one to four miles overland to Wood Creek. This portage, which the Haudenosaunee called ''De-o-Wain-Sta'', was known as the ''Oneida Carry'' or ''The Great Carrying Place'' in English, and as ''Trow Plat'' in Dutch. After relaunching into Wood Creek (called Kah-ne-go-dick by the Haudenosaunee), the ''bateaux'' would navigate downstream to Oneida Lake, the Oswego River, and ultimately Lake Ontario at Oswego. Lake Ontario was the gateway to all the Great Lakes stretching another thousand miles inland. The only other significant waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the continental interior wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
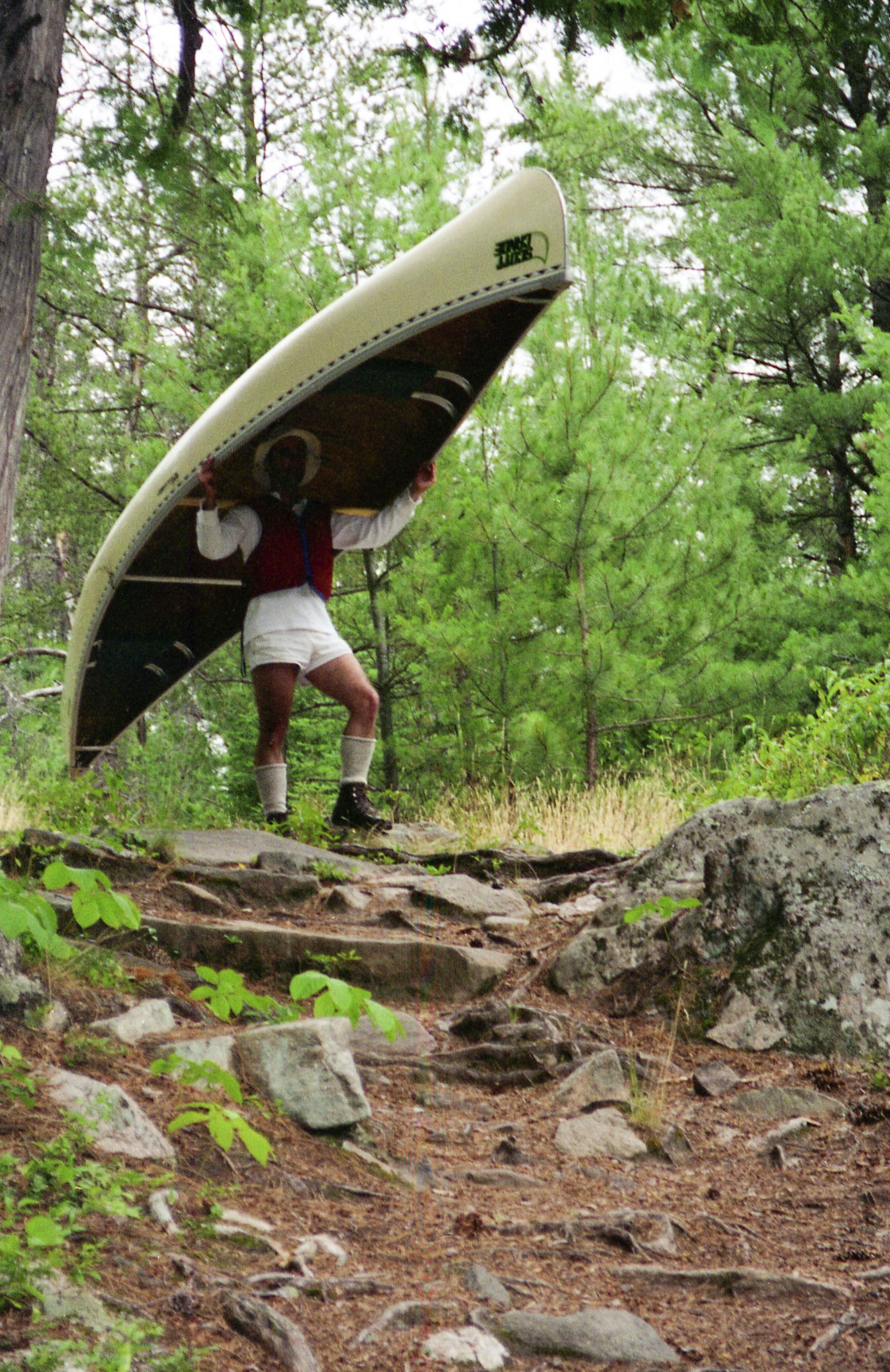
Portage
Portage or portaging (Canada: ; ) is the practice of carrying water craft or cargo over land, either around an obstacle in a river, or between two bodies of water. A path where items are regularly carried between bodies of water is also called a ''portage.'' The term comes from French, where means "to carry," as in "portable". In Canada, the term "carrying-place" was sometimes used. Early French explorers in New France and French Louisiana encountered many rapids and cascades. The Native Americans carried their canoes over land to avoid river obstacles. Over time, important portages were sometimes provided with canals with locks, and even portage railways. Primitive portaging generally involves carrying the vessel and its contents across the portage in multiple trips. Small canoes can be portaged by carrying them inverted over one's shoulders and the center strut may be designed in the style of a yoke to facilitate this. Historically, voyageurs often employed tump line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Ticonderoga
Fort Ticonderoga (), formerly Fort Carillon, is a large 18th-century star fort built by the French at a narrows near the south end of Lake Champlain, in northern New York, in the United States. It was constructed by Canadian-born French military engineer Michel Chartier de Lotbinière, Marquis de Lotbinière between October 1755 and 1757, during the action in the "North American theater" of the Seven Years' War, often referred to in the US as the French and Indian War. The fort was of strategic importance during the 18th-century colonial conflicts between Great Britain and France, and again played an important role during the Revolutionary War. The site controlled a river portage alongside the mouth of the rapids-infested La Chute River, in the between Lake Champlain and Lake George. It was thus strategically placed for the competition over trade routes between the British-controlled Hudson River Valley and the French-controlled Saint Lawrence River Valley. The terra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of Saratoga
The Battles of Saratoga (September 19 and October 7, 1777) marked the climax of the Saratoga campaign, giving a decisive victory to the Americans over the British in the American Revolutionary War. British General John Burgoyne led an invasion army of 7,200–8,000 men southward from Canada in the Champlain Valley, hoping to meet a similar British force marching northward from New York City and another British force marching eastward from Lake Ontario; the goal was to take Albany, New York. The southern and western forces never arrived, and Burgoyne was surrounded by American forces in upstate New York short of his goal. He fought two battles which took place 18 days apart on the same ground south of Saratoga, New York. He gained a victory in the first battle despite being outnumbered, but lost the second battle after the Americans returned with an even larger force. Burgoyne found himself trapped by much larger American forces with no relief, so he retreated to Saratoga (now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hon Yost Schuyler
Johannes Justus (Hon Yost) Schuyler (January 1, 1744 – 1810) was a Tory with patriot roots, who was used by American General Benedict Arnold to repel the British and Indian forces of Colonel Barry St. Leger and Joseph Brant from their siege of Fort Stanwix following the Battle of Oriskany during the American Revolution. Early life He was the son of Peter D. Schuyler (b.1723) and Elisabeth Barbara Herkimer. His mother was the sister of American General Nicholas Herkimer (1728–1777) and loyalist Johan Jost Herkimer (1732–1795). His father was a cousin of American General Philip Schuyler (see Schuyler family). Hon Yost grew up in the Mohawk Valley in the Colony of New York, prior to the American Revolution. Hon Yost's parents were poor and apparently he socialized more with the Mohawks (who sided with the British during the war) than with the white patriots of the area. He has been variously described as dim-witted, coarse and ignorant, a half idiot, a madman, and a luna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sortie (siege Warfare)
A sortie (from the French word meaning ''exit'' or from Latin root ''surgere'' meaning to "rise up") is a deployment or dispatch of one military unit, be it an aircraft, ship, or troops, from a strongpoint. The term originated in siege warfare. In aviation In military aviation, a sortie is a combat mission of an individual aircraft, starting when the aircraft takes off. For example, one mission involving six aircraft would tally six sorties. The sortie rate is the number of sorties that a given unit can support in a given time. In siege warfare In siege warfare, the word ''sortie'' refers specifically to a sudden issuing of troops against the enemy from a defensive position—that is, an attack launched against the besiegers by the defenders. If the sortie is through a sally port, the verb ''to sally'' may be used interchangeably with ''to sortie''. Purposes of sorties include harassment of enemy troops, destruction of siege weaponry and engineering works, joining the rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Oriskany
The Battle of Oriskany ( or ) was a significant engagement of the Saratoga campaign of the American Revolutionary War, and one of the bloodiest battles in the conflict between the Americans and Great Britain. On August 6, 1777, a party of Loyalists and several hundred Indian allies from different tribes ambushed an American military party that was marching to relieve the siege of Fort Stanwix. This was one of the few battles in which the majority of the participants were Americans; Patriots and allied Oneidas fought against Loyalists and allied Iroquois in the absence of British regular soldiers. There was also a detachment of Hessians in the British force, as well as Western Indians including members of the Mississaugas. The Patriot relief force came up the Mohawk Valley under the command of General Nicholas Herkimer and numbered about 800 men of the Tryon County militia, plus a party of approximately 60 Oneida warriors. British commander Barry St. Leger authorized an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between New York City and Jersey City, eventually draining into the Atlantic Ocean at Lower New York Bay. The river serves as a political boundary between the states of New Jersey and New York at its southern end. Farther north, it marks local boundaries between several New York counties. The lower half of the river is a tidal estuary, deeper than the body of water into which it flows, occupying the Hudson Fjord, an inlet which formed during the most recent period of North American glaciation, estimated at 26,000 to 13,300 years ago. Even as far north as the city of Troy, the flow of the river changes direction with the tides. The Hudson River runs through the Munsee, Lenape, Mohican, Mohawk, and Haudenosaunee homelands. Prior to European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saratoga Campaign
The Saratoga campaign in 1777 was an attempt by the British high command for North America to gain military control of the strategically important Hudson River valley during the American Revolutionary War. It ended in the surrender of the British army, which historian Edmund Morgan argues, "was a great turning point of the war, because it won for Americans the foreign assistance which was the last element needed for victory." The primary thrust of the campaign was planned and initiated by General John Burgoyne. Commanding a main force of some 8,000 men, he moved south in June from Quebec, boated south on Lake Champlain to Fort Ticonderoga and from there boated south on Lake George, then marched down the Hudson Valley to Saratoga. He initially skirmished there with the Patriot defenders with mixed results. The turning point of the campaign happened in August at the Battle of Bennington when militia forces from Vermont, New Hampshire, and Massachusetts defeated, killed, and ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Burgoyne
General John Burgoyne (24 February 1722 – 4 August 1792) was a British general, dramatist and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1761 to 1792. He first saw action during the Seven Years' War when he participated in several battles, most notably during the Portugal Campaign of 1762. Burgoyne is best known for his role in the American Revolutionary War. He designed an invasion scheme and was appointed to command a force moving south from Canada to split away New England and end the rebellion. Burgoyne advanced from Canada but his slow movement allowed the Americans to concentrate their forces. Instead of coming to his aid according to the overall plan, the British Army in New York City moved south to capture Philadelphia. Burgoyne fought two small battles near Saratoga but was surrounded by American forces and, with no relief in sight, surrendered his entire army of 6,200 men on 17 October 1777. His surrender, says historian Edmund Morgan, "was a great turnin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)