|
Shuttle Train
A shuttle train is a train that runs back and forth between two points, especially if it offers a frequent service over a short route. Shuttle trains are used in various ways, in various parts of the world. They commonly operate as a fixed consist, and run non-stop between their termini. They can be used to carry passengers, freight, or both. Examples Airport shuttle trains An airport shuttle train may run between an airport and some other location, or connect two or more terminals. The second is usually in the form of a driverless people mover. Canada The UP Express train in Toronto, Ontario connects you to the Pearson Airport, making secondary stops at Bloor and Weston from Union Station. The train connects with the provincial transit network, GO Transit and the city-wide underground subway network, the Toronto subway. Italy A shuttle train connects Galileo Galilei Airport in Pisa with Pisa Central railway station. It operates daily and takes five minutes. U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trenitalia
Trenitalia is the primary train operator in Italy. A subsidiary of Ferrovie dello Stato Italiane, itself owned by the Italian government, the company was established in 2000 following a European Union directive on the deregulation of rail transport. History The Italian government formed Trenitalia to comply with European regulations. The European Commission's First Railway Directive from 1991 (91/440/EC) required separation of accounting between entities which manage the rail infrastructure and entities which provide the actual rail transportation. On 1 June 2000, therefore, Italy created Trenitalia as the primary rail transportation company and on 1 July 2001 established Rete Ferroviaria Italiana (RFI) as the company overseeing the rail network. However, the separation was only formal, since both are subsidiaries of the Ferrovie dello Stato Italiane holding and are owned wholly by the government. Trenitalia operated freight rail services under the Trenitalia Cargo brand until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
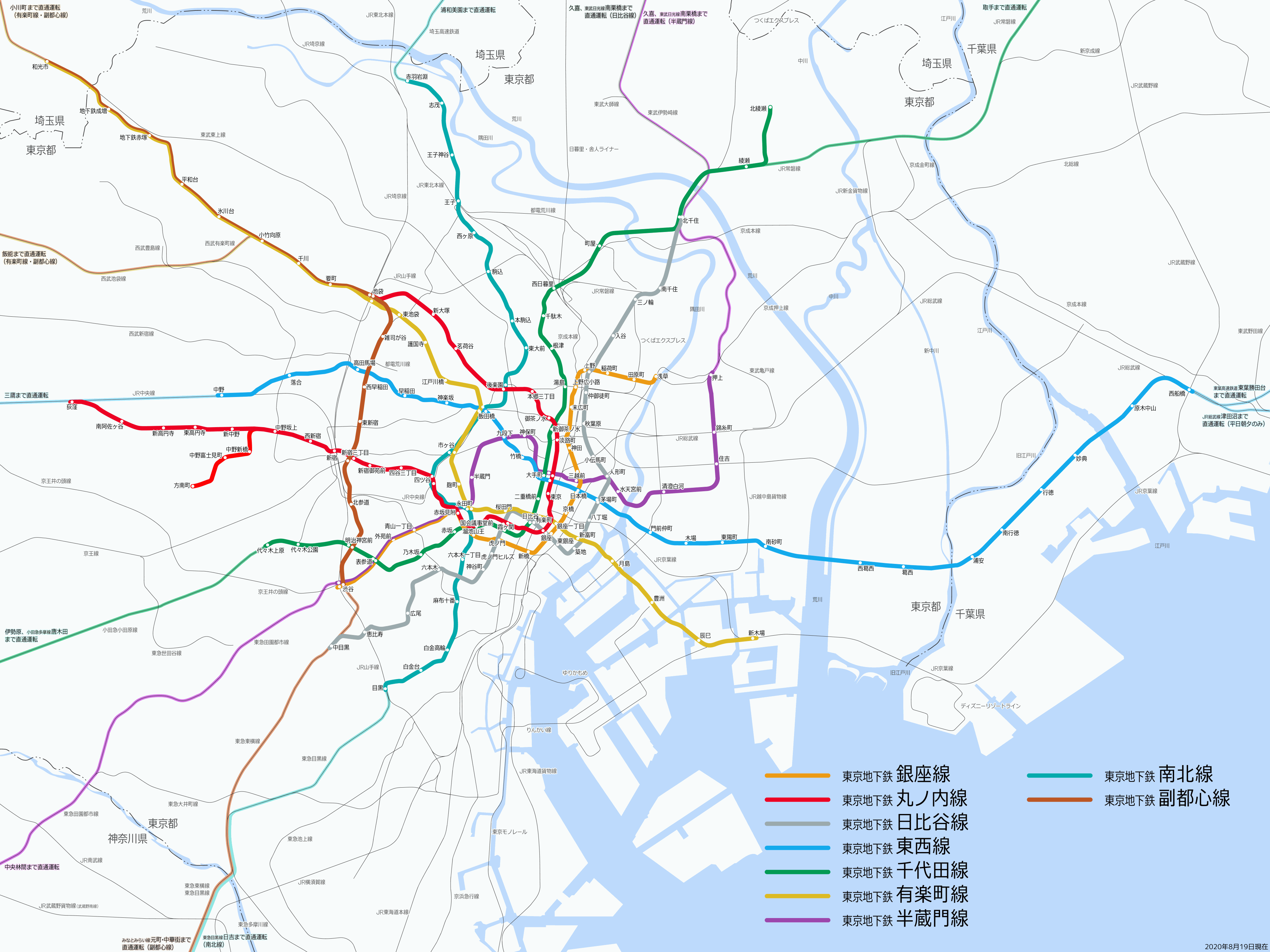
Tokyo Metro
The is a major rapid transit system in Tokyo, Japan, operated by the Tokyo Metro Co. With an average daily ridership of 6.84 million passengers, the Tokyo Metro is the larger of the two subway operators in the city; the other being the Toei Subway, with 2.85 million average daily rides. Organization Tokyo Metro is operated by , a joint-stock company jointly owned by the Government of Japan and the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. The company, founded as a part of then-Prime Minister Junichiro Koizumi's policy of converting statutory corporations into joint-stock companies, replaced the , commonly known as Eidan or TRTA, on April 1, 2004. TRTA was administered by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, and jointly funded by the national and metropolitan governments. It was formed in 1941 as a part-nationalization of the Tokyo Underground Railway and Tokyo Rapid Railway (now both form the Tokyo Metro Ginza Line), although its oldest lines date back to 1927 wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aichi Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshū. Aichi Prefecture has a population of 7,552,873 () and a geographic area of with a population density of . Aichi Prefecture borders Mie Prefecture to the west, Gifu Prefecture and Nagano Prefecture to the north, and Shizuoka Prefecture to the east. Overview Nagoya is the capital and largest city of Aichi Prefecture, and the fourth-largest city in Japan, with other major cities including Toyota, Okazaki, and Ichinomiya. Aichi Prefecture and Nagoya form the core of the Chūkyō metropolitan area, the third-largest metropolitan area in Japan and one of the largest metropolitan areas in the world. Aichi Prefecture is located on Japan's Pacific Ocean coast and forms part of the Tōkai region, a subregion of the Chūbu region and Kansai region. Aichi Prefecture is home to the Toyota Motor Corporation. Aichi Prefecture had many locations with the Higashiyama Zoo and Botanical Gardens, The Chubu Centrair Inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyota, Aichi
, formerly known as Koromo, is a city in Aichi Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 426,162 and a population density of 464 people per km2. The total area was . It is located about 35 minutes from Nagoya by way of the Meitetsu Toyota Line. Several of Toyota Motor Corporation's manufacturing plants, including the Tsutsumi plant, are located here. The longstanding ties between the Toyota Motor Corporation and the town of Toyota-shi, formerly known as , gave the town its current name. The city's flag (and seal), is a unicursal hexagram. Geography Toyota is located in north-central Aichi Prefecture, and is the largest city in the prefecture in terms of area. The city area is mountainous to the north, with peaks averaging around 1000 feet (328 m) in height along its northern border with Nagano and Gifu Prefectures. Much of the mountainous northern portion of the city is within the Aichi Kōgen Quasi-National Park. Toyota is within a two-hour drive of Nagoy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shin-Toyota Station
260px, Platforms in May 2015 260px, Track layout is a railway station in the city of Toyota, Aichi Prefecture, Japan, operated by the third sector Aichi Loop Railway Company. Lines Shin-Toyota Station is served by the Aichi Loop Line, and is located 19.5 kilometers from the starting point of the line at . Station layout The station has two elevated side platforms, with the station building located underneath. The station building has automated ticket machines, TOICA automated turnstiles and is staffed. Platforms Adjacent stations Station history Shin-Toyota Station was opened on April 26, 1976 as a passenger station on the Japan National Railways (JNR) Okata Line connecting with Shin-Toyota. With the privatization of the JNR on April 1, 1987, the station came under control of JR Central. The station was transferred to the Aichi Loop Railway Company on January 31, 1988. The station building was rebuilt in 1991. Passenger statistics In fiscal 2017, the station was u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikawa-Toyota Station
260px, Platforms in May 2015 is a railway station in the city of Toyota, Aichi Prefecture, Japan, operated by the third sector Aichi Loop Railway Company. Lines Mikawa-Toyota Station is served by the Aichi Loop Line, and is located 15.9 kilometers from the starting point of the line at . Station layout The station has two has two opposed side platforms, connected by a footbridge. The station building has automated ticket machines, TOICA automated turnstiles and is staffed. Platforms Adjacent stations Station history Mikawa-Toyota Station was opened on December 27, 1937 as a station on the privately held Mikawa Railway Okazaki Line. The Mikawa Railway was merged with Meitetsu June 1, 1941, and the Okazaki Line became the Meitetsu Okazaki Line. The station name was renamed on October 1, 1959. On August 30, 1973, the extension from this station to Koromo Station was discontinued. The station was transferred to the Japan National Railways (JNR) Okata Line connecting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aichi Loop Line
The is a Japanese railway line connecting Okazaki Station in Okazaki, Aichi, Okazaki and Kōzōji Station in Kasugai, Aichi, Kasugai, operated by the . The company or the line is abbreviated as . This is the only line the company operates. Despite its name, the line is not a true loop, but a north-south line situated east of Nagoya, Aichi, Nagoya, which can be considered as an unclosed loop (with the JR Tōkaidō Main Line, Tokaido line and Chūō Main Line, Chuo Line serving as the portions of the circle). The Aichi Loop Railway is a Public-Private_Partnerships_In_Japan, third sector company, with shares held by public sector such as Aichi Prefecture, the city of Toyota, Aichi, Toyota, and also by private companies. Unlike typical third-sector lines in Japan, the Aichi Loop Line makes a profit, since the line functions as a commuter rail line for nearby Toyota, Toyota Motor factories. Basic data *Operators, distances: **Aichi Loop Railway (Category 1) ***Okazaki - Kōzōji: 45 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
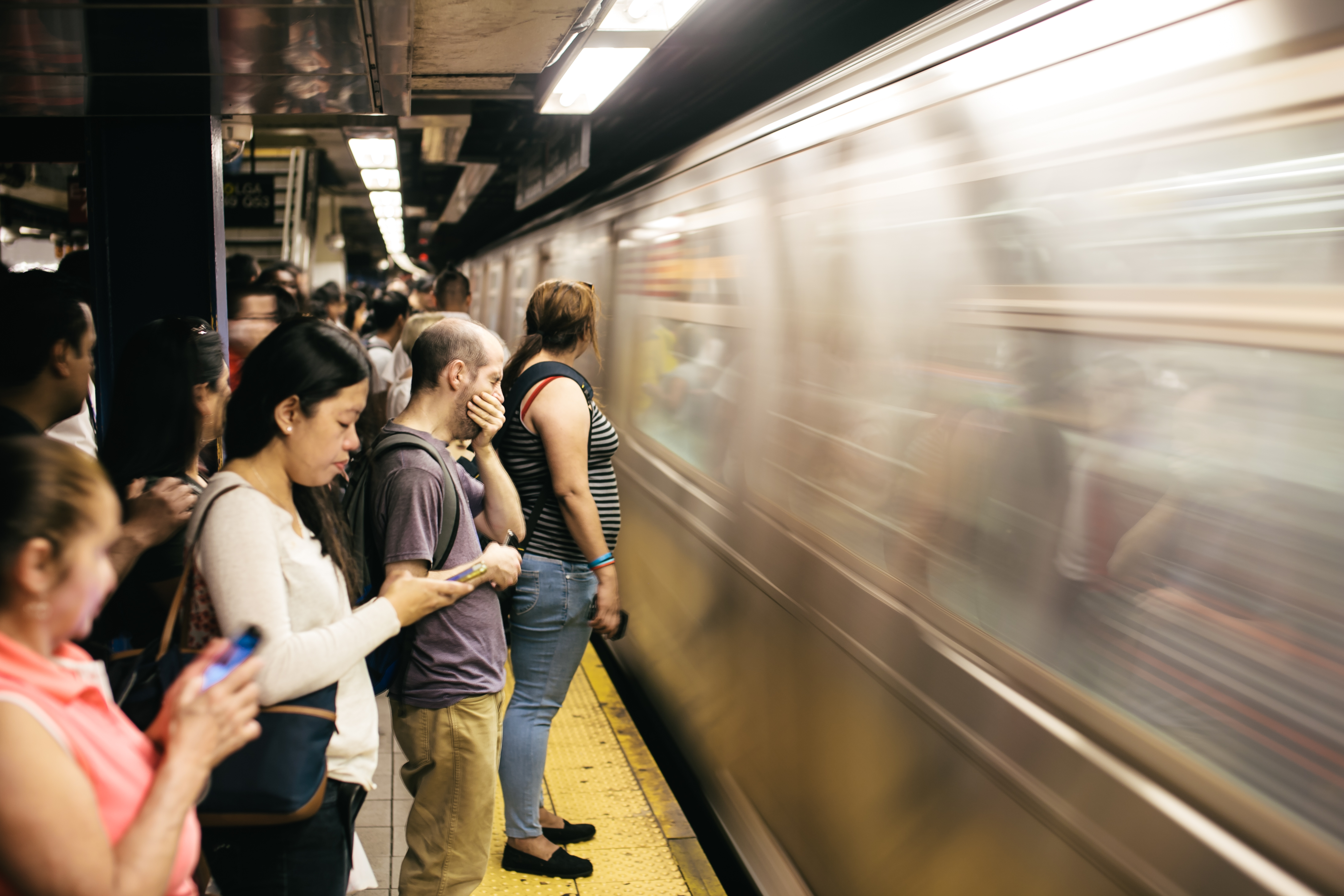
Rush Hour
A rush hour (American English, British English) or peak hour ( Australian English) is a part of the day during which traffic congestion on roads and crowding on public transport is at its highest. Normally, this happens twice every weekday: once in the morning and once in the afternoon or evening, the times during which the most people commute. The term is often used for a period of peak congestion that may last for more than one hour. The term is very broad, but often refers specifically to private automobile transportation traffic, even when there is a large volume of cars on a road but not many people, or if the volume is normal but there is some disruption of speed. By analogy to vehicular traffic, the term Internet rush hour has been used to describe periods of peak data network usage, resulting in delays and slower delivery of data packets. Definition The name is sometimes a misnomer, as the peak period often lasts more than one hour and the "rush" refers to the vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interchange Station
An interchange station or a transfer station is a train station for more than one railway route in a public transport system that allows passengers to change from one route to another, often without having to leave a station or pay an additional fare. Transfer may occur within the same mode, or between rail modes, or to buses (for stations with bus termini attached). Such stations usually have more platforms than single route stations. These stations can exist in either commercial centers or on the city outskirts in residential areas. Cities typically plan for land use around interchange stations for development. Passengers may be required to pay extra fare for the interchange if they leave a paid area. History With the opening of the Woodside and Birkenhead Dock Street Tramway in 1873, Birkenhead Dock railway station in Birkenhead, England probably became the world's first tram to train interchange station. Examples Verney Junction interchange station in Buckinghamsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commuter Rail
Commuter rail, or suburban rail, is a passenger rail transport service that primarily operates within a metropolitan area, connecting commuters to a central city from adjacent suburbs or commuter towns. Generally commuter rail systems are considered heavy rail, using electrified or diesel trains. Distance charges or zone pricing may be used. The term can refer to systems with a wide variety of different features and service frequencies, but is often used in contrast to rapid transit or light rail. Similar non-English terms include ''Treno suburbano'' in Italian, '' Cercanías'' in Spanish, Aldiriak in Basque, Rodalia in Catalan/Valencian, Proximidades in Galician, '' Proastiakos'' in Greek, ''Train de banlieue'' in French, '' Banliyö treni '' in Turkish, ''Příměstský vlak'' or ''Esko'' in Czech, '' Elektrichka'' in Russian, ''Pociąg podmiejski '' in Polish and ''Pendeltåg'' in Swedish. Some services share similarities with both commuter rail and high-frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Tunnel
A tunnel is an underground passageway, dug through surrounding soil, earth or rock, and enclosed except for the entrance and exit, commonly at each end. A pipeline is not a tunnel, though some recent tunnels have used immersed tube construction techniques rather than traditional tunnel boring methods. A tunnel may be for foot or vehicular road traffic, for rail traffic, or for a canal. The central portions of a rapid transit network are usually in the tunnel. Some tunnels are used as sewers or aqueducts to supply water for consumption or for hydroelectric stations. Utility tunnels are used for routing steam, chilled water, electrical power or telecommunication cables, as well as connecting buildings for convenient passage of people and equipment. Secret tunnels are built for military purposes, or by civilians for smuggling of weapons, contraband, or people. Special tunnels, such as wildlife crossings, are built to allow wildlife to cross human-made barriers safely. Tun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |