|
Shuttarna II
Shuttarna II (or Šuttarna) was a king of the Hurrian kingdom of Mitanni in the early 14th century BC. Shuttarna was a descendant and probably a son of the great Mitannian king Artatama I. He was an ally of the Egyptian Pharaoh Amenhotep III and the diplomatic dealings of the kings are briefly recorded in the Amarna letters EA#182, EA#183 and EA#184. Shuttarna's daughter Kilu-Hepa (sometimes spelled Gilukhepa) was given to Amenhotep III in marriage to seal the alliance between the two royal houses in the Pharaoh's 10th regnal year, taking with her a great dowry. During the reign of Shuttarna, the kingdom of Mitanni reached its height of power and prosperity. From Alalakh in the west, Mitanni shared its border with Egypt in northern Syria, approximately by the river Orontes. Two tablets sealed by Shuttarna were found at Tall Bazi on the Euphrates. Other tablets sealed by him were found at Alalakh, Tell Brak, Nuzi and Umm el-Marra.Sallaberger, Walther, Berthold Einwag & Adelheid O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurrian
The Hurrians (; cuneiform: ; transliteration: ''Ḫu-ur-ri''; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri or Hurriter) were a people of the Bronze Age Near East. They spoke a Hurrian language and lived in Anatolia, Syria and Northern Mesopotamia. The largest and most influential Hurrian nation was the kingdom of Mitanni, its ruling class perhaps being Indo-Aryan speakers. The population of the Hittite Empire in Anatolia included a large population of Hurrians, and there is significant Hurrian influence in Hittite mythology. By the Early Iron Age, the Hurrians had been assimilated with other peoples. The state of Urartu later covered some of the same area. Language The Hurrian language is closely related to the Urartian language, the language of the ancient kingdom of Urartu. Together they form the Hurro-Urartian language family. The external connections of the Hurro-Urartian languages are disputed. There exist various proposals for a genetic relationship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
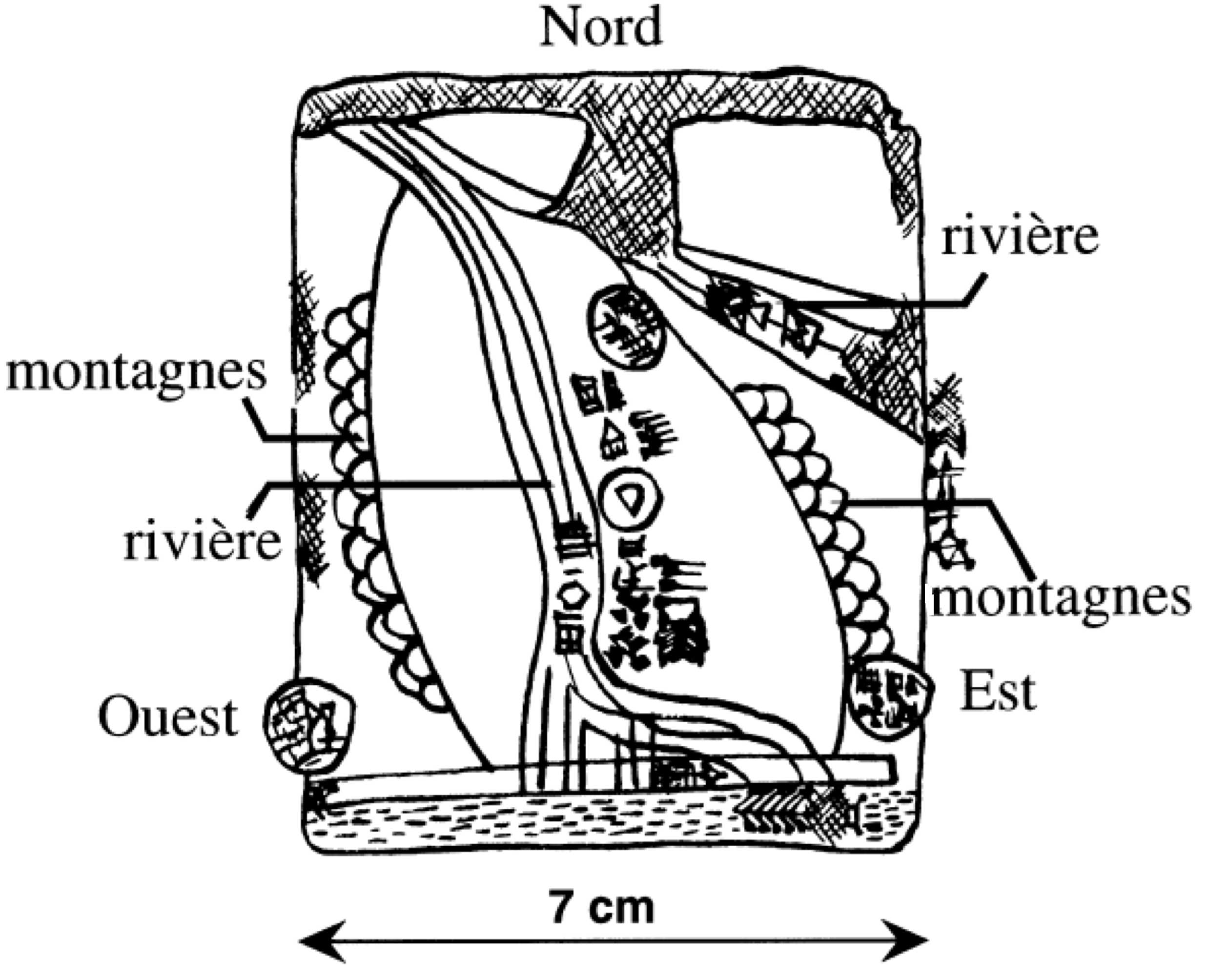
Umm El-Marra
Umm el-Marra, ( ar, أم المرى), east of modern Aleppo in the Jabbul Plain of northern Syria, was one of the ancient Near East's oldest cities, located on a crossroads of two trade routes northwest of Ebla, in a landscape that was much more fertile than it is today. Possibly this is the city of Tuba mentioned in Egyptian inscriptions listing cities that were defeated or destroyed in the Pharaoh Thutmose III's north Syrian campaign. The city of Tuba is also mentioned in epigraphic remains from Ebla, Mari, and Alalakh. History Umm el-Marra probably had three to five thousand inhabitants between 2800 BCE and about 2100/2000 BCE, when Tuba and other cities in the Jabbul Plain experienced a mysterious collapse of central authority that lasted about 200 years. Partial answers to the question, why these early centers were so brittle, may lie in the effects of sustained drought on overstressed primitive agriculture. Dr Glenn Schwartz of Johns Hopkins, who has been doing field archae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artashumara
Artashumara Akkadian language, Akkadian: ), brother of Tushratta and son of Shuttarna II, briefly held the throne of Mitanni in the fourteenth century BC. Reign He is known only from a single mention in a tablet found in Tell Brak "Artassumara the king, son of Shuttarna the king" and a mention in Amarna letter 17. According to the later, after the death of Shuttarna II he briefly took power but was then murdered (by someone named Tuhi) and succeeded by his brother TushrattaArtzi, P., "The Diplomatic Service in Action: The Mitanni File”, in: R. Cohen and R. Westbrook (eds.): Amarna Diplomacy: The Beginnings of International Relations, Baltimore, London: 205–211, 2000 See also *Mitanni References Hurrian kings 14th-century BC rulers {{ANE-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tushratta
Tushratta (Akkadian: and ) was a king of Mitanni, c. 1358–1335 BCE, at the end of the reign of Amenhotep III and throughout the reign of Akhenaten. He was the son of Shuttarna II. Tushratta stated that he was the grandson of Artatama I. His sister Gilukhipa (Gilu-ḫepa in Hurrian) and his daughter Tadukhipa (Tadu-ḫepa in Hurrian) were married to the Egyptian pharaoh Amenhotep III; Tadukhipa later married Akhenaten who took over his father's royal harem. He had been placed on the throne after the murder of his brother Artashumara. He was probably quite young at the time and was destined to serve as a figurehead only but he managed to dispose of the murderer. A tablet was found in a Mitanni building at Tell Brak which stated it was witnessed "in the presence of Tushratta, the king" and had a seal of an earlier king Shaushtatar on the reverse which was a common practice. Name Recorded in three distinct spellings—, , —Tushratta's name is an Akkadianised rendition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-central Anatolia (around 1650 BC). This empire reached its height during the mid-14th century BC under Šuppiluliuma I, when it encompassed an area that included most of Anatolia as well as parts of the northern Levant and Upper Mesopotamia. Between the 15th and 13th centuries BC, the Empire of Hattusa—in modern times conventionally called the Hittite Empire—came into conflict with the New Kingdom of Egypt, the Middle Assyrian Empire and the empire of Mitanni for control of the Near East. The Middle Assyrian Empire eventually emerged as the dominant power and annexed much of the Hittite Empire, while the remainder was sacked by Phrygian newcomers to the region. After BC, during the Late Bronze Age collapse, the Hittites splintered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrapha
Arrapha or Arrapkha (Akkadian: ''Arrapḫa''; ar, أررابخا ,عرفة) was an ancient city in what today is northeastern Iraq, thought to be on the site of the modern city of Kirkuk. In 1948, ''Arrapha'' became the name of the residential area in Kirkuk which was built by the North Oil Company as a settlement for its workers. History The first written record of Arrapha is attested from the Neo-Sumerian Empire (c. 22nd to 21st century BC). Ancient Arrapha was a part of Sargon of Akkad's Akkadian Empire (2335–2154 BC), and the city was exposed to the raids of the Lullubi during Naram-Sin's reign. The city was occupied around 2150 BC by the Gutians. Arrapha was the capital of the short-lived Guti kingdom (Gutium) before it was destroyed and the Gutians driven from Mesopotamia by the Neo-Sumerian Empire c. 2090 BC. Arrapha became a part of the Old Assyrian Empire (c. 2025–1750 BC) before Hammurabi briefly subjected Assyria to the short-lived Babylonian Empire, after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the Assyrians from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC, then to a territorial state, and eventually an empire from the 14th century BC to the 7th century BC. Spanning from the early Bronze Age to the late Iron Age, modern historians typically divide ancient Assyrian history into the Early Assyrian ( 2600–2025 BC), Old Assyrian ( 2025–1364 BC), Middle Assyrian ( 1363–912 BC), Neo-Assyrian (911–609 BC) and post-imperial (609 BC– AD 630) periods, based on political events and gradual changes in language. Assur, the first Assyrian capital, was founded 2600 BC but there is no evidence yet discovered that the city was independent until the collapse of the Third Dynasty of Ur in the 21st century BC, when a line of independent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washshukanni
Washukanni (also spelled Waššukanni) was the capital of the Hurrian kingdom of Mitanni, from around 1500 BC to the 13th century BC. Location The precise location of Waššukanni is unknown. A proposal by Dietrich Opitz located it under the largely unexcavated mound of Tell el Fakhariya, near Tell Halaf in Syria. This position was supported by M. Oppenheim and more recently by others. A neutron activation comparison with clay from relevant Amarna tablets appeared to rule out Tell Fakhariya. This idea was also rejected by Edward Lipinski. However, this identification received a new support by Stefano de Martino, Mirko Novák and Dominik Bonatz due to recent archaeological excavations by a German team. This is counterbalanced by the fact that despite many seasons of excavations over the years no documentation of the name of the Mittani capital has yet been found. History Waššukanni is known to have been sacked by the Hittites under Suppiluliuma I (reigned c. 1344–1322 B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khabur (Euphrates)
The Khabur River is the largest perennial tributary to the Euphrates in Syria. Although the Khabur originates in Turkey, the karstic springs around Ras al-Ayn are the river's main source of water. Several important wadis join the Khabur north of Al-Hasakah, together creating what is known as the Khabur Triangle, or Upper Khabur area. From north to south, annual rainfall in the Khabur basin decreases from over 400 mm to less than 200 mm, making the river a vital water source for agriculture throughout history. The Khabur joins the Euphrates near the town of Busayrah. Geography The course of the Khabur can be divided in two distinct zones: the Upper Khabur area or Khabur Triangle north of Al-Hasakah, and the Middle and Lower Khabur between Al-Hasakah and Busayrah. Tributaries The tributaries to the Khabur are listed from east to west. Most of these wadis only carry water for part of the year. * Wadi Radd *Wadi Khnezir *Wadi Jarrah * Jaghjagh River *Wadi Khanzir *Wad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuzi
Nuzi (or Nuzu; Akkadian Gasur; modern Yorghan Tepe, Iraq) was an ancient Mesopotamian city southwest of the city of Arrapha (modern Kirkuk), located near the Tigris river. The site consists of one medium-sized multiperiod tell and two small single period mounds. History The site showed occupation as far back as the late Uruk period. The city, then named Gasur, was founded in the third millennium during the time of the Akkadian Empire. In the middle of the second millennium the Hurrians gained control of the town and renamed it Nuzi. The history of the site during the intervening period is unclear, though the presence of a few cuneiform tablets from the Old Assyrian Empire indicates that trade with nearby Assur was taking place. After the fall of the Hurrian kingdom of Mitanni to Ashur-uballit I of the Middle Assyrian Empire, Nuzi went into gradual decline. Note that while the Hurrian period is well known from full excavation of those strata, the earlier history is not as rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitanni
Mitanni (; Hittite cuneiform ; ''Mittani'' '), c. 1550–1260 BC, earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, c. 1600 BC; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat (''Hanikalbat'', ''Khanigalbat'', cuneiform ') in Assyrian records, or '' Naharin'' in Egyptian texts, was a Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria and southeast Anatolia (modern-day Turkey). Since no histories or royal annals/chronicles have yet been found in its excavated sites, knowledge about Mitanni is sparse compared to the other powers in the area, and dependent on what its neighbours commented in their texts. The Hurrians were in the region as of the late 3rd millennium BC. A king of Urkesh with a Hurrian name, Tupkish, was found on a clay sealing dated c. 2300 BC at Tell Mozan.Salvini, Mirjo. "The earliest evidences of the Hurrians before the formation of the reign of Mittanni." Urkesh and the Hurrians Studies in Honor of Lloyd Cotsen. Urkesh/Mozan Studies Bibliotheca Mesopotamica. Malibu: Undena Publicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Brak
Tell Brak (Nagar, Nawar) was an ancient city in Syria; its remains constitute a tell located in the Upper Khabur region, near the modern village of Tell Brak, 50 kilometers north-east of Al-Hasaka city, Al-Hasakah Governorate. The city's original name is unknown. During the second half of the third millennium BC, the city was known as Nagar and later on, Nawar. Starting as a small settlement in the seventh millennium BC, Tell Brak evolved during the fourth millennium BC into one of the biggest cities in Upper Mesopotamia, and interacted with the cultures of southern Mesopotamia. The city shrank in size at the beginning of the third millennium BC with the end of Uruk period, before expanding again around c. 2600 BC, when it became known as Nagar, and was the capital of a regional kingdom that controlled the Khabur river valley. Nagar was destroyed around c. 2300 BC, and came under the rule of the Akkadian Empire, followed by a period of independence as a Hurrian city-st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |