|
Shin Shwe Of Pagan
, image = , caption = , reign = 1270 – 1287 , coronation = , succession = Queen consort of Burma , predecessor = , successor = , suc-type = Successor , reg-type = , regent = , spouse = Narathihapate , issue = Mi Saw U , issue-link = , full name = , house = Pagan , father = , mother = , birth_date = , birth_place = , death_date = , death_place = , date of burial = , place of burial = , religion = Theravada Buddhism , signature = Shin Shwe ( my, ရှင်ရွှေ, ) was a principal queen consort of King Narathihapate of the Pagan Dynasty of Burma (Myanmar).Hmannan Vol. 1 2003: 348 She was the mother of Queen Mi Saw U of Pagan and later Pinya, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narathihapate
Narathihapate ( my, နရသီဟပတေ့, ; also Sithu IV of Pagan; 23 April 1238 – 1 July 1287) was the last king of the Pagan Empire who reigned from 1256 to 1287. The king is known in Burmese history as the "Taruk-Pyay Min" ("the King who fled from the Taruks")Coedès 1968: 183 for his flight from Pagan (Bagan) to Lower Burma in 1285 during the first Mongol invasion (1277–87) of the kingdom. He eventually submitted to Kublai Khan, founder of the Yuan dynasty in January 1287 in exchange for a Mongol withdrawal from northern Burma. But when the king was assassinated six months later by his son Thihathu, the Viceroy of Prome, the 250-year-old Pagan Empire broke apart into multiple petty states. The political fragmentation of the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery would last for another 250 years until the mid-16th century. The king is unkindly remembered in the royal chronicles, which in addition to calling a cowardly king who fled from the invaders, also call him " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mi Saw U
, image = , caption = , reign = 7 February 1313 – February 1325 , coronation = , succession = Chief queen consort of Pinya , predecessor = new office , successor = Atula Maha Dhamma Dewi , suc-type = Successor , reign1 = 17 December 1297 – 7 February 1313 , coronation1 = 20 October 1309 , succession1 = Chief queen consort of Pinle , predecessor1 = ''new office'' , successor1 = ''disestablished'' , reign2 = 1290s – 17 December 1297 , coronation2 = , succession2 = Queen of the Central Palace of Pagan , predecessor2 = ''vacant'' , successor2 = ''disestablished'' , spouse = Kyawswa (1289–1297) Thihathu (1297–1325) , issue = Uzana I Kyawswa I Nawrahta , issue-link = , full name = , house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
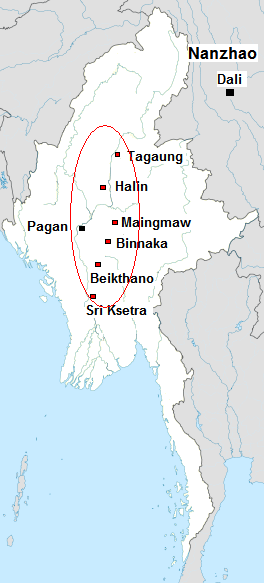
Pagan Kingdom
The Kingdom of Pagan ( my, ပုဂံခေတ်, , ; also known as the Pagan Dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan Dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-day Myanmar. Pagan's 250-year rule over the Irrawaddy River, Irrawaddy valley and its periphery laid the foundation for the ascent of Burmese language and Burmese culture, culture, the spread of Bamar people, Bamar ethnicity in Upper Myanmar, and the growth of Theravada Buddhism in Myanmar and in mainland Southeast Asia.Lieberman 2003: 88–123 The kingdom grew out of a small 9th-century settlement at Bagan, Pagan (present-day Bagan) by the Bamar, Mranma/Burmans, who had recently entered the Irrawaddy valley from the Kingdom of Nanzhao. Over the next two hundred years, the small principality gradually grew to absorb its surrounding regions until the 1050s and 1060s when King Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, for the first time unifying und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theravada Buddhism
''Theravāda'' () ( si, ථේරවාදය, my, ထေရဝါဒ, th, เถรวาท, km, ថេរវាទ, lo, ເຖຣະວາດ, pi, , ) is the most commonly accepted name of Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school's adherents, termed Theravādins, have preserved their version of Gautama Buddha's teaching or ''Dharma (Buddhism), Buddha Dhamma'' in the Pāli Canon for over two millennia. The Pāli Canon is the most complete Buddhist canon surviving in a Indo-Aryan languages, classical Indian language, Pali, Pāli, which serves as the school's sacred language and ''lingua franca''.Crosby, Kate (2013), ''Theravada Buddhism: Continuity, Diversity, and Identity'', p. 2. In contrast to ''Mahāyāna'' and ''Vajrayāna'', Theravāda tends to be conservative in matters of doctrine (''pariyatti'') and monastic discipline (''vinaya''). One element of this conservatism is the fact that Theravāda rejects the authenticity of the Mahayana sutras (which appeared c. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pagan Dynasty
The Kingdom of Pagan ( my, ပုဂံခေတ်, , ; also known as the Pagan Dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan Dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-day Myanmar. Pagan's 250-year rule over the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery laid the foundation for the ascent of Burmese language and culture, the spread of Bamar ethnicity in Upper Myanmar, and the growth of Theravada Buddhism in Myanmar and in mainland Southeast Asia.Lieberman 2003: 88–123 The kingdom grew out of a small 9th-century settlement at Pagan (present-day Bagan) by the Mranma/Burmans, who had recently entered the Irrawaddy valley from the Kingdom of Nanzhao. Over the next two hundred years, the small principality gradually grew to absorb its surrounding regions until the 1050s and 1060s when King Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, for the first time unifying under one polity the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. By t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explains, the English spellings of both Myanmar and Burma assume a non-rhotic variety of English, in which the letter r before a consonant or finally serves merely to indicate a long vowel: �mjænmɑː, ˈbɜːmə So the pronunciation of the last syllable of Myanmar as ɑːror of Burma as ɜːrməby some speakers in the UK and most speakers in North America is in fact a spelling pronunciation based on a misunderstanding of non-rhotic spelling conventions. The final ''r'' in ''Myanmar'' was not intended for pronunciation and is there to ensure that the final a is pronounced with the broad ''ah'' () in "father". If the Burmese name my, မြန်မာ, label=none were spelled "Myanma" in English, this would be pronounced at the end by all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinya Kingdom
The Kingdom of Pinya ( my, ပင်းယခေတ်, ), also known as the Vijaia State (၀ိဇယတိုင်း), was the kingdom that ruled Central Myanmar (Burma) from 1313 to 1365. It was the successor state of Myinsaing, the polity that controlled much of Upper Burma between 1297 and 1313. Founded as the de jure successor state of the Pagan Empire by Thihathu, Pinya faced internal divisions from the start. The northern province of Sagaing led by Thihathu's eldest son Saw Yun successfully fought for autonomy in 1315−17, and formally seceded in 1325 after Thihathu's death. The rump Pinya Kingdom was left embroiled in an intense rivalry between Thihathu's other sons Uzana I and Kyawswa I until 1344. Pinya had little control over its vassals; its southernmost vassals Toungoo (Taungoo) and Prome (Pyay) were practically independent. Central authority briefly returned during Kyawswa I's reign (1344−50) but broke down right after his death. In the 1350s, Kyawswa II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uzana I Of Pinya
, image = , caption = , reign = February 1325 – 1 September 1340 , coronation = , succession = King of Pinya , predecessor = Thihathu , successor = Sithu , suc-type = Successor , reg-type = Chief Minister , regent = Ananda Pyissi , spouse = Atula Maha Dhamma Dewi , issue = Sithu Min Oo Thihapate Saw Pa Oh Mway Medaw , issue-link = , full name = Anawrahta Maha Dipati , house = Myinsaing , father = Kyawswa of Pagan , mother = Mi Saw U , birth_date = June 1298 Tuesday, Waso 660 ME , birth_place = Pinle, Myinsaing Regency , death_date = 1356/1357 (aged 58) 718 ME , death_place = Mekkhaya, Pinya Kingdom , date of burial = , place of burial = , religion = Theravada Buddhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyawswa I Of Pinya
Kyawswa I of Pinya ( my, ငါးစီးရှင် ကျော်စွာ, ; ; 1299–1350) was king of Pinya from 1344 to 1350. His six-year reign briefly restored unity in southern Upper Burma although his authority over his southernmost vassals remained largely nominal. He suddenly died in 1350, and came to be regarded as one of the major Burmese folk spirits, known as Nga-zi Shin Nat. Early life Born in 1299,Hmannan Vol. 1 2003: 384 Kyawswa was the elder son of Queen Mi Saw U of Pagan and Thihathu, Co-Regent of Myinsaing. He grew up at the Pinle Palace with his younger brother Nawrahta; three half-siblings Uzana, Saw Yun, and Saw Pale; and one stepbrother Tarabya.Hmannan Vol. 1 2003: 371–372 Kyawswa grew up as second in the line of succession after Uzana. (Eager to be seen as a legitimate successor to the Pagan line,Htin Aung 1967: 76–77 Thihathu ranked his stepson Uzana, of Pagan royalty from both sides, first; and Kyawswa, of Pagan royalty the maternal side, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hmannan Yazawin
''Hmannan Maha Yazawindawgyi'' ( my, မှန်နန်း မဟာ ရာဇဝင်တော်ကြီး, ; commonly, ''Hmannan Yazawin''; known in English as the '' Glass Palace Chronicle'') is the first official chronicle of Konbaung Dynasty of Burma (Myanmar). It was compiled by the Royal Historical Commission between 1829 and 1832.Hla Pe 1985: 39–40 The compilation was based on several existing chronicles and local histories, and the inscriptions collected on the orders of King Bodawpaya, as well as several types of poetry describing epics of kings. Although the compilers disputed some of the earlier accounts, they by and large retained the accounts given ''Maha Yazawin'', the standard chronicle of Toungoo Dynasty. The chronicle, which covers events right up to 1821, right before the First Anglo-Burmese War (1824–1826), was not written purely from a secular history perspective but rather to provide "legitimation according to religious criteria" of the monarchy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)