|
Shin-bang
Shin-bang is a general sense of discomfort or pain in the lower anterior portion of the tibia that contacts the tongue of a ski boot, especially when pressed against the boot. It should not to be confused with shin-bite, which is a condition where the shin is rubbed raw due to irritation inside of the ski boot. Causes of Shin-bang There are multiple possible causes of shin-bang. Most notable causes include: ski boots that are too big, skiing in a "back seat" posture, ski boots that are too stiff, aggressive skiing, and landing jumps or drops in a back seat fashion. Reasons for these causes: Ski boots that are too big: With ski boots that are too large, one's foot and ankle are able to slide forward and backward. When this motion happens, intermittent contact between the shin and the tongue or upper cuff of the ski boot takes place. This intermittent contact usually continues through the duration of one's ski day especially on aggressive terrain that can cause the skier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discomfort
Comfort (or being comfortable'')'' is a sense of physical or psychological ease, often characterized as a lack of hardship. Persons who are lacking in comfort are uncomfortable, or experiencing discomfort. A degree of psychological comfort can be achieved by recreating experiences that are associated with pleasant memories, such as engaging in familiar activities,Daniel Miller, ''The Comfort of Things'' (2009). maintaining the presence of familiar objects, and consumption of comfort foods. Comfort is a particular concern in health care, as providing comfort to the sick and injured is one goal of healthcare, and can facilitate recovery.Katharine Kolcaba, ''Comfort Theory and Practice: A Vision for Holistic Health Care and Research'' (2003). Persons who are surrounded with things that provide psychological comfort may be described as being "in their comfort zone". Because of the personal nature of positive associations, psychological comfort is highly subjective. The use of " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strain (injury)
A strain is an acute or chronic soft tissue injury that occurs to a muscle, tendon, or both. The equivalent injury to a ligament is a sprain. Generally, the muscle or tendon overstretches and partially tears, under more physical stress than it can withstand, often from a sudden increase in duration, intensity, or frequency of an activity. Strains most commonly occur in the foot, leg, or back. Immediate treatment typically includes five steps abbreviated as P.R.I.C.E.: protection, rest, ice, compression, elevation. Signs and symptoms Typical signs and symptoms of a strain include pain, functional loss of the involved structure, muscle weakness, contusion, and localized inflammation. A strain can range from mild overstretching to severe tears, depending on the extent of injury. Cause A strain can occur as a result of improper body mechanics with any activity (e.g., contact sports, lifting heavy objects) that can induce mechanical trauma or injury. Generally, the muscle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strap
A strap, sometimes also called strop, is an elongated wikt:flap, flap or ribbon, usually of leather or other flexible materials. Thin straps are used as part of clothing or baggage, or bedding such as a sleeping bag. See for example spaghetti strap, shoulder strap. A strap differs from a belt (clothing), belt mainly in that a strap is usually integral to the item of clothing; either can be used in combination with buckles. Straps are also used as fasteners to attach, secure, carry, or bind items, to objects, animals (for example a saddle on a horse) and people (for example a watch on a wrist), or even to tie down people and animals, as on an apparatus for corporal punishment. Occasionally a strap is specified after what it binds or holds, e.g. chin strap. Webbing is a particular type of strap that is a strong fabric woven as a flat strip or tube that is also often used in place of rope. Modern webbing is typically made from exceptionally high-strength material and is used in aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsiflex
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athlete
An athlete (also sportsman or sportswoman) is a person who competes in one or more sports that involve physical strength, speed, or endurance. Athletes may be professionals or amateurs. Most professional athletes have particularly well-developed physiques obtained by extensive physical training and strict exercise accompanied by a strict dietary regimen. Definitions The word "athlete" is a romanization of the el, άθλητὴς, ''athlētēs'', one who participates in a contest; from ἄθλος, ''áthlos'' or ἄθλον, ''áthlon'', a contest or feat. The primary definition of "sportsman" according to Webster's ''Third Unabridged Dictionary'' (1960) is, "a person who is active in sports: as (a): one who engages in the sports of the field and especially in hunting or fishing." Physiology Athletes involved in isotonic exercises have an increased mean left ventricular end-diastolic volume and are less likely to be depressed. Due to their strenuous physical activities, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used for treating pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus arteriosus in a premature baby. It can be used by mouth or intravenously. It typically begins working within an hour. Common side effects include heartburn and a rash. Compared to other NSAIDs, it may have other side effects such as gastrointestinal bleeding. It increases the risk of heart failure, kidney failure, and liver failure. At low doses, it does not appear to increase the risk of heart attack; however, at higher doses it may. Ibuprofen can also worsen asthma. While whether it is safe in early pregnancy is unclear, it appears to be harmful in later pregnancy, so is not recommended. Like other NSAIDs, it works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins by decreasing the activity of the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX). Ibuprofen is a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
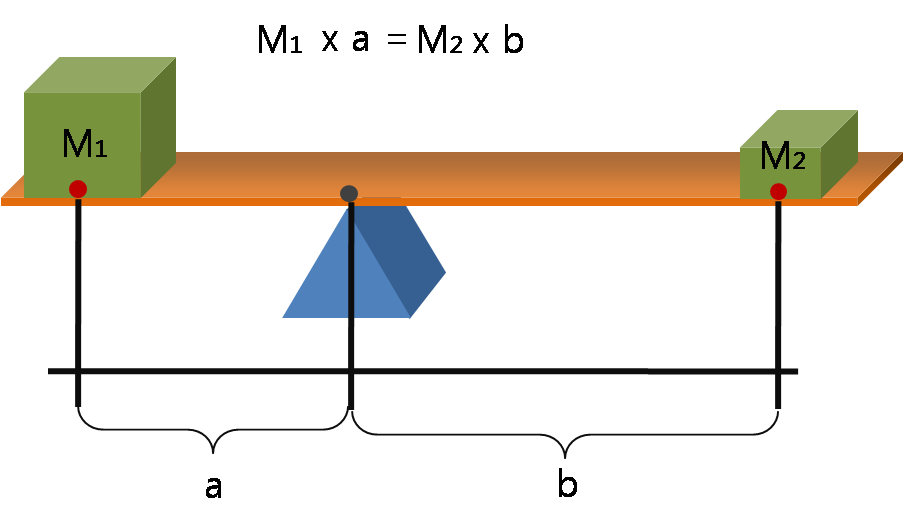
Lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or ''fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is divided into three types. Also, leverage is mechanical advantage gained in a system. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists. A lever amplifies an input force to provide a greater output force, which is said to provide leverage. The ratio of the output force to the input force is the mechanical advantage of the lever. As such, the lever is a mechanical advantage device, trading off force against movement. Etymology The word "lever" entered English around 1300 from Old French, in which the word was ''levier''. This sprang from the stem of the verb ''lever'', meaning "to raise". The verb, in turn, goes back to the Latin ''levare'', itself from the adjective ''levis'', meaning "light" (as in "not heavy"). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress Fracture
A stress fracture is a fatigue-induced bone fracture caused by repeated stress over time. Instead of resulting from a single severe impact, stress fractures are the result of accumulated injury from repeated submaximal loading, such as running or jumping. Because of this mechanism, stress fractures are common overuse injuries in athletes. Stress fractures can be described as small cracks in the bone, or hairline fractures. Stress fractures of the foot are sometimes called "march fractures" because of the injury's prevalence among heavily marching soldiers. Stress fractures most frequently occur in weight-bearing bones of the lower extremities, such as the tibia and fibula (bones of the lower leg), metatarsal and navicular bones (bones of the foot). Less common are stress fractures to the femur, pelvis, and sacrum. Treatment usually consists of rest followed by a gradual return to exercise over a period of months. Signs and symptoms Stress fractures are typically discovered after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landing
Landing is the last part of a flight, where a flying animal, aircraft, or spacecraft returns to the ground. When the flying object returns to water, the process is called alighting, although it is commonly called "landing", "touchdown" or " splashdown" as well. A normal aircraft flight would include several parts of flight including taxi, takeoff, climb, cruise, descent and landing. Aircraft Aircraft usually land at an airport on a firm runway or helicopter landing pad, generally constructed of asphalt concrete, concrete, gravel or grass. Aircraft equipped with pontoons (floatplane) or with a boat hull-shaped fuselage (a flying boat) are able to land on water. Aircraft also sometimes use skis to land on snow or ice. To land, the airspeed and the rate of descent are reduced such that the object descends at a low enough rate to allow for a gentle touch down. Landing is accomplished by slowing down and descending to the runway. This speed reduction is accomplished by re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability to withstand significant amounts of tension. Tendons are similar to ligaments; both are made of collagen. Ligaments connect one bone to another, while tendons connect muscle to bone. Structure Histologically, tendons consist of dense regular connective tissue. The main cellular component of tendons are specialized fibroblasts called tendon cells (tenocytes). Tenocytes synthesize the extracellular matrix of tendons, abundant in densely packed collagen fibers. The collagen fibers are parallel to each other and organized into tendon fascicles. Individual fascicles are bound by the endotendineum, which is a delicate loose connective tissue containing thin collagen fibrils and elastic fibres. Groups of fascicles are bounded by the epitenon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscles
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes. It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout its life cycle, starting when, under suitable conditions, the ice crystals form in the atmosphere, increase to millimeter size, precipitate and accumulate on surfaces, then metamorphose in place, and ultimately melt, slide or sublimate away. Snowstorms organize and develop by feeding on sources of atmospheric moisture and cold air. Snowflakes nucleate around particles in the atmosphere by attracting supercooled water droplets, which freeze in hexagonal-shaped crystals. Snowflakes take on a variety of shapes, basic among these are platelets, needles, columns and rime. As snow accumulates into a snowpack, it may blow into drifts. Over time, accumulated snow metamorphoses, by sintering, sublimation and freeze-thaw. Where the climate is co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |