|
Sheshi Scarabs Locations
Maaibre Sheshi (also Sheshy) was a ruler of areas of Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period. The dynasty, chronological position, duration and extent of his reign are uncertain and subject to ongoing debate. The difficulty of identification is mirrored by problems in determining events from the end of the Middle Kingdom to the arrival of the Hyksos in Egypt. Nonetheless, Sheshi is, in terms of the number of artifacts attributed to him, the best-attested king of the period spanning the end of the Middle Kingdom and the Second Intermediate period; roughly from c. 1800 BC until 1550 BC. Hundreds of scaraboid seals bearing his name have been found throughout Canaan, Egypt, Nubia, and as far away as Carthage, where some were still in use 1,500 years after his death. Three competing hypotheses have been put forth for the dynasty to which Sheshi belonged. First hypothesis supported by Egyptologists such as Nicolas Grimal, William C. Hayes, and Donald B. Redford believe he shoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William C
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Ayres Ward
William Ayres Ward (June 10, 1928 – September 13, 1996) was an American Egyptologist. Biography Born in Chicago, Ward studied at the Butler University in Indianapolis and received his B.A. in History of religions in 1951. Then, he attained a MA in Egyptology at the University of Chicago in 1955 and a PhD in Semitic languages at the Brandeis University in 1958. He then taught in Beirut, first at the Beirut College for Women and later, since 1963, at the American University of Beirut. From 1986 until his death in 1996, he was a visiting professor at Brown University in Providence, Rhode Island. His main areas of research included the relations between Egypt and Levant, Egyptian-Semitic etymology, as well as scarabs and titles of the Old and Middle Kingdom of Egypt. Sources * Leonard H. Lesko Leonard H. Lesko (born 1938) was Chairman of the Department of Egyptology at Brown University and held the Charles Edwin Wilbour Professorship. In 1961, he received a B.A. in Classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avaris
Avaris (; Egyptian: ḥw.t wꜥr.t, sometimes ''hut-waret''; grc, Αὔαρις, Auaris; el, Άβαρις, Ávaris; ar, حوّارة, Hawwara) was the Hyksos capital of Egypt located at the modern site of Tell el-Dab'a in the northeastern region of the Nile Delta. As the main course of the Nile migrated eastward, its position at the hub of Egypt's delta emporia made it a major capital suitable for trade. It was occupied from about the 18th century BC until its capture by Ahmose I. Etymology The name in the Egyptian language of the 2nd millennium BC was probably pronounced *Ḥaʔət-Waʕrəʔ “House of the Region” and denotes the capital of an administrative division of the land (''wʕr.t''). Today, the name ''Hawara'' survives, referring to the site at the entrance to Faiyum. Alternatively, Clement of Alexandria referred to the name of this city as "Athyria". Excavations In 1885, the Swiss Édouard Naville started the first excavations in the area around Tell-el-Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakbim Sekhaenre
Sekhaenre Yakbim or Yakbmu was a ruler during the Second Intermediate Period of Egypt. Although his dynastic and temporal collocation is disputed, Danish Egyptologist Kim Ryholt believes that he likely was the founder of the Levantine-blooded Fourteenth Dynasty, while in older literature he was mainly considered a member of the Sixteenth Dynasty. Identification His name never appears inside a cartouche, which was a pharaonic prerogative; nevertheless, on his seals he is usually called "the good god, Sekhaenre" (or simply "Sekhaenre") and " the son of Ra, Yakbim". There is no direct evidence that Yakbim's throne name was Sekhaenre. This theory is based on stylistic features of the seals and was proposed by William Ayres Ward and later elaborated on by Ryholt; Daphna Ben-Tor disputed this identification, pointing out that the seals of the several rulers living during this period are too similar to make such correlations on the basis of mere design features. Assuming that Ward was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheshi Scarabs Locations
Maaibre Sheshi (also Sheshy) was a ruler of areas of Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period. The dynasty, chronological position, duration and extent of his reign are uncertain and subject to ongoing debate. The difficulty of identification is mirrored by problems in determining events from the end of the Middle Kingdom to the arrival of the Hyksos in Egypt. Nonetheless, Sheshi is, in terms of the number of artifacts attributed to him, the best-attested king of the period spanning the end of the Middle Kingdom and the Second Intermediate period; roughly from c. 1800 BC until 1550 BC. Hundreds of scaraboid seals bearing his name have been found throughout Canaan, Egypt, Nubia, and as far away as Carthage, where some were still in use 1,500 years after his death. Three competing hypotheses have been put forth for the dynasty to which Sheshi belonged. First hypothesis supported by Egyptologists such as Nicolas Grimal, William C. Hayes, and Donald B. Redford believe he shoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenomen (Ancient Egypt)
The prenomen, also called cartouche name or throne name ( egy, 𓆥 nswt-bjtj "of the Sedge and Bee") of ancient Egypt, was one of the five royal names of pharaohs. The first pharaoh to have a Sedge and Bee name was Den during the First Dynasty. Most Egyptologists believe that the prenomen was a regnal name. Others think that it originally represented the birth name of the rulers. The term "of the Sedge and Bee" is written by the hieroglyphs representing a sedge, representing Upper Egypt (𓇓 Gardiner M23) and a bee, representing Lower Egypt (𓆤 L2), each combined with the feminine ending ''t'' (𓏏 X1), read as ''nsw.t'' and ''bj.t'' respectively; the adjectival nisba ending ''-j'' is not represented in writing. During the first three dynasties, the prenomen was depicted either alone or in pair with the Nebty name. Semerkhet was the first pharaoh who devoted his prenomen to the Two Ladies. From Pharaoh Huni, the probable last king of the Third Dynasty onward, the pren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scaraboid Seal
Scarabs were popular amulets and impression seals in ancient Egypt. They survive in large numbers and, through their inscriptions and typology, are an important source of information for archaeologists and historians of the ancient world. They also represent a significant body of ancient art. For reasons that are not clear (although likely connected to the religious significance of the Egyptian god Khepri), amulets in the form of scarab beetles had become enormously popular in Ancient Egypt by the early Middle Kingdom (approx. 2000 BCE) and remained popular for the rest of the pharaonic period and beyond. During that long period the function of scarabs repeatedly changed. Primarily amulets, they were also inscribed for use as personal or administrative seals or were incorporated into jewelry. Some scarabs were created for political or diplomatic purposes to commemorate or advertise royal achievements. By the early New Kingdom, ''heart scarabs'' had become part of the battery of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nubia
Nubia () (Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), or more strictly, Al Dabbah. It was the seat of one of the earliest civilizations of ancient Africa, the Kerma culture, which lasted from around 2500 BC until its conquest by the New Kingdom of Egypt under Pharaoh Thutmose I around 1500 BC, whose heirs ruled most of Nubia for the next 400 years. Nubia was home to several empires, most prominently the Kingdom of Kush, which conquered Egypt in the eighth century BC during the reign of Piye and ruled the country as its 25th Dynasty (to be replaced a century later by the native Egyptian 26th Dynasty). From the 3rd century BC to 3rd century AD, northern Nubia would be invaded and annexed to Egypt, ruled by the Greeks and Romans. This territory would be known in the Greco-Roman world as Dodekasc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerma Culture
The Kerma culture or Kerma kingdom was an early civilization centered in Kerma, Sudan. It flourished from around 2500 BC to 1500 BC in ancient Nubia. The Kerma culture was based in the southern part of Nubia, or "Upper Nubia" (in parts of present-day northern and central Sudan), and later extended its reach northward into Lower Nubia and the border of Egypt. The polity seems to have been one of a number of Nile Valley states during the Middle Kingdom of Egypt. In the Kingdom of Kerma's latest phase, lasting from about 1700 to 1500 BC, it absorbed the Sudanese kingdom of Sai and became a sizable, populous empire rivaling Egypt. Around 1500 BC, it was absorbed into the New Kingdom of Egypt, but rebellions continued for centuries. By the eleventh century BC, the more-Egyptianized Kingdom of Kush emerged, possibly from Kerma, and regained the region's independence from Egypt. Site The primary site of Kerma that forms the heart of the Kingdom of Kerma includes both an extensive town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kim Ryholt
Kim Steven Bardrum Ryholt (born 19 June 1970) is a professor of Egyptology at the University of Copenhagen and a specialist on Egyptian history and literature. He is director of the research centeCanon and Identity Formation in the Earliest Literate Societiesunder the University of Copenhagen Programme of Excellence (since 2008) and director of The Papyrus Carlsberg Collection & Project (since 1999). Research One of his most significant publications is a 1997 book titled ''The Political Situation in Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period c. 1800–1550 B.C.'' Aidan Dodson, a prominent English Egyptologist, calls Ryholt's book "fundamental" for an understanding of the Second Intermediate Period because it reviews the political history of this period and contains an updated—and more accurate—reconstruction of the Turin Canon since the 1959 publication of Alan Gardiner's ''Royal Canon of Egypt.'' It also contains an extensive catalogue of all the known monuments, inscriptions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
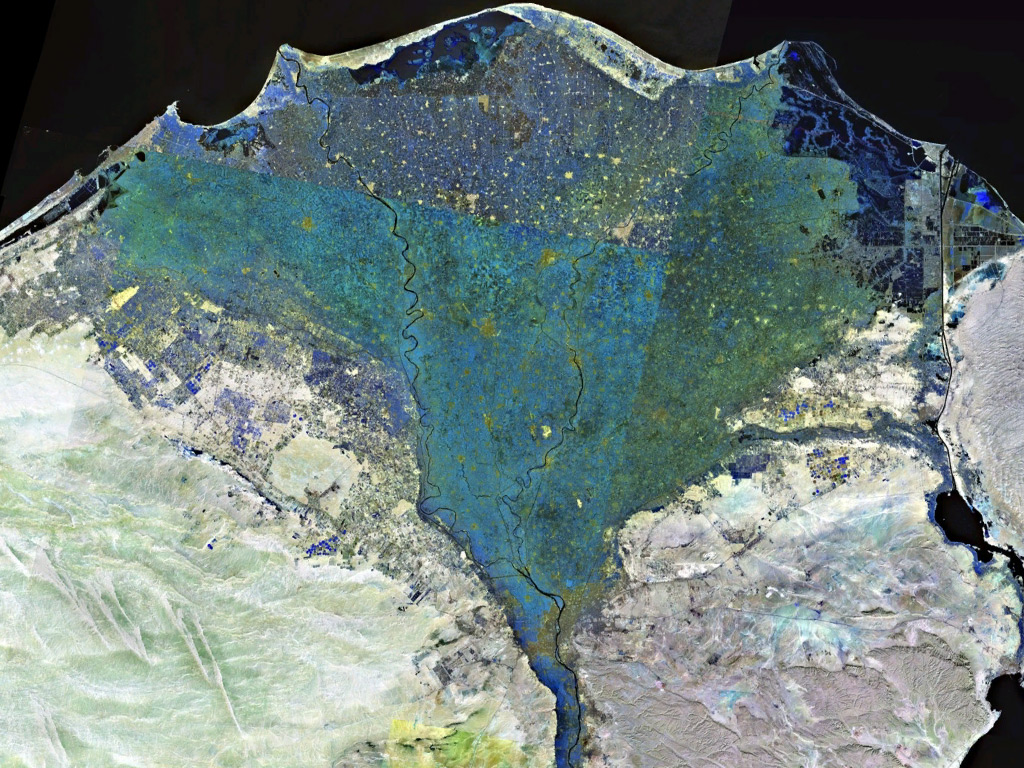
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers of Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same name. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta and enters the coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)