|
Shepseskare Scarab
Shepseskare or Shepseskara (Egyptian for "Noble is the Soul of Ra") was an Ancient Egyptian pharaoh Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the an ..., the fourth or fifth ruler of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt, Fifth Dynasty (2494–2345 BC) during the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom period. Shepseskare lived in the mid-25th century BC and was probably the owner of an unfinished pyramid in Abusir, which was abandoned after a few weeks of work in the earliest stages of its construction. Following historical sources, Shepseskare was traditionally believed to have reigned for seven years, succeeding Neferirkare Kakai and preceding Neferefre on the throne, making him the fourth ruler of the dynasty. He is the most obscure ruler of this dynasty and the Egyptologist Miroslav Verner h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Émile Jules Daressy
Georges Émile Jules Daressy (19 March 1864 – 28 February 1938) was a French Egyptologist. He worked from 1887 in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo. Amongst his responsibilities was the museum's move from Bulaq to Giza in 1891, and then to the present-day location in 1901. He is an author of the general catalog of the museum. He was the first Egyptologist to publish (1901) and translate (1906) the ''Akhmim wooden tablets.'' He excavated throughout Egypt, most notably in the Valley of the Kings, Medinet Habu, Karnak, Luxor, Malkata and Abydos Abydos may refer to: *Abydos, a progressive metal side project of German singer Andy Kuntz * Abydos (Hellespont), an ancient city in Mysia, Asia Minor * Abydos (''Stargate''), name of a fictional planet in the '' Stargate'' science fiction universe .... Publications * , Le Caire, 1893. * , Le Caire, 1897. * , 1898. * , Le Caire : , 1901, (). * , Le Caire : , 1902, (). * , Le Caire : , 1903, (). * , Le Caire : Imprimerie de l'Inst. Franc̜ais d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
25th Century BC
The 25th century BC was a century that lasted from the year 2500 BC to 2401 BC. Events * c. 2900–2334 BC: Mesopotamian wars of the Early Dynastic period. * c. 2560 BC: Construction of the Great Pyramid of Giza is completed. * c. 2500 BC: Rice was first introduced to Malaysia * c. 2500 BC: Scribal schools flourish throughout Sumer. * c. 2500 BC: Assyria is established. * c. 2500 BC: Cylinder seal from Sumer and its impression are made. It is now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York. * c. 2500 BC: Excavation and development of the Hypogeum of Ħal-Saflieni at Paola, Malta, a subterranean temple complex subsequently used as a necropolis. * c. 2500 BC: The Pyramid of Khafre, Giza, is built. * c. 2500 BC: The sculpture Khafre Enthroned is made. * c. 2500 BC: People in Peru rely on fish and mussels for food. *c. 2500 BC: Evidence of long-distance trade routes in South America. * c. 2500 BC: Skara Brae is abandoned after approximately 600 years of occupation. * c. 2500� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flinders Petrie
Sir William Matthew Flinders Petrie ( – ), commonly known as simply Flinders Petrie, was a British Egyptologist and a pioneer of systematic methodology in archaeology and the preservation of artefacts. He held the first chair of Egyptology in the United Kingdom, and excavated many of the most important archaeological sites in Egypt in conjunction with his wife, Hilda Urlin. Some consider his most famous discovery to be that of the Merneptah Stele, an opinion with which Petrie himself concurred. Undoubtedly at least as important is his 1905 discovery and correct identification of the character of the Proto-Sinaitic script, the ancestor of almost all alphabetic scripts. Petrie developed the system of dating layers based on pottery and ceramic findings. He remains controversial for his pro-eugenics views; he was a dedicated believer in the superiority of the Northern peoples over the Latinate and Southern peoples. Early life Petrie was born on 3 June 1853 in Charlton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shepseskare Scarab
Shepseskare or Shepseskara (Egyptian for "Noble is the Soul of Ra") was an Ancient Egyptian pharaoh Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the an ..., the fourth or fifth ruler of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt, Fifth Dynasty (2494–2345 BC) during the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom period. Shepseskare lived in the mid-25th century BC and was probably the owner of an unfinished pyramid in Abusir, which was abandoned after a few weeks of work in the earliest stages of its construction. Following historical sources, Shepseskare was traditionally believed to have reigned for seven years, succeeding Neferirkare Kakai and preceding Neferefre on the throne, making him the fourth ruler of the dynasty. He is the most obscure ruler of this dynasty and the Egyptologist Miroslav Verner h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
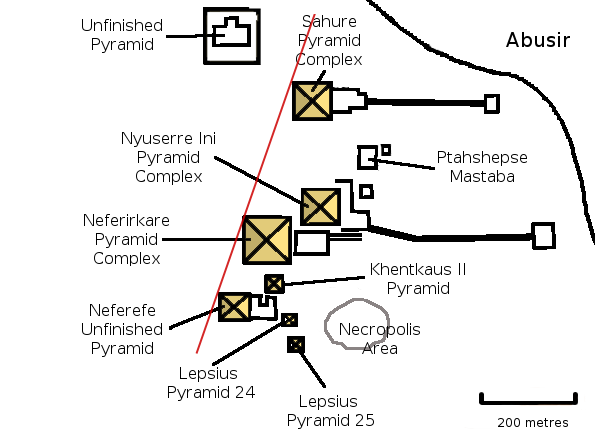
Sanctuary Of The Knife
The pyramid of Neferefre, also known as the pyramid of Raneferef, (in ancient Egyptian ''Nṯrỉ bꜣw Nfr-f-Rꜥ'' ("Divine is Neferefre's power")) is a 25th century BC unfinished pyramid complex built for the Egyptian pharaoh Neferefre of the Fifth Dynasty. Neferefre's unfinished pyramid is the third and final one built on the Abusir diagonal – a figurative line connecting the Abusir pyramids with Heliopolis – of the necropolis, sited south-west of Neferirkare's pyramid. The pyramid was hastily converted into a square mastaba or primeval mound after Neferefre's early death. In the period between his death and mummification, an improvised, north-south oriented limestone mortuary temple was built on a strip of platform originally intended for the casing of the pyramid. It is unclear who constructed this initial phase of the temple, though clay sealings found in its vicinity suggest that it may have been the ephemeral ruler Shepseskare who commissioned it. During the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Neferefre
The pyramid of Neferefre, also known as the pyramid of Raneferef, (in Egyptian language, ancient Egyptian ''Nṯrỉ bꜣw Nfr-f-Rꜥ'' ("Divine is Neferefre's power")) is a 25th century BC unfinished Egyptian pyramid, pyramid complex built for the Egyptian pharaoh Neferefre of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt, Fifth Dynasty. Neferefre's unfinished pyramid is the third and final one built on the Abusir diagonal – a figurative line connecting the Abusir pyramids with Heliopolis (ancient Egypt), Heliopolis – of the necropolis, sited south-west of Pyramid of Neferirkare, Neferirkare's pyramid. The pyramid was hastily converted into a mastaba, square mastaba or Nu (mythology), primeval mound after Neferefre's early death. In the period between his death and mummification, an improvised, north-south oriented limestone mortuary temple was built on a strip of platform originally intended for the casing of the pyramid. It is unclear who constructed this initial phase of the temple, though cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hathor
Hathor ( egy, ḥwt-ḥr, lit=House of Horus, grc, Ἁθώρ , cop, ϩⲁⲑⲱⲣ, Meroitic: ) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sky god Horus and the sun god Ra, both of whom were connected with kingship, and thus she was the symbolic mother of their earthly representatives, the pharaohs. She was one of several goddesses who acted as the Eye of Ra, Ra's feminine counterpart, and in this form she had a vengeful aspect that protected him from his enemies. Her beneficent side represented music, dance, joy, love, sexuality, and maternal care, and she acted as the consort of several male deities and the mother of their sons. These two aspects of the goddess exemplified the Egyptian conception of femininity. Hathor crossed boundaries between worlds, helping deceased souls in the transition to the afterlife. Hathor was often depicted as a cow, symbolizing her maternal a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpentine Subgroup
Serpentine subgroup (part of the kaolinite-serpentine group in the category of phyllosilicates) are greenish, brownish, or spotted minerals commonly found in serpentinite. They are used as a source of magnesium and asbestos, and as decorative stone. The name comes from the greenish colour and smooth or scaly appearance from the Latin , meaning "serpent rock". Serpentine subgroup is a set of common rock-forming hydrous magnesium iron phyllosilicate () minerals, resulting from the metamorphism of the minerals that are contained in mafic to ultramafic rocks. They may contain minor amounts of other elements including chromium, manganese, cobalt or nickel. In mineralogy and gemology, serpentine may refer to any of the 20 varieties belonging to the serpentine subgroup. Owing to admixture, these varieties are not always easy to individualize, and distinctions are not usually made. There are three important mineral polymorphs of serpentine: antigorite, lizardite and chrysotile. Serpen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairo Museum
The Museum of Egyptian Antiquities, known commonly as the Egyptian Museum or the Cairo Museum, in Cairo, Egypt, is home to an extensive collection of ancient Egyptian antiquities. It has 120,000 items, with a representative amount on display and the remainder in storerooms. Built in 1901 by the Italian construction company, Garozzo-Zaffarani, to a design by the French architect Marcel Dourgnon, the edifice is one of the largest museums in the region. As of March 2019, the museum was open to the public. In 2022, the museum is due to be superseded by the newer and larger Grand Egyptian Museum at Giza. History The Egyptian Museum of Antiquities contains many important pieces of ancient Egyptian history. It houses the world's largest collection of Pharaonic antiquities. The Egyptian government established the museum built in 1835 near the Ezbekieh Garden and later moved to the Cairo Citadel. In 1855, Archduke Maximilian of Austria was given all of the artifacts by the Egyptia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder Seal
A cylinder seal is a small round cylinder, typically about one inch (2 to 3 cm) in length, engraved with written characters or figurative scenes or both, used in ancient times to roll an impression onto a two-dimensional surface, generally wet clay. According to some sources, cylinder seals were invented around 3500 BC in the Near East, at the contemporary sites of Uruk in southern Mesopotamia and slightly later at Susa in south-western Iran during the Proto-Elamite period, and they follow the development of stamp seals in the Halaf culture or slightly earlier. They are linked to the invention of the latter's cuneiform writing on clay tablets. Other sources, however, date the earliest cylinder seals to a much earlier time, to the Late Neolithic period (7600-6000 BC), hundreds of years before the invention of writing. Cylinder seals are a form of impression seal, a category which includes the stamp seal and finger ring seal. They survive in fairly large numbers and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memphis, Egypt
, alternate_name = , image = , alt = , caption = Ruins of the pillared hall of Ramesses IIat Mit Rahina , map_type = Egypt#Africa , map_alt = , map_size = , relief = , coordinates = , location = Mit Rahina, Giza Governorate, Egypt , region = Lower Egypt , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = Unknown, was already in existence during Iry-Hor's reignP. Tallet, D. Laisnay: ''Iry-Hor et Narmer au Sud-Sinaï (Ouadi 'Ameyra), un complément à la chronologie des expéditios minière égyptiene'', in: BIFAO 112 (2012), 381–395available online/ref> , material = , built = Earlier than 31st century BC , abandoned = 7th century AD , epochs = Early Dynastic Period to Early Middle Ages , cultures = , dependency_of = , occupants = , event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.png)



