|
Shahed-136
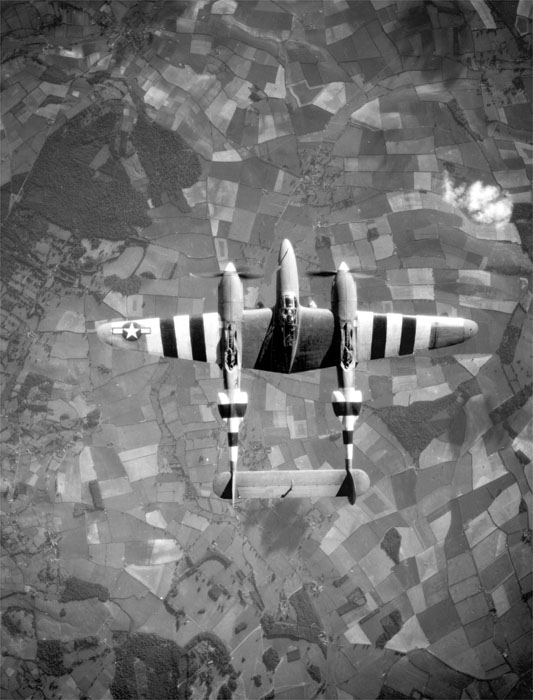
The HESA Shahed 136 ( fa, شاهد ۱۳۶, literally "Witness-136"), or Geran-2 in Russian service, is an Iranian loitering munition in the form of an autonomous pusher-prop drone. It is designed and manufactured by Shahed Aviation Industries. The munition is designed to attack ground targets from a distance, fired in multiples from a launch rack (in batches of five upwards) to overwhelm air defenses by consuming their resources during the attack. The first public footage of the drone were released in December 2021. Overview Description The aircraft has a cropped delta-wing shape, with a central fuselage blending into the wings and stabilizing rudders at the tips. The nose section contains a warhead estimated to weigh . The engine sits in the rear of the fuselage and drives a two-bladed propeller in a "pusher" arrangement. The munition is long with a wingspan of , flies at over , and weighs about . The range has been estimated as between usable in a pre-programmed dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahed 131
The Shahed 131, or Geran-1 in Russian service, is an Iranian-made drone which came to prominence in October 2022 during the Russian invasion of Ukraine. It is powered by a Wankel engine model Shahed-783/788. Janes created an in-depth technical summary of the machine. Design The Shahed-131 is powered by the Serat-1 Wankel engine, which is a copy of the Beijing Micropilot UAV Control System Ltd MDR-208 Wankel engine. An engine of this type was used for the drone in the 2019 Aramco attack in Abqaiq, which was referred to the UN Secretariat as part of the Resolution 2231 2020 investigations. The Shahed-131 flight control unit was found to be able to connect with Iridium satellites, which in theory allows the flight path to be altered mid flight. The flight controller has a backup inertial navigation system by MEMS gyroscope. Its primary instructions are derived from a commercial-grade GPS unit. Designs for the Kentron ARD-10 loitering drone were sold to Iran Aviation Industrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limbach L550E
The Limbach L550E is a German aircraft engine, designed and produced by Limbach Flugmotoren of Königswinter.Bayerl, Robby; Martin Berkemeier; et al: ''World Directory of Leisure Aviation 2011-12'', pages 240-241. WDLA UK, Lancaster UK, 2011. ISSN 1368-485X Design and development The L550E is an air-cooled horizontally-opposed four-cylinder two-stroke gasoline engine developing at 7500 rpm which can drive a propeller either directly or geared. It employs a single magneto ignition, four carburettors, and is lubricated by oil mixture lubrication with a fuel to oil ratio of 25:1 for mineral oil or 50:1 for synthetic oil. Iranian copy Since at least 2014, the Iranian firm Mado has marketed a copy of the L550E. The Mado variant is used for the Iranian Shahed-136 The HESA Shahed 136 ( fa, شاهد ۱۳۶, literally "Witness-136"), or Geran-2 in Russian service, is an Iranian loitering munition in the form of an autonomous pusher-prop drone. It is designed and manufactured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loitering Munition
A loitering munition (also known as a suicide droneLoitering Munitions – In Focus Center for the Study of the Drone, Feb 2017 or drone) is an aerial weapon system category in which the loiters (waits passively) around the target area for some time and attacks only once a target is located. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Reconnaissance
Aerial reconnaissance is reconnaissance for a military or strategic purpose that is conducted using reconnaissance aircraft. The role of reconnaissance can fulfil a variety of requirements including artillery spotting, the collection of imagery intelligence, and the observation of enemy maneuvers. History Early developments After the French Revolution, the new rulers became interested in using the balloon to observe enemy manoeuvres and appointed scientist Charles Coutelle to conduct studies using the balloon ''L'Entreprenant'', the first military reconnaissance aircraft. The balloon found its first use in the 1794 conflict with Austria, where in the Battle of Fleurus they gathered information. Moreover, the presence of the balloon had a demoralizing effect on the Austrian troops, which improved the likelihood of victory for the French troops. To operate such balloons, a new unit of the French military, the French Aerostatic Corps, was established; this organisatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Navigation System
An inertial navigation system (INS) is a navigation device that uses motion sensors (accelerometers), rotation sensors ( gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning the position, the orientation, and the velocity (direction and speed of movement) of a moving object without the need for external references. Often the inertial sensors are supplemented by a barometric altimeter and sometimes by magnetic sensors ( magnetometers) and/or speed measuring devices. INSs are used on mobile robots and on vehicles such as ships, aircraft, submarines, guided missiles, and spacecraft. Other terms used to refer to inertial navigation systems or closely related devices include inertial guidance system, inertial instrument, inertial measurement unit (IMU) and many other variations. Older INS systems generally used an inertial platform as their mounting point to the vehicle and the terms are sometimes considered synonymous. Overview Inertial navigation is a self-cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TI Fluid Systems
TI Fluid Systems is a British multinational company which develops, manufactures and supplies automotive fluid storage, carrying and delivery systems. The company serves the automotive aftermarket through Bundy, Walbro and Marwal brands. The company's headquarters are located in Oxford, England, with Corporate Offices based in Auburn Hills, Michigan, U.S. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index. History The company traces its history back to the Bundy Corporation, which was founded in 1922 and supplied petroleum fuel lines to the Ford Model T. It was acquired by TI Group plc in 1988. After Smiths Group acquired TI Group in 2000, Smiths Group transferred its newly acquired automotive business into a corporate entity in 2001 thereby creating TI Automotive. In 2007, the company was acquired by a consortium of private equity investors. The company was forced to go through a debt-to-equity swap in 2009 following the global economic down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
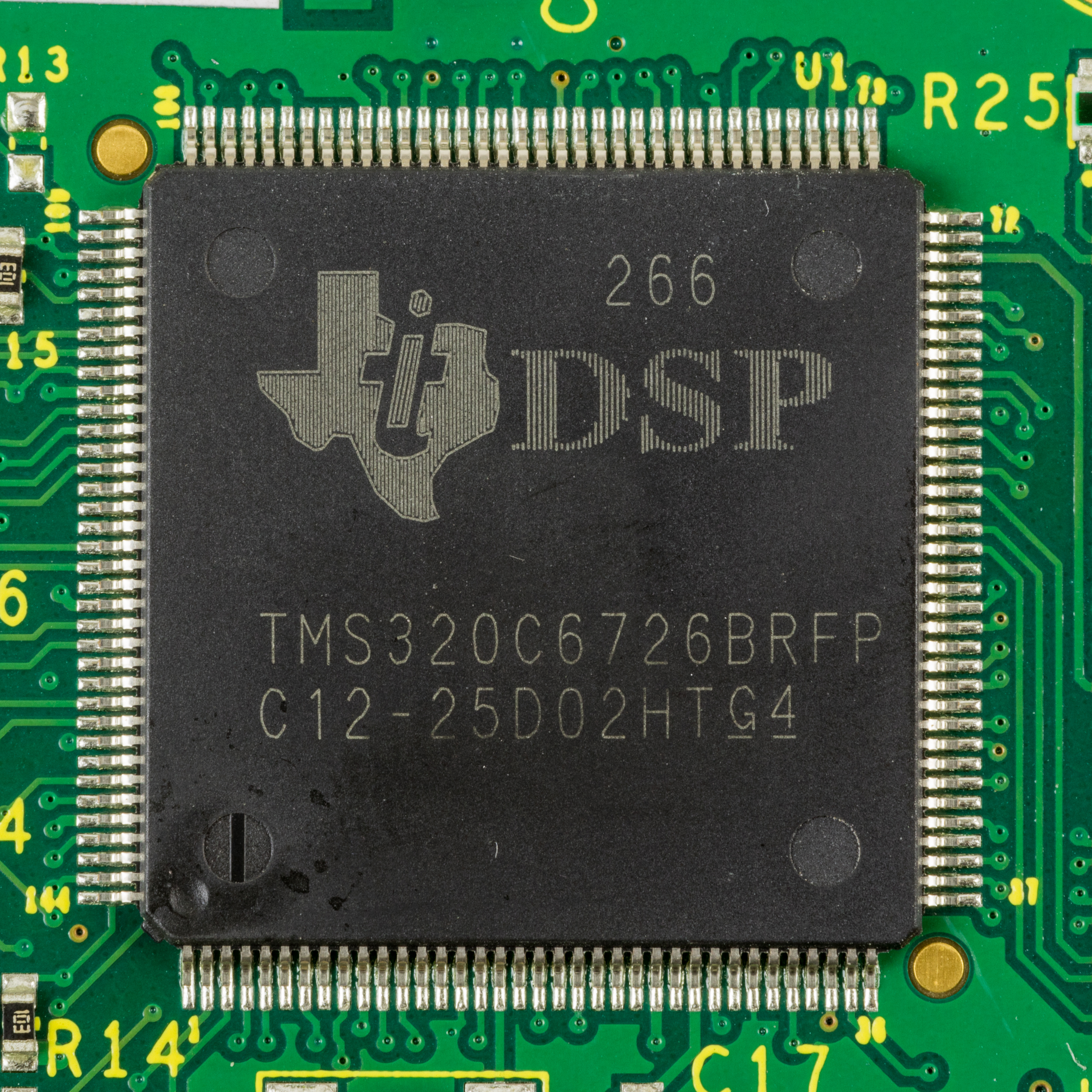
Texas Instruments TMS320
Texas Instruments TMS320 is a blanket name for a series of digital signal processors (DSPs) from Texas Instruments. It was introduced on April 8, 1983 through the TMS32010 processor, which was then the fastest DSP on the market. The processor is available in many different variants, some with fixed-point arithmetic and some with floating point arithmetic. The TMS320 processors were fabricated on MOS integrated circuit chips, including both NMOS and CMOS variants. The floating point DSP TMS320C3x, which exploits delayed branch logic, has as many as three delay slots. The flexibility of this line of processors has led to it being used not merely as a co-processor for digital signal processing but also as a main CPU. Newer implementations support standard IEEE JTAG control for boundary scan and/or in-circuit debugging. The original TMS32010 and its subsequent variants is an example of a CPU with a modified Harvard architecture, which features separate address spaces for instruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microchip Technology
Microchip Technology Inc. is a publicly-listed American corporation that manufactures microcontroller, mixed-signal, analog and Flash-IP integrated circuits. Its products include microcontrollers ( PIC, dsPIC, AVR and SAM), Serial EEPROM devices, Serial SRAM devices, embedded security devices, radio frequency (RF) devices, thermal, power and battery management analog devices, as well as linear, interface and wireless products. Its corporate headquarters is located in Chandler, Arizona. Its wafer fabs are located in Tempe, Arizona, Gresham, Oregon, and Colorado Springs, Colorado. Its assembly/test facilities are in Chachoengsao, Thailand, and Calamba and Cabuyao, Philippines. Sales for the fiscal year ending on March 31, 2019 were $5.35 billion. Microchip Technology offers support and reso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-dropout Regulator
A low-dropout regulator (LDO regulator) is a DC linear voltage regulator that can regulate the output voltage even when the supply voltage is very close to the output voltage. The advantages of an LDO regulator over other DC-to-DC voltage regulators include the absence of switching noise (as no switching takes place), smaller device size (as neither large inductors nor transformers are needed), and greater design simplicity (usually consists of a reference, an amplifier, and a pass element). The disadvantage is that, unlike switching regulators, linear DC regulators must dissipate power, and thus heat, across the regulation device in order to regulate the output voltage. History The adjustable low-dropout regulator debuted on April 12, 1977 in an ''Electronic Design'' article entitled "''Break Loose from Fixed IC Regulators''". The article was written by Robert Dobkin, an IC designer then working for National Semiconductor. Because of this, National Semiconductor claims the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Devices
Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI), also known simply as Analog, is an American multinational semiconductor company specializing in data conversion, signal processing and power management technology, headquartered in Wilmington, Massachusetts. The company manufactures analog, mixed-signal and digital signal processing (DSP) integrated circuits (ICs) used in electronic equipment. These technologies are used to convert, condition and process real-world phenomena, such as light, sound, temperature, motion, and pressure into electrical signals. Analog Devices has approximately 100,000 customers in the following industries: communications, computer, instrumentation, military/aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics applications.Bloomberg.ADI: Analog Devices Inc Summary" Retrieved January 30, 2011. History The company was founded by two MIT graduates, Ray Stata and Matthew Lorber in 1965. The same year, the company released its first product, the model 101 op amp,Richard Wilson, El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RF Module
An RF module (short for radio-frequency module) is a (usually) small electronic device used to transmit and/or receive radio signals between two devices. In an embedded system it is often desirable to communicate with another device wirelessly. This wireless communication may be accomplished through optical communication or through radio-frequency (RF) communication. For many applications, the medium of choice is RF since it does not require line of sight. RF communications incorporate a transmitter and a receiver. They are of various types and ranges. Some can transmit up to 500 feet. RF modules are typically fabricated using RF CMOS technology. RF modules are widely used in electronic design owing to the difficulty of designing radio circuitry. Good electronic radio design is notoriously complex because of the sensitivity of radio circuits and the accuracy of components and layouts required to achieve operation on a specific frequency. In addition, reliable RF communication cir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altera
Altera Corporation was a manufacturer of programmable logic devices (PLDs) headquartered in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1983 and acquired by Intel in 2015. The main product lines from Altera were the flagship Stratix series, mid-range Arria series, and lower-cost Cyclone series system on a chip field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs); the MAX series complex programmable logic device and non-volatile FPGAs; Quartus design software; and Enpirion PowerSoC DC-DC power solutions. The company was founded in 1983 by semiconductor veterans Rodney Smith, Robert Hartmann, James Sansbury, and Paul Newhagen with $500,000 in seed money. The name of the company was a play on "alterable", the type of chips the company created. In 1984, the company formed a long-running design partnership with Intel, and 1988, became a public company via an initial public offering. In 1994, Altera acquired the PLD business of Intel for $50 million. On December 28, 2015, the company was acquired by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_Cyclone_III_(cropped).jpg)