RF Module on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
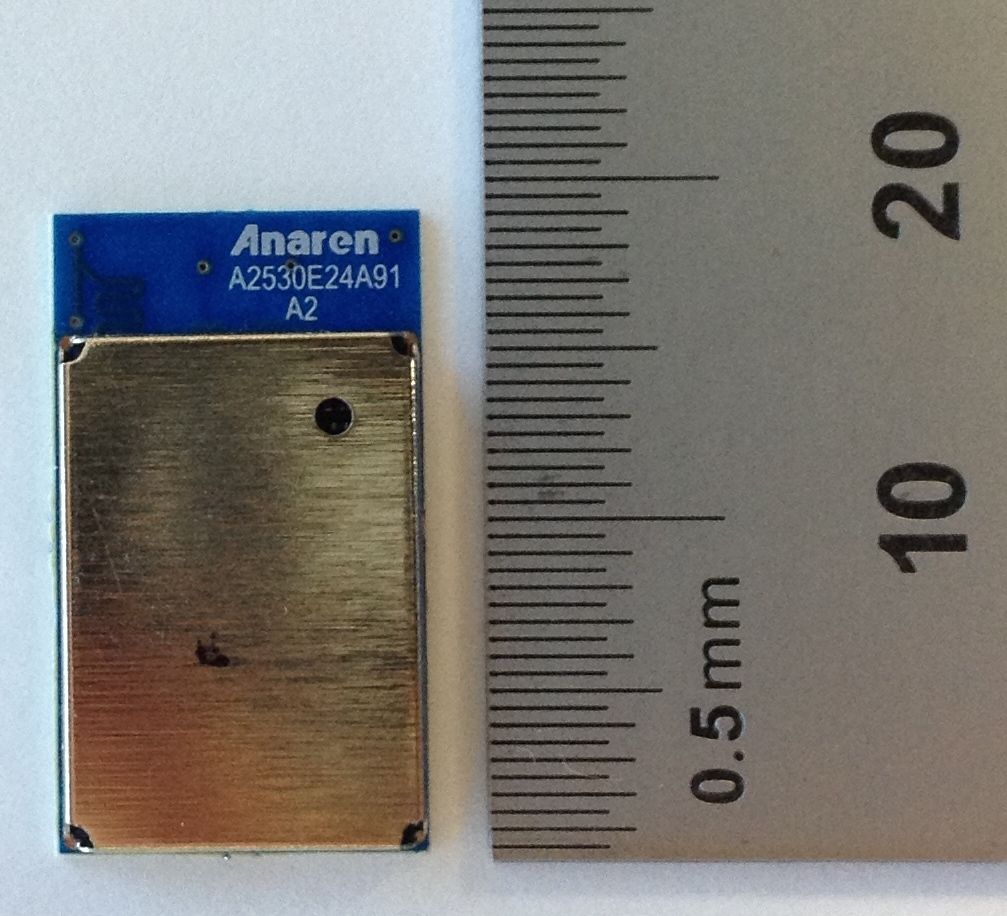 An RF module (short for radio-frequency module) is a (usually) small electronic device used to transmit and/or receive radio signals between two devices. In an
An RF module (short for radio-frequency module) is a (usually) small electronic device used to transmit and/or receive radio signals between two devices. In an
 A variety of methods are used to attach an RF module to a
A variety of methods are used to attach an RF module to a
FCCCEANATEL
etc.) does hardly ever cover the final product. However, this does not mean that full compliance testing is required when integrating a compliant RF module. Integrating a compliant module has a lot of advantages. The RF module is essential in this day’s consumer product but also only a part of the final product. Radio modules have evolved during the years. Onboard voltage regulators, integrated antenna generally try to ensure that the radio phenomena stay the same no matter of their host. You can refer to most RF spectrum measurements on a modular level for compliance when testing and certifying your product at an ISO 17025 accredited EMC, RF laboratory. At the end it is the final product that needs to comply with the regulations. Aspects as health, safety, Radiated susceptibility can not be covered on a modular level.
 An RF module (short for radio-frequency module) is a (usually) small electronic device used to transmit and/or receive radio signals between two devices. In an
An RF module (short for radio-frequency module) is a (usually) small electronic device used to transmit and/or receive radio signals between two devices. In an embedded system
An embedded system is a computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is ''embedded'' as ...
it is often desirable to communicate with another device wireless
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most ...
ly. This wireless communication may be accomplished through optical communication
Optical communication, also known as optical telecommunication, is communication at a distance using light to carry information. It can be performed visually or by using electronic devices. The earliest basic forms of optical communication date b ...
or through radio-frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the upp ...
(RF) communication. For many applications, the medium of choice is RF since it does not require line of sight. RF communications incorporate a transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna (radio), antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which i ...
and a receiver. They are of various types and ranges. Some can transmit up to 500 feet. RF modules are typically fabricated using RF CMOS
RF CMOS is a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) technology that integrates radio-frequency (RF), analog and digital electronics on a mixed-signal CMOS (complementary MOS) RF circuit chip. It is widely used in modern wire ...
technology.
RF modules are widely used in electronic design owing to the difficulty of designing radio circuitry. Good electronic radio design is notoriously complex because of the sensitivity of radio circuits and the accuracy of components and layouts required to achieve operation on a specific frequency. In addition, reliable RF communication circuit requires careful monitoring of the manufacturing process to ensure that the RF performance is not adversely affected. Finally, radio circuits are usually subject to limits on radiated emissions, and require Conformance testing
Conformance testing — an element of conformity assessment, and also known as compliance testing, or type testing — is testing or other activities that determine whether a process, product, or service complies with the requirements of a specifi ...
and certification by a standardization
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization ...
organization such as ETSI
The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) is an independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the field of information and communications. ETSI supports the development and testing of global technical standard ...
or the U.S. Federal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains jurisdiction ...
(FCC). For these reasons, design engineers will often design a circuit for an application which requires radio communication and then "drop in" a pre-made radio module rather than attempt a discrete
Discrete may refer to:
*Discrete particle or quantum in physics, for example in quantum theory
* Discrete device, an electronic component with just one circuit element, either passive or active, other than an integrated circuit
*Discrete group, a ...
design, saving time and money on development.
RF modules are most often used in medium and low volume products for consumer applications such as garage door openers, wireless alarm or monitoring systems, industrial remote controls, smart sensor applications, and wireless home automation systems. They are sometimes used to replace older infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
communication designs as they have the advantage of not requiring line-of-sight operation.
Several carrier frequencies are commonly used in commercially available RF modules, including those in the industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) radio bands such as 433.92 MHz, 915 MHz, and 2400 MHz. These frequencies are used because of national and international regulations governing the used of radio for communication. Short Range Devices
A short-range device (SRD), described by ECC Recommendation 70-03, is a radio-frequency transmitter device used in telecommunication for the transmission of information, which has low capability of causing harmful interference to other radio e ...
may also use frequencies available for unlicensed such as 315 MHz and 868 MHz.
RF modules may comply with a defined protocol for RF communications such as Zigbee
Zigbee is an IEEE 802.15.4-based specification for a suite of high-level communication protocols used to create personal area networks with small, low-power digital radios, such as for home automation, medical device data collection, and othe ...
, Bluetooth Low Energy
Bluetooth Low Energy (Bluetooth LE, colloquially BLE, formerly marketed as Bluetooth Smart) is a wireless personal area network technology designed and marketed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (Bluetooth SIG) aimed at novel applications in ...
, or Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio wave ...
, or they may implement a proprietary protocol
In telecommunications, a proprietary protocol is a communications protocol owned by a single organization or individual.
Intellectual property rights and enforcement
Ownership by a single organization gives the owner the ability to place restricti ...
.
Types of RF modules
The term RF module can be applied to many different types, shapes and sizes of small electronic sub assemblycircuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in Electrical engineering, electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a L ...
. It can also be applied to modules across a huge variation of functionality and capability. RF modules typically incorporate a printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in Electrical engineering, electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a L ...
, transmit or receive circuit, antenna
Antenna ( antennas or antennae) may refer to:
Science and engineering
* Antenna (radio), also known as an aerial, a transducer designed to transmit or receive electromagnetic (e.g., TV or radio) waves
* Antennae Galaxies, the name of two collid ...
, and serial interface
In computing, a serial port is a serial communication interface through which information transfers in or out sequentially one bit at a time. This is in contrast to a parallel port, which communicates multiple bits simultaneously in parallel. T ...
for communication to the host processor.
Most standard, well known types are covered here:
* transmitter module
* receiver module
* transceiver module
* system on a chip
A system on a chip or system-on-chip (SoC ; pl. ''SoCs'' ) is an integrated circuit that integrates most or all components of a computer or other electronic system. These components almost always include a central processing unit (CPU), memory ...
module.
Transmitter modules
An RF transmitter module is a small PCB sub-assembly capable of transmitting a radio wave and modulating that wave to carry data. Transmitter modules are usually implemented alongside amicrocontroller
A microcontroller (MCU for ''microcontroller unit'', often also MC, UC, or μC) is a small computer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable i ...
which will provide data to the module which can be transmitted. RF transmitters are usually subject to regulatory requirements which dictate the maximum allowable transmitter power output In radio transmission, transmitter power output (TPO) is the actual amount of power (in watts) of radio frequency (RF) energy that a transmitter produces at its output.
This is not the amount of power that a radio station reports as its power, as i ...
, harmonics
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', the ...
, and band edge requirements.
Receiver modules
An RF receiver module receives the modulated RF signal, and demodulates it. There are two types of RF receiver modules:superheterodyne receiver
A superheterodyne receiver, often shortened to superhet, is a type of radio receiver that uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original carr ...
s and superregenerative receivers. Superregenerative modules are usually low cost and low power designs using a series of amplifiers to extract modulated data from a carrier wave. Superregenerative modules are generally imprecise as their frequency of operation varies considerably with temperature and power supply voltage. Superheterodyne receivers have a performance advantage over superregenerative; they offer increased accuracy and stability over a large voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to m ...
and temperature range. This stability comes from a fixed crystal design which in the past tended to mean a comparatively more expensive product. However, advances in receiver chip design now mean that currently there is little price difference between superheterodyne and superregenerative receiver modules.
Transceiver modules
An RF transceiver module incorporates both a transmitter and receiver. The circuit is typically designed forhalf-duplex
A duplex communication system is a point-to-point system composed of two or more connected parties or devices that can communicate with one another in both directions. Duplex systems are employed in many communications networks, either to allow ...
operation, although full-duplex
A duplex communication system is a point-to-point system composed of two or more connected parties or devices that can communicate with one another in both directions. Duplex systems are employed in many communications networks, either to allow ...
modules are available, typically at a higher cost due to the added complexity.
System on a chip (SoC) module
An SoC module is the same as a transceiver module, but it is often made with an onboard microcontroller. The microcontroller is typically used to handle radio data packetisation or managing a protocol such as an IEEE 802.15.4 compliant module. This type of module is typically used for designs that require additional processing for compliance with a protocol when the designer does not wish to incorporate this processing into the host microcontroller.Host microcontroller interface
RF modules typically communicate with an embedded system, such as a microcontroller or a microprocessor. The communication protocols includeUART
A universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter (UART ) is a computer hardware device for asynchronous serial communication in which the data format and transmission speeds are configurable. It sends data bits one by one, from the least significan ...
, used in Digi International
Digi International is an American Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technology company headquartered in Hopkins, Minnesota. The company was founded in 1985 and went public as Digi International in 1989. The company initially offered intelligen ...
's X-Bee modules, Serial Peripheral Interface Bus
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a synchronous serial communication interface specification used for short-distance communication, primarily in embedded systems. The interface was developed by Motorola in the mid-1980s and has become a ...
used in Anaren's AIR modules and Universal Serial Bus
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard that establishes specifications for cables, connectors and protocols for connection, communication and power supply (interfacing) between computers, peripherals and other computers. A broad ...
used in Roving Networks' modules. Although the module may use a standardized protocol for wireless communication, the commands sent over the microcontroller interface are typically not standardized as each vendor has its own proprietary communications format. The speed of the microcontroller interface depends on the speed of the underlying RF protocol used: higher speed RF protocols such as Wi-Fi require a high-speed serial interface such as USB whereas protocols with a slower data rate such as Bluetooth Low Energy may use a UART interface.
RF signal modulation
There are several types of digital signal modulation methods commonly used in RF transmitter and receiver modules: *ASK
Ask is the active verb for a direct question.
Ask may also refer to:
Places
* Ask, Akershus, a village in Gjerdrum municipality, Viken county, Norway
* Ask, Buskerud, a village in Ringerike municipality, Viken county, Norway
* Ask, Vestland, a ...
* OOK
Ook, OoK or OOK may refer to:
* Ook Chung (born 1963), Korean-Canadian writer from Quebec
* On-off keying, in radio technology
* Toksook Bay Airport (IATA code OOK), in Alaska
* Ook!, an esoteric programming language based on Brainfuck
* Ook, th ...
* FSK FSK may refer to:
* FSK (band), a German band
* Federal Counterintelligence Service, (Russian ') of Russia
* Fiskerton railway station, in England
* Forskolin, a diterpene
* Forsvarets Spesialkommando, a Norwegian special forces unit
* Fort Scott M ...
* direct-sequence spread spectrum
In telecommunications, direct-sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) is a spread-spectrum modulation technique primarily used to reduce overall signal interference. The direct-sequence modulation makes the transmitted signal wider in bandwidth than t ...
* frequency-hopping spread spectrum
Frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) is a method of transmitting radio signals by rapidly changing the carrier frequency among many distinct frequencies occupying a large spectral band. The changes are controlled by a code known to both tra ...
.
The detailed description, advantages and disadvantages are listed in the linked articles above.
Main factors affecting RF module performance
As with any other RF device, the performance of an RF module will depend on a number of factors. For example, by increasing the transmitter power, a larger communication distance will be achieved. However, this will also result in a higher electrical power drain on the transmitter device, which will cause shorter operating life for battery powered devices. Also, using a higher transmit power will make the system more prone to interference with other RF devices, and may in fact possibly cause the device to become illegal depending on the jurisdiction. Correspondingly, increasing the receiver sensitivity will also increase the effective communication range, but will also potentially cause malfunction due to interference from other RF devices. The performance of the overall system may be improved by using matched antennas at each end of the communication link, such as those described earlier. Finally, the labeled remote distance of any particular system is normally measured in an open-air line of sight configuration without any interference, but often there will be obstacles such as walls, floors, or dense construction to absorb the radio wave signals, so the effective operational distance will in most practical instances be less than specified.Module physical connection
 A variety of methods are used to attach an RF module to a
A variety of methods are used to attach an RF module to a printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in Electrical engineering, electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a L ...
, either with through-hole technology
In electronics, through-hole technology (also spelled "thru-hole") is a manufacturing scheme in which leads on the components are inserted through holes drilled in printed circuit boards (PCB) and soldered to pads on the opposite side, either by ...
or surface-mount technology
Surface-mount technology (SMT), originally called planar mounting, is a method in which the electrical components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). An electrical component mounted in this manner is referred ...
. Through-hole technology allows the module to be inserted or removed without soldering. Surface-mount technology allows the module to be attached to the PCB without an additional assembly step. Surface-mount connections used in RF modules include land grid array
The land grid array (LGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits (ICs) that is notable for having the pins on the socket (when a socket is used) rather than the integrated circuit. An LGA can be electrically connected to a ...
(LGA) and castellated pads. The LGA package allows for small module sizes as the pads are all beneath the module but connections must be X-rayed to verify connectivity. Castellated Holes enable optical inspection of the connection but will make the module footprint physically larger to accommodate the pads.
Wireless protocols used in RF modules
RF modules, especially SoC modules, are frequently used to communicate according to a pre-defined wireless standard, including: *Zigbee
Zigbee is an IEEE 802.15.4-based specification for a suite of high-level communication protocols used to create personal area networks with small, low-power digital radios, such as for home automation, medical device data collection, and othe ...
* Bluetooth Low Energy
Bluetooth Low Energy (Bluetooth LE, colloquially BLE, formerly marketed as Bluetooth Smart) is a wireless personal area network technology designed and marketed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (Bluetooth SIG) aimed at novel applications in ...
* Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio wave ...
* IEEE 802.15.4
IEEE 802.15.4 is a technical standard which defines the operation of a low-rate wireless personal area network (LR-WPAN). It specifies the physical layer and media access control for LR-WPANs, and is maintained by the IEEE 802.15 working group, ...
* Z-Wave
Z-Wave is a wireless communications protocol used primarily for residential and commercial building automation. It is a mesh network using low-energy radio waves to communicate from device to device, allowing for wireless control of smart home d ...
However, RF modules also frequently communicate using proprietary protocols, such as those used in garage door openers.
Typical applications
* Vehicle monitoring *Remote control
In electronics, a remote control (also known as a remote or clicker) is an electronic device used to operate another device from a distance, usually wirelessly. In consumer electronics, a remote control can be used to operate devices such as ...
* Telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ data collection, collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic data transmission, transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Gr ...
* Small-range wireless network
* Wireless meter reading
* Access control systems
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial c ...
* Wireless home security systems
* Area paging
* Industrial data acquisition system
* Radio tags reading
* RF contactless smart cards
* Wireless data terminals
* Wireless fire protection systems
* Biological signal acquisition
* Hydrological and meteorological monitoring
* Robot remote control
* Wireless data transmissions
* Digital video
Digital video is an electronic representation of moving visual images (video) in the form of encoded digital data. This is in contrast to analog video, which represents moving visual images in the form of analog signals. Digital video comprises ...
/audio transmission
* Digital home automation, such as remote light/switch
* Industrial remote control, telemetry and remote sensing
* Alarm systems and wireless transmission for various types of low-rate digital signal
* Remote control for various types of household appliances
A major appliance, also known as a large domestic appliance or large electric appliance or simply a large appliance, large domestic, or large electric, is a non-portable or semi-portable machine used for routine housekeeping tasks such as cookin ...
and electronics projects
* Many other applications field related to RF wireless controlling
* Mobile web server
A Mobile Web Server is software designed for modern-day smartphones to host personal web servers, through the use of open sourced software, such as, i-jetty, an open source software, based on jetty. I-jetty is an open source web container, serv ...
for elderly people monitoring
RF module certification in case of final product integration
Final regulatory product compliance based on an integrated, compliant RF module (as most IoT devices these day's) is a common misunderstanding. A module compliant to the essential requirements of the countries regulationFCC
etc.) does hardly ever cover the final product. However, this does not mean that full compliance testing is required when integrating a compliant RF module. Integrating a compliant module has a lot of advantages. The RF module is essential in this day’s consumer product but also only a part of the final product. Radio modules have evolved during the years. Onboard voltage regulators, integrated antenna generally try to ensure that the radio phenomena stay the same no matter of their host. You can refer to most RF spectrum measurements on a modular level for compliance when testing and certifying your product at an ISO 17025 accredited EMC, RF laboratory. At the end it is the final product that needs to comply with the regulations. Aspects as health, safety, Radiated susceptibility can not be covered on a modular level.
External links
* *{{cite book, last = Fairall, first = John, title = An Introduction to low power radio, url = http://www.rfsolutions.co.uk/acatalog/info_BK_RADIOINTRO.html, year = 2002, publisher = RF Solutions Ltd, isbn = 978-0-9537231-0-2 Remote control