|
Serratus Anterior
The serratus anterior is a muscle that originates on the surface of the 1st to 8th ribs at the side of the chest and inserts along the entire anterior length of the medial border of the scapula. The serratus anterior acts to pull the scapula forward around the thorax. The muscle is named from Latin: ''serrare'' = to saw, referring to the shape, ''anterior'' = on the front side of the body. Structure Serratus anterior normally originates by nine or ten muscle slips – branches from either the first to ninth ribs or the first to eighth ribs. Because two slips usually arise from the second rib, the number of slips is greater than the number of ribs from which they originate. The muscle is inserted along the medial border of the scapula between the superior and inferior angles along with being inserted along the thoracic vertebrae. The muscle is divided into three named parts depending on their points of insertions: #the serratus anterior superior is inserted near the superior a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectoralis Major
The pectoralis major () is a thick, fan-shaped or triangular convergent muscle, situated at the chest of the human body. It makes up the bulk of the chest muscles and lies under the breast. Beneath the pectoralis major is the pectoralis minor, a thin, triangular muscle. The pectoralis major's primary functions are flexion, adduction, and internal rotation of the humerus. The pectoral major may colloquially be referred to as "pecs", "pectoral muscle", or "chest muscle", because it is the largest and most superficial muscle in the chest area. Structure It arises from the anterior surface of the sternal half of the clavicle from breadth of the half of the anterior surface of the sternum, as low down as the attachment of the cartilage of the sixth or seventh rib; from the cartilages of all the true ribs, with the exception, frequently, of the first or seventh, and from the aponeurosis of the abdominal external oblique muscle. From this extensive origin the fibers converge toward the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synergist Muscle
Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle such as their actions, structure, size, and location. Types There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle, or "voluntary muscle", is a striated muscle tissue that primarily joins to bone with tendons. Skeletal muscle enables movement of bones, and maintains posture. The widest part of a muscle that pulls on the tendons is known as the belly. Muscle slip A muscle slip is a slip of muscle that can either be an anatomical variant, or a branching of a muscle as in rib connections of the serratus anterior muscle. Smooth muscle Smooth muscle is involuntary and found in parts of the body where it conveys action without conscious intent. The majority of this type of muscle tissue is found in the digestive and urinary systems where it acts by propelling forward food, chyme, and feces in the former and ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chest
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments. The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures. Many diseases may affect the chest, and one of the most common symptoms is chest pain. Etymology The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ ''thorax'' "breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via la, thorax. Plural: ''thoraces'' or ''thoraxes''. Human thorax Structure In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. It is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, spine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrupedalism
Quadrupedalism is a form of locomotion where four limbs are used to bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four limbs is said to be a quadruped (from Latin ''quattuor'' for "four", and ''pes'', ''pedis'' for "foot"). Quadruped animals are found among both vertebrates and invertebrates. Quadrupeds vs. tetrapods Although the words ‘quadruped’ and ‘tetrapod’ are both derived from terms meaning ‘four-footed’, they have distinct meanings. A tetrapod is any member of the taxonomic unit Tetrapoda (which is defined by descent from a specific four-limbed ancestor), whereas a quadruped actually uses four limbs for locomotion. Not all tetrapods are quadrupeds and not all entities that could be described as ‘quadrupedal’ are tetrapods. This last meaning includes certain artificial objects; almost all quadruped ''organisms'' are tetrapods (with the exception of some raptorial arthropods adapted fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cursorial
A cursorial organism is one that is adapted specifically to run. An animal can be considered cursorial if it has the ability to run fast (e.g. cheetah) or if it can keep a constant speed for a long distance (high endurance). "Cursorial" is often used to categorize a certain locomotor mode, which is helpful for biologists who examine behaviors of different animals and the way they move in their environment. Cursorial adaptations can be identified by morphological characteristics (e.g. loss of lateral digits as in ungulate species), physiological characteristics, maximum speed, and how often running is used in life. There is much debate over how to define a cursorial animal specifically. The most accepted definitions include that a cursorial organism could be considered adapted to long-distance running at high speeds or has the ability to accelerate quickly over short distances. Among vertebrates, animals under 1 kg of mass are rarely considered cursorial, and cursorial behaviors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
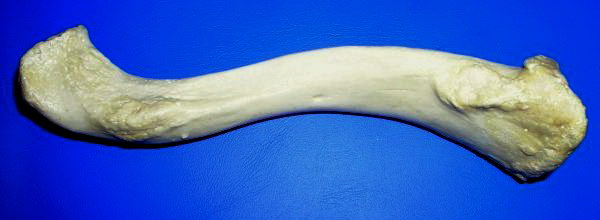
Clavicle
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from the Latin ''clavicula'' ("little key"), because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the arm to the trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it acts as a strut to k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenoid Cavity
The glenoid fossa of the scapula or the glenoid cavity is a bone part of the shoulder. The word ''glenoid'' is pronounced or (both are common) and is from el, gléne, "socket", reflecting the shoulder joint's ball-and-socket form. It is a shallow, pyriform articular surface, which is located on the lateral angle of the scapula. It is directed laterally and forward and articulates with the head of the humerus; it is broader below than above and its vertical diameter is the longest. This cavity forms the glenohumeral joint along with the humerus. This type of joint is classified as a synovial, ball and socket joint. The humerus is held in place within the glenoid cavity by means of the long head of the biceps tendon. This tendon originates on the superior margin of the glenoid cavity and loops over the shoulder, bracing humerus against the cavity. The rotator cuff also reinforces this joint more specifically with the supraspinatus tendon to hold the head of the humerus in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including humans). Primates arose 85–55 million years ago first from small terrestrial mammals, which adapted to living in the trees of tropical forests: many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging environment, including large brains, visual acuity, color vision, a shoulder girdle allowing a large degree of movement in the shoulder joint, and dextrous hands. Primates range in size from Madame Berthe's mouse lemur, which weighs , to the eastern gorilla, weighing over . There are 376–524 species of living primates, depending on which classification is used. New primate species continue to be discovered: over 25 species were described in the 2000s, 36 in the 2010s, and three in the 2020s. Primates have large bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winged Scapula
A winged scapula (scapula alata) is a skeletal medical condition in which the shoulder blade protrudes from a person's back in an abnormal position. In rare conditions it has the potential to lead to limited functional activity in the upper extremity to which it is adjacent. It can affect a person's ability to lift, pull, and push weighty objects. In some serious cases, the ability to perform activities of daily living such as changing one's clothes and washing one's hair may be hindered. The name of this condition comes from its appearance, a wing-like resemblance, due to the medial border of the scapula sticking straight out from the back. Scapular winging has been observed to disrupt scapulohumeral rhythm, contributing to decreased flexion and abduction of the upper extremity, as well as a loss in power and the source of considerable pain. A winged scapula is considered normal posture in young children, but not older children and adults. Signs and symptoms The severity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a lack of physical exercise, alcoholism, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at first menstruation, having children late in life or not at all, older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About 5–10% of cases are the result of a genetic predisposition inherited from a person's parents, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 among others. Breast cancer most commonly develops in cells from the lining of milk ducts and the lobules that supply these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axilla
The axilla (also, armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superiorly by the imaginary plane between the superior borders of the first rib, clavicle and scapula (above which are considered part of the neck), medially by the serratus anterior muscle and thoracolumbar fascia, anteriorly by the pectoral muscles and posteriorly by the subscapularis, teres major and latissimus dorsi muscle. The soft skin covering the lateral axilla contains many hair and sweat glands. In humans, the formation of body odor happens mostly in the axilla. These odorant substances have been suggested by some to serve as pheromones, which play a role related to mate selection, although this is a controversial topic within the scientific community. The underarms seem more important than the pubic area for emitting body odor, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


.jpg)