|
Cursorial
A cursorial organism is one that is adapted specifically to run. An animal can be considered cursorial if it has the ability to run fast (e.g. cheetah) or if it can keep a constant speed for a long distance (high endurance). "Cursorial" is often used to categorize a certain locomotor mode, which is helpful for biologists who examine behaviors of different animals and the way they move in their environment. Cursorial adaptations can be identified by morphological characteristics (e.g. loss of lateral digits as in ungulate species), physiological characteristics, maximum speed, and how often running is used in life. There is much debate over how to define a cursorial animal specifically. The most accepted definitions include that a cursorial organism could be considered adapted to long-distance running at high speeds or has the ability to accelerate quickly over short distances. Among vertebrates, animals under 1 kg of mass are rarely considered cursorial, and cursorial behavior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature, '' Eohippus'', into the large, single-toed animal of today. Humans began domesticating horses around 4000 BCE, and their domestication is believed to have been widespread by 3000 BCE. Horses in the subspecies ''caballus'' are domesticated, although some domesticated populations live in the wild as feral horses. These feral populations are not true wild horses, as this term is used to describe horses that have never been domesticated. There is an extensive, specialized vocabulary used to describe equine-related concepts, covering everything from anatomy to life stages, size, colors, markings, breeds, locomotion, and behavior. Horses are adapted to run, allowing them to quickly escape predators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prey
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory, as seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush or pursuit predation, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack is successful, the predator kills the prey, removes any inedible parts like the shell or spines, and eats it. Predators are adapted and often highly specialized for hunting, with acute senses such as vision, hearing, or smell. Many predatory animals, both vertebrate and inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
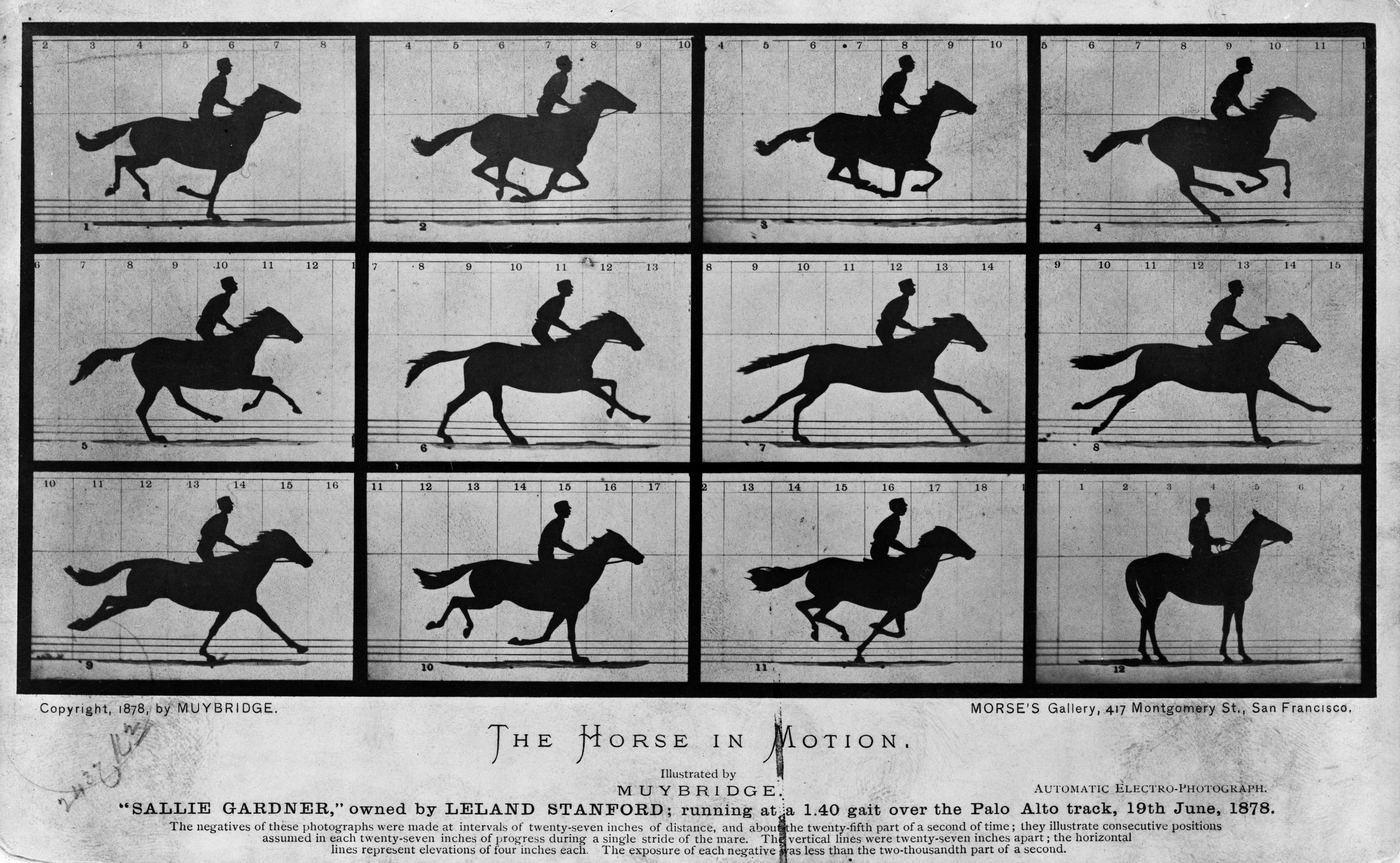
The Horse In Motion
''The Horse in Motion'' is a series of cabinet cards by Eadweard Muybridge, including six cards that each show a sequential series of six to twelve "automatic electro-photographs" depicting the movement of a horse. Muybridge shot the photographs in June 1878. An additional card reprinted the single image of the horse "Occident" trotting at high speed, which had previously been published by Muybridge in 1877. The series became the first example of chronophotography, an early method to photography, photographically record the passing of time, mainly used to document the different phases of locomotion for scientific study. It formed an important step in the development of Film, motion pictures for years to come. Muybridge's work was commissioned by Leland Stanford, the industrialist, former Governor of California, and horseman, who was interested in horse gait analysis. in 1882, Stanford had a book published about the project, also entitled ''The Horse in Motion'', with circa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capybara
The capybaraAlso called capivara (in Brazil), capiguara (in Bolivia), chigüire, chigüiro, or fercho (in Colombia and Venezuela), carpincho (in Argentina, Paraguay and Uruguay) and ronsoco (in Peru). or greater capybara (''Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris'') is a giant cavy rodent native to South America. It is the largest living rodent and a member of the genus '' Hydrochoerus''. The only other extant member is the lesser capybara (''Hydrochoerus isthmius''). Its close relatives include guinea pigs and rock cavies, and it is more distantly related to the agouti, the chinchilla, and the nutria. The capybara inhabits savannas and dense forests, and lives near bodies of water. It is a highly social species and can be found in groups as large as 100 individuals, but usually live in groups of 10–20 individuals. The capybara is hunted for its meat and hide and also for grease from its thick fatty skin. It is not considered a threatened species. Etymology Its common name is derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theropod
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally carnivorous, although a number of theropod groups evolved to become herbivores and omnivores. Theropods first appeared during the Carnian age of the late Triassic period 231.4 million years ago ( Ma) and included all the large terrestrial carnivores from the Early Jurassic until at least the close of the Cretaceous, about 66 Ma. In the Jurassic, birds evolved from small specialized coelurosaurian theropods, and are today represented by about 10,500 living species. Biology Diet and teeth Theropods exhibit a wide range of diets, from insectivores to herbivores and carnivores. Strict carnivory has always been considered the ancestral diet for theropods as a group, and a wider variety of diets was historically considered a ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangaroo
Kangaroos are four marsupials from the family Macropodidae (macropods, meaning "large foot"). In common use the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, the red kangaroo, as well as the antilopine kangaroo, eastern grey kangaroo, and western grey kangaroo. Kangaroos are indigenous to Australia and New Guinea. The Australian government estimates that 42.8 million kangaroos lived within the commercial harvest areas of Australia in 2019, down from 53.2 million in 2013. As with the terms " wallaroo" and "wallaby", "kangaroo" refers to a paraphyletic grouping of species. All three terms refer to members of the same taxonomic family, Macropodidae, and are distinguished according to size. The largest species in the family are called "kangaroos" and the smallest are generally called "wallabies". The term "wallaroos" refers to species of an intermediate size. There are also the tree-kangaroos, another type of macropod, which inhabit the tropi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agouti
The agouti (, ) or common agouti is any of several rodent species of the genus ''Dasyprocta''. They are native to Middle America, northern and central South America, and the southern Lesser Antilles. Some species have also been introduced elsewhere in the West Indies. They are related to guinea pigs and look quite similar, but they are larger and have longer legs. The species vary considerably in colour, being brown, reddish, dull orange, greyish, or blackish, but typically with lighter underparts. Their bodies are covered with coarse hair, which is raised when alarmed. They weigh and are in length, with short, hairless tails. The related pacas were placed by some authorities in a genus called ''Agouti'', though ''Cuniculus'' has priority and is the correct term. In West Africa (especially Ivory Coast), the name "agouti" designates the greater cane rat which, while an agricultural pest, is often sought as a bushmeat delicacy. The Spanish term is ''agutí.'' In Mexico, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ungulates
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, camels, sheep, deer, and hippopotamuses. Cetaceans such as whales, dolphins, and porpoises are also classified as even-toed ungulates, although they do not have hooves. Most terrestrial ungulates use the hoofed tips of their toes to support their body weight while standing or moving. The term means, roughly, "being hoofed" or "hoofed animal". As a descriptive term, "ungulate" normally excludes cetaceans as they do not possess most of the typical morphological characteristics of other ungulates, but recent discoveries indicate that they were also descended from early artiodactyls. Ungulates are typically herbivorous and many employ specialized gut bacteria to allow them to digest cellulose. Some modern species, such as pigs, are omnivorous, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly understood, comprise wild subspecies. The wolf is the largest extant member of the family Canidae. It is also distinguished from other ''Canis'' species by its less pointed ears and muzzle, as well as a shorter torso and a longer tail. The wolf is nonetheless related closely enough to smaller ''Canis'' species, such as the coyote and the golden jackal, to produce fertile hybrids with them. The banded fur of a wolf is usually mottled white, brown, gray, and black, although subspecies in the arctic region may be nearly all white. Of all members of the genus ''Canis'', the wolf is most specialized for cooperative game hunting as demonstrated by its physical adaptations to tackling large prey, its more social nature, and its highly advanced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
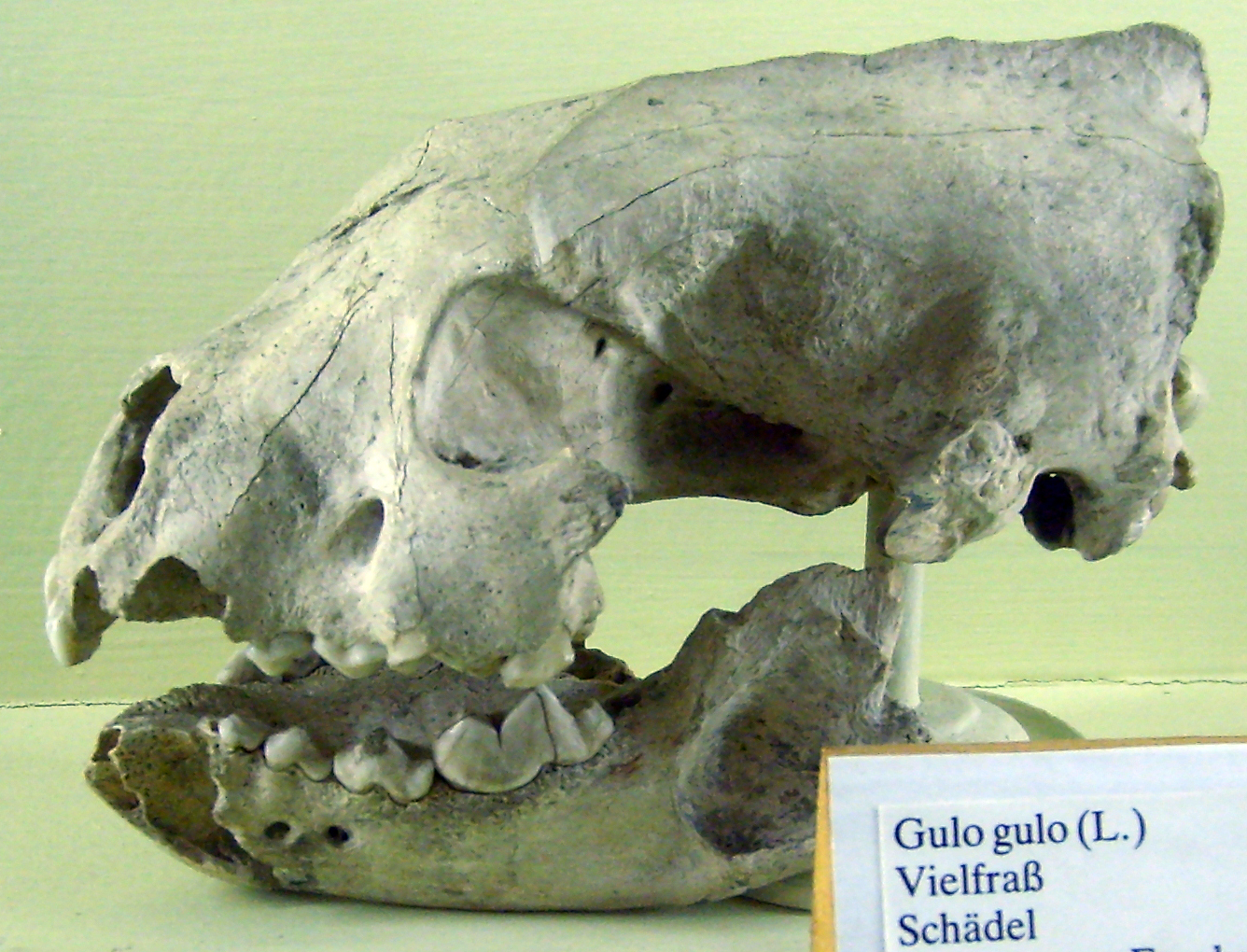
Wolverines
The wolverine (), (''Gulo gulo''; ''Gulo'' is Latin for " glutton"), also referred to as the glutton, carcajou, or quickhatch (from East Cree, ''kwiihkwahaacheew''), is the largest land-dwelling species of the family Mustelidae. It is a muscular carnivore and a solitary animal. The wolverine has a reputation for ferocity and strength out of proportion to its size, with the documented ability to kill prey many times larger than itself. The wolverine is found primarily in remote reaches of the Northern boreal forests and subarctic and alpine tundra of the Northern Hemisphere, with the greatest numbers in Northern Canada, the U.S. state of Alaska, the mainland Nordic countries of Europe, and throughout western Russia and Siberia. Its population has steadily declined since the 19th century owing to trapping, range reduction and habitat fragmentation. The wolverine is now essentially absent from the southern end of its range in both Europe and North America. Taxonomy Genetic ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelurosauria
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs. Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, tyrannosaurs, ornithomimosaurs, and maniraptorans; Maniraptora includes birds, the only known dinosaur group alive today. Most feathered dinosaurs discovered so far have been coelurosaurs. Philip J. Currie had considered it likely and probable that all coelurosaurs were feathered. However, several skin impressions found for some members of this group show pebbly, scaly skin, indicating that feathers did not completely replace scales in all taxa. In the past, Coelurosauria was used to refer to all small theropods, but this classification has since been abolished. Anatomy Bodyplan The studying of anatomical traits in coelurosaurs indicates that the last common ancestor had evolved the ability to eat and digest plant matter, adapting to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theropoda
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally carnivorous, although a number of theropod groups evolved to become herbivores and omnivores. Theropods first appeared during the Carnian age of the late Triassic period 231.4 million years ago ( Ma) and included all the large terrestrial carnivores from the Early Jurassic until at least the close of the Cretaceous, about 66 Ma. In the Jurassic, birds evolved from small specialized coelurosaurian theropods, and are today represented by about 10,500 living species. Biology Diet and teeth Theropods exhibit a wide range of diets, from insectivores to herbivores and carnivores. Strict carnivory has always been considered the ancestral diet for theropods as a group, and a wider variety of diets was historically considered a characteris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_with_its_prey.jpg)

.jpg)

.png)


