|
Sergei Medvedev (revolutionary)
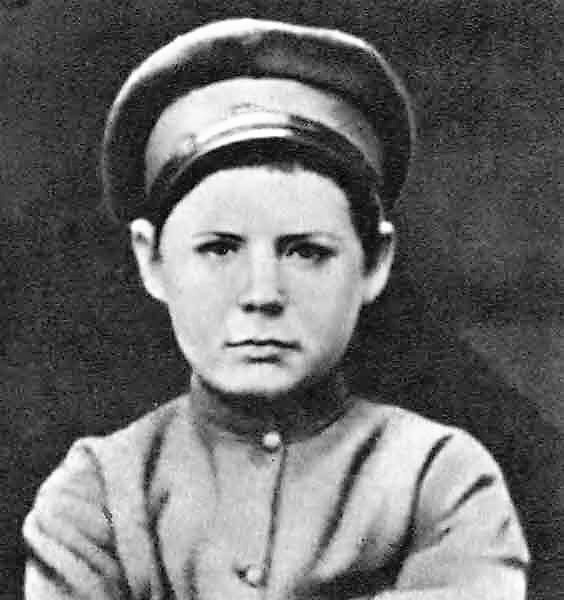
Sergei Pavlovich Medvedev (russian: Серге́й Па́влович Медве́дев; 15 March 1885 – 10 September 1937) was a Russian Bolshevik revolutionary, metalworker, and trade union organizer. He was born into the peasant estate in a family of Russians, Russian ethnicity in Kortino, Moscow Governorate and grew up in the countryside near Moscow and in St. Petersburg. After receiving a primary school education, he began factory work at age thirteen. He first worked at the Obukhov State Plant, Obukhov factory in St. Petersburg and participated in the 1901 Obukhov strike. He became a socialist at age fifteen and joined the Bolsheviks when the Russian Social Democratic Workers Party split in 1903. Medvedev was active in the revolutionary underground, organizing illegal party cells. The tsarist government sentenced him numerous times to prison and to terms of exile within Russia. Medvedev was also an organizer in the underground section of the insurance movement in 1912- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergej Pavlovic Medvedev
Sergius is a male given name of Ancient Roman origin after the name of the Latin ''gens'' Sergia or Sergii of regal and republican ages. It is a common Christian name, in honor of Saint Sergius, or in Russia, of Saint Sergius of Radonezh, and has been the name of four popes. It has given rise to numerous variants, present today mainly in the Romance (Serge, Sergio, Sergi) and Slavic languages (Serhii, Sergey, Serguei). It is not common in English, although the Anglo-French name Sergeant is possibly related to it. Etymology The name originates from the Roman ''nomen'' (patrician family name) ''Sergius'', after the name of the Roman ''gens'' of Latin origins Sergia or Sergii from Alba Longa, Old Latium, counted by Theodor Mommsen as one of the oldest Roman families, one of the original 100 ''gentes originarie''. It has been speculated to derive from a more ancient Etruscan name but the etymology of the nomen Sergius is problematic. Chase hesitantly suggests a connection with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Congress Of The Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
The 10th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks) was held during March 8–16, 1921 in Moscow, Russia. The congress dealt with the issues of the party opposition, the New Economic Policy, and the Kronstadt Rebellion, which started halfway through the Congress. The Congress was attended by 694 voting delegates and 296 non-voting delegates. Agenda The Agenda consisted of: # Report of the Central Committee; # Report of the Control Commission; # The trade unions' economic role; # The Socialist Republic in a capitalist encirclement foreign trade, concessions, etc.; # Food supply, surplus-food appropriation, tax in kind and fuel crisis, # Problems of Party organisation; # The Party's current tasks in the nationalities question; # Reorganisation of the army and the militia question; # The Chief Administration for Political Education and the Party's propaganda and agitation work; # Report of the R.C.P.'s representative in the Comintern, and its current tasks; # Report of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1885 Births
Events January–March * January 3– 4 – Sino-French War – Battle of Núi Bop: French troops under General Oscar de Négrier defeat a numerically superior Qing Chinese force, in northern Vietnam. * January 4 – The first successful appendectomy is performed by Dr. William W. Grant, on Mary Gartside. * January 17 – Mahdist War in Sudan – Battle of Abu Klea: British troops defeat Mahdist forces. * January 20 – American inventor LaMarcus Adna Thompson patents a roller coaster. * January 24 – Irish rebels damage Westminster Hall and the Tower of London with dynamite. * January 26 – Mahdist War in Sudan: Troops loyal to Mahdi Muhammad Ahmad conquer Khartoum; British commander Charles George Gordon is killed. * February 5 – King Leopold II of Belgium establishes the Congo Free State, as a personal possession. * February 9 – The first Japanese arrive in Hawaii. * February 16 – Charles Dow publishes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Article 58
Article 58 of the Russian SFSR Penal Code was put in force on 25 February 1927 to arrest those suspected of counter-revolutionary activities. It was revised several times. In particular, its Article 58-1 was updated by the listed sub-articles and put in force on 8 June 1934. This article introduced the formal notion of the enemy of workers: those subject to articles 58-2 — 58-13 (those under 58-1 were "traitors", 58-14 were "saboteurs"). Penal codes of other republics of the Soviet Union also had articles of similar nature. Summary Note: In this section, the phraseology of article 58 is given in quotes. The article covered the following offenses. *58-1: Definition of counter-revolutionary activity: A counter-revolutionary action is any action aimed at overthrowing, undermining or weakening of the power of workers' and peasants' Soviets... and governments of the USSR and Soviet and autonomous republics, or at the undermining or weakening of the external security of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergey Kirov
Sergei Mironovich Kirov (né Kostrikov; 27 March 1886 – 1 December 1934) was a Soviet politician and Bolshevik revolutionary whose assassination led to the first Great Purge. Kirov was an early revolutionary in the Russian Empire and member of the Bolshevik faction of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party. Kirov became an Old Bolshevik and personal friend to Joseph Stalin, rising through the Communist Party of the Soviet Union ranks to become head of the party in Leningrad and a member of the Politburo. On 1 December 1934, Kirov was shot and killed by Leonid Nikolaev at his offices in the Smolny Institute for unknown reasons; Nikolaev and several suspected accomplices were convicted in a show trial and executed less than 30 days later. Kirov's death was later used as a pretext for Stalin's escalation of political repression in the Soviet Union and the events of the Great Purge, with complicity as a common charge for the condemned in the Moscow Trials. Kirov's assassina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omsk
Omsk (; rus, Омск, p=omsk) is the administrative center and largest city of Omsk Oblast, Russia. It is situated in southwestern Siberia, and has a population of over 1.1 million. Omsk is the third largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk and Krasnoyarsk, and the twelfth-largest city in Russia. It is an essential transport node, serving as a train station for the Trans-Siberian Railway and as a staging post for the Irtysh River. During the Imperial era, Omsk was the seat of the Governor General of Western Siberia and, later, of the Governor General of the Steppes. For a brief period during the Russian Civil War in 1918–1920, it served as the capital of the anti-Bolshevik Russian State and held the imperial gold reserves. Omsk serves as the episcopal see of the bishop of Omsk and Tara, as well as the administrative seat of the Imam of Siberia. The mayor is Sergey Shelest. Etymology The city of Omsk is named after the Om river. This hydronym in the dialect of Bara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergo Ordzhonikidze
Sergo Konstantinovich Ordzhonikidze,, ; russian: Серго Константинович Орджоникидзе, Sergo Konstantinovich Ordzhonikidze) born Grigol Konstantines dze Orjonikidze, russian: Григорий Константинович Орджоникидзе (18 February 1937), was a Georgian Bolshevik and Soviet politician. Born and raised in Georgia, Ordzhonikidze joined the Bolsheviks at an early age and quickly rose within the ranks to become an important figure within the group. Arrested and imprisoned several times by the Russian police, he was in Siberian exile when the February Revolution began in 1917. Returning from exile, Ordzhonikidze took part in the October Revolution that brought the Bolsheviks to power. During the subsequent Civil War he played an active role as the leading Bolshevik in the Caucasus, overseeing the invasions of Azerbaijan, Armenia, and Georgia. He backed their union into the Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic (T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commissariat Of Heavy Industry
The People's Commissariat of Heavy Industry (Narkomtiazhprom; russian: Народный комиссариат тяжёлой промышленности СССР) was a government ministry in the Soviet Union in 1930s. Brief overview The People's Commissariat of Heavy Industry, known by the acronym NKTP, was founded in 1932 out of the Supreme Soviet of the National Economy and was responsible for all heavy industrial goods, including mining, machinery and defense goods. The defense industry assets were separated in December 1936, with the creation of the People's Commissariat of the Defense Industry, and in August 1937 there was set up the People's Commissariat for Mechanical Engineering. In early 1939 the NKTP was divided into six separate commissariats. Succeeding commissariats * People's Commissariat of the Defense Industry * People's Commissariat for Mechanical Engineering * People's Commissariat of Fuel Industry * People's Commissariat of Ferrous Metallurgy * People's Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Industry
Heavy industry is an industry that involves one or more characteristics such as large and heavy products; large and heavy equipment and facilities (such as heavy equipment, large machine tools, huge buildings and large-scale infrastructure); or complex or numerous processes. Because of those factors, heavy industry involves higher capital intensity than light industry does, and it is also often more heavily cyclical in investment and employment. Though important to economic development and industrialization of economies, heavy industry can also have significant negative side effects: both local communities and workers frequently encounter health risks, heavy industries tend to produce byproducts that both pollute the air and water, and the industrial supply chain is often involved in other environmental justice issues from mining and transportation. Because of their intensity, heavy industries are also significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions that cause climat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baku
Baku (, ; az, Bakı ) is the capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region. Baku is located below sea level, which makes it the lowest lying national capital in the world and also the largest city in the world located below sea level. Baku lies on the southern shore of the Absheron Peninsula, alongside the Bay of Baku. Baku's urban population was estimated at two million people as of 2009. Baku is the primate city of Azerbaijan—it is the sole metropolis in the country, and about 25% of all inhabitants of the country live in Baku's metropolitan area. Baku is divided into twelve administrative raions and 48 townships. Among these are the townships on the islands of the Baku Archipelago, and the town of Oil Rocks built on stilts in the Caspian Sea, away from Baku. The Inner City of Baku, along with the Shirvanshah's Palace and Maiden Tower, were inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2000. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandra Kollontai
Alexandra Mikhailovna Kollontai (russian: Алекса́ндра Миха́йловна Коллонта́й, née Domontovich, Домонто́вич; – 9 March 1952) was a Russian revolutionary, politician, diplomat and Theoretician (Marxism), Marxist theoretician. Serving as the People's Commissariat, People's Commissar for Welfare in Vladimir Lenin's government in 1917–1918, she was a highly prominent woman within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, Bolshevik party and the first woman in history to become an official member of a governing cabinet.Encyclopedia of Women's Autobiography p. 326. - "In the first Soviet government, formed in the fall of 1917, Kollontai was appointed people's commissar (minister) for social welfare. She was the only woman in the cabinet but also the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
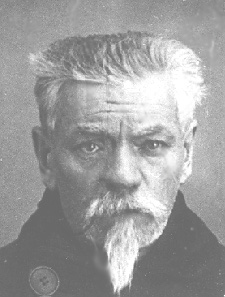
.jpg)





