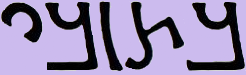|
Septimius Antiochus
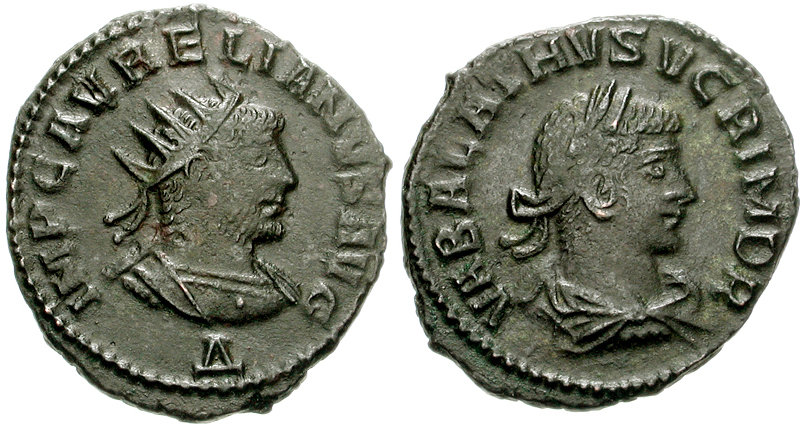
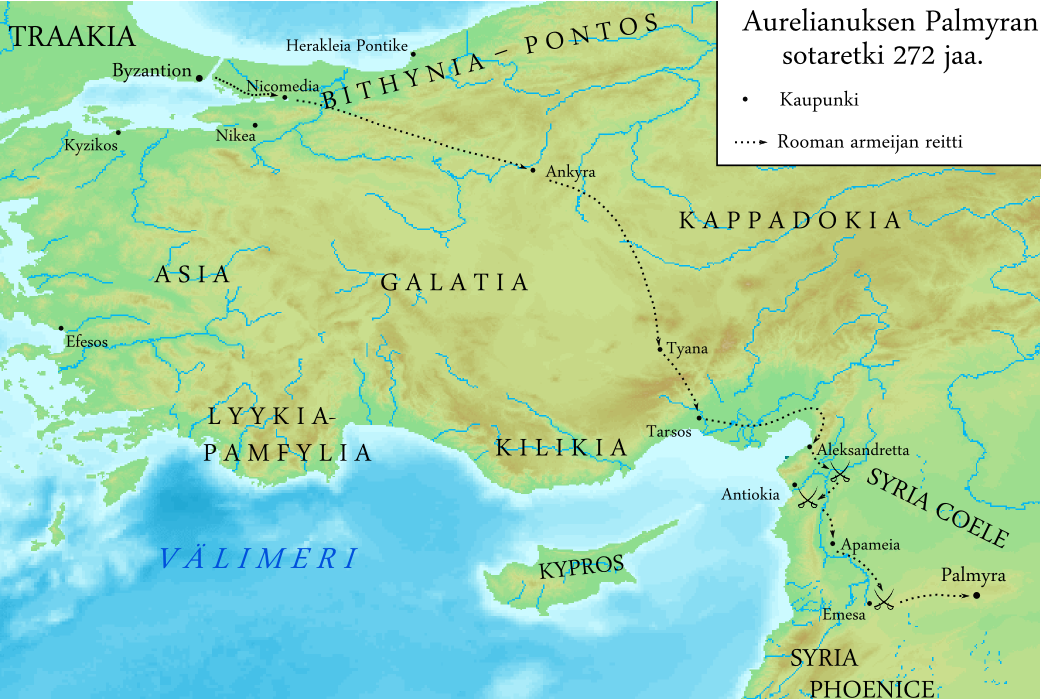
Septimius Antiochus (died after 273) was a Roman usurper in Syria during the 3rd century. In 272 AD Emperor Aurelian had defeated the breakaway Kingdom of Palmyra; its king Vaballathus and his mother Zenobia were in Roman captivity. In 273 AD another rebellion against Roman rule broke out in Palmyra. The rebels first approached Aurelian's governor Marcellinus to become emperor, but he pretended to consider the offer as he sent a letter to Aurelian warning of the rebellion. While the rebels were waiting they decided to elevate Septimius Antiochus, the reputed son of Zenobia, to the purple. Receiving Marcellinus's letter, the Emperor reacted quickly, and in the spring of 273 the city was brought back under Roman rule. Aurelian punished the city heavily, but allegedly spared Antiochus. Antiochus claimed to be descended from Queen Cleopatra VII Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Usurper
Roman usurpers were individuals or groups of individuals who obtained or tried to obtain power by force and without legitimate legal authority. Usurpation was endemic during the Roman imperial era, especially from the crisis of the third century onwards, when political instability became the rule. The first dynasty of the Roman Empire, the Julio-Claudians (27 BC – 68 AD), justified the imperial throne by familial ties, namely with the connection (although only through adoption) with Augustus, the first emperor. Eventually, conflicts within the Julio-Claudian family triggered a series of murders, which led to the demise of the line. Nero died with public enemy status, and following his suicide, a short civil war began, known as the Year of the Four Emperors. The Flavian dynasty started with Vespasian, only to end with the assassination of his second son, Domitian. The 2nd century was a period of relative peace that was marked by the rule of the so-called Five Good Emperors, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria (Roman Province)
Roman Syria was an early Roman province annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC by Pompey in the Third Mithridatic War following the defeat of King of Armenia Tigranes the Great. Following the partition of the Herodian Kingdom of Judea into tetrarchies in 6 AD, it was gradually absorbed into Roman provinces, with Roman Syria annexing Iturea and Trachonitis. Provincia Syria Syria was annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC, when Pompey the Great had the Seleucid king Antiochus XIII Asiaticus executed and deposed his successor Philip II Philoromaeus. Pompey appointed Marcus Aemilius Scaurus to the post of Proconsul of Syria. Following the fall of the Roman Republic and its transformation into the Roman Empire, Syria became a Roman imperial province, governed by a Legate. During the early empire, the Roman army in Syria accounted for three legions with auxiliaries who defended the border with Parthia. In 6 AD Emperor Augustus deposed the ethnarch Herod Archelaus and united J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crisis Of The Third Century
The Crisis of the Third Century, also known as the Military Anarchy or the Imperial Crisis (AD 235–284), was a period in which the Roman Empire nearly collapsed. The crisis ended due to the military victories of Aurelian and with the ascension of Diocletian and his implementation of reforms in 284, including the Tetrarchy. The crisis began in 235 with the assassination of Emperor Severus Alexander by his own troops. During the following 50-year period, the Empire saw the combined pressures of barbarian invasions and migrations into the Roman territory, civil wars, peasant rebellions and political instability, with multiple usurpers competing for power. This led to the debasement of currency and economic collapse, with the Plague of Cyprian contributing to the disorder. Roman troops became more reliant over time on the growing influence of the barbarian mercenaries known as foederati. Roman commanders in the field, although nominally working for Rome, became increasingly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurelian
Aurelian ( la, Lucius Domitius Aurelianus; 9 September 214 October 275) was a Roman emperor, who reigned during the Crisis of the Third Century, from 270 to 275. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited the Roman Empire after it had nearly disintegrated under the pressure of barbarian invasions and internal revolts. Born in humble circumstances, near the Danube River, he entered the Roman military in 235, and climbed up the ranks. He went on to lead the cavalry of the emperor Gallienus, until Gallienus' assassination in 268. Following that, Claudius Gothicus became emperor until his own death in 270. Claudius' brother Quintillus ruled the empire for three months, before Aurelian became emperor. During his reign, he defeated the Alamanni after a devastating war. He also defeated the Goths, Vandals, Juthungi, Sarmatians, and Carpi. Aurelian restored the Empire's eastern provinces after his conquest of the Palmyrene Empire in 273. The follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmyrene Empire
The Palmyrene Empire was a short-lived breakaway state from the Roman Empire resulting from the Crisis of the Third Century. Named after its capital city, Palmyra, it encompassed the Roman provinces of Syria Palaestina, Arabia Petraea, and Egypt, as well as large parts of Asia Minor. The Palmyrene Empire was ruled by Queen Zenobia, officially as regent for her son Vaballathus, who inherited the throne in 267 at age ten. In 270, Zenobia rapidly conquered most of the Roman east, attempting to maintain relations with Rome as a legitimate power. In 271, she claimed the imperial title for both herself and her son, fighting a short war with the Roman emperor Aurelian, who conquered Palmyra and captured Zenobia. A year later the Palmyrenes rebelled, which led Aurelian to destroy Palmyra. Despite its brief existence, the Palmyrene Empire is remembered for having been ruled by one of the most ambitious and powerful women in antiquity. It is also hailed in Syria, where it plays an import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaballathus
Septimius Vaballathus (Palmyrene Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; ar, وهب اللات, translit=Wahb Allāt; 259 – c. 274 AD) was emperor of the Palmyrene Empire centred at Palmyra in the region of Syria. He came to power as a child under his regent mother Zenobia, who led a revolt against the Roman Empire and formed the independent Palmyrene Empire. Early life Lucius Julius Aurelius Septimius Vaballathus was born and raised in the city of Palmyra, an oasis settlement in the Syrian Desert in 259 to the king of kings of Palmyra, Odaenathus, and his second wife, queen consort of Palmyra, Zenobia. Vaballathus is the Latinized form of his Palmyrene name, ''Wahballāt'', "Gift of Allāt". As the Arabian goddess Allāt came to be identified with Athena, he used ''Athenodorus'' as the Greek form of his name. He had a half-brother, Hairan I, born from his father and another woman, who reigned as co-king of kings with his father, and a lesser-known brother, Hairan II. He also might have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenobia
Septimia Zenobia (Palmyrene Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; AD 240 – c. 274) was a third-century queen of the Palmyrene Empire in Syria. Many legends surround her ancestry; she was probably not a commoner and she married the ruler of the city, Odaenathus. Her husband became king in 260, elevating Palmyra to supreme power in the Near East by defeating the Sassanians and stabilizing the Roman East. After Odaenathus' assassination, Zenobia became the regent of her son Vaballathus and held de facto power throughout his reign. In 270, Zenobia launched an invasion that brought most of the Roman East under her sway and culminated with the annexation of Egypt. By mid-271 her realm extended from Ancyra, central Anatolia, to southern Egypt, although she remained nominally subordinate to Rome. However, in reaction to the campaign of the Roman emperor Aurelian in 272, Zenobia declared her son emperor and assumed the title of empress (declaring Palmyra's secession from Rome). The Romans were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcellinus (consul 275)
Aurelius/Iulius Marcellinus (his '' nomen'' is uncertain) was a Roman soldier and Imperial functionary who had a brilliant equestrian career and was elevated to the Senate when he was chosen by the Emperor Aurelian as his consular colleague. His appointment as ''Consul'' is thought to have been a reward for his loyalty and steadfastness in 273 when, as Aurelian's deputy in charge of the eastern provinces of the Empire where the authority of the Imperial Government had only recently been restored, he resisted attempts to suborn him by a rebellious faction in the city of Palmyra. His promotion was unusual in that he had not achieved the rank of Praetorian Prefect, the level of seniority in the Imperial Service at which equestrian officials might hope to be elevated to the Senate. However, this practice, which was to become a regular feature during the reign of Diocletian, was still inchoate in 275 AD. Obviously a man of considerable capabilities who had attracted the Imperial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleopatra VII
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a diplomat, naval commander, linguist, and medical author; see and . A member of the Ptolemaic dynasty, she was a descendant of its founder Ptolemy I Soter, a Macedonian Greek general and companion of Alexander the Great. writes about Ptolemy I Soter: "The Ptolemaic dynasty, of which Cleopatra was the last representative, was founded at the end of the fourth century BC. The Ptolemies were not of Egyptian extraction, but stemmed from Ptolemy Soter, a Macedonian Greek in the entourage of Alexander the Great."For additional sources that describe the Ptolemaic dynasty as " Macedonian Greek", please see , , , and . Alternatively, describes them as a "Macedonian, Greek-speaking" dynasty. Other sources such as and describe the Ptolemies as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rulers Of Palmyra
A ruler, sometimes called a rule, line gauge, or scale, is a device used in geometry and technical drawing, as well as the engineering and construction industries, to distance measurement, measure distances or draw straight lines. Variants Rulers have long been made from different materials and in multiple sizes. Some are wooden. Plastics have also been used since they were invented; they can be molded with length markings instead of being wikt:scribe, scribed. Metal is used for more durable rulers for use in the workshop; sometimes a metal edge is embedded into a wooden desk ruler to preserve the edge when used for straight-line cutting. in length is useful for a ruler to be kept on a desk to help in drawing. Shorter rulers are convenient for keeping in a pocket. Longer rulers, e.g., , are necessary in some cases. Rigid wooden or plastic yardsticks, 1 yard long, and meter sticks, 1 meter long, are also used. Classically, long measuring rods were used for large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |