|
Sentinel Gap
Sentinel Gap is a water gap formed by the Columbia River in the Saddle Mountains, near Mattawa, Washington, Mattawa in Washington (state), Washington state. The gap is "a water gap where erosion by the Columbia River was able to keep pace with folding, faulting and uplifting across the Saddle Mountain anticline". During Missoula Floods, Ice Age floods in which waters from the Channeled Scablands found passage to the Pacific Ocean here and at Wallula Gap, this opening was "repeatedly reamed out, which probably widened and steepened the walls of the gap". Strandlines from the floods can be seen on the basalt walls of the gap. Washington State Route 243, SR 243 runs along the east side of the river through the gap, and the river is spanned by the Beverly Railroad Bridge. The gap is located between the Wanapum Dam, Wanapum and Priest Rapids Dam, Priest Rapids dams. Priest Rapids, for which the dam was named, are now submerged beneath the dam's reservoir about downstream from Sent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strandlines
A high water mark is a point that represents the maximum rise of a body of water over land. Such a mark is often the result of a flood, but high water marks may reflect an all-time high, an annual high (highest level to which water rose that year) or the high point for some other division of time. Knowledge of the high water mark for an area is useful in managing the development of that area, particularly in making preparations for flood surges. High water marks from floods have been measured for planning purposes since at least as far back as the civilizations of ancient Egypt. It is a common practice to create a physical marker indicating one or more of the highest water marks for an area, usually with a line at the level to which the water rose, and a notation of the date on which this high water mark was set. This may be a free-standing flood level sign or other marker, or it may be affixed to a building or other structure that was standing at the time of the flood that se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priest Rapids
Priest Rapids was a narrow, fast-flowing stretch of the Columbia River, located in the central region of the U.S. state of Washington. It was flooded by the construction of the Priest Rapids Dam in the 1950s. Before the dam's construction, the river dropped 20 feet (6 m) over a short distance. In total Priest Rapids consisted of seven separate cataracts along a 9-mile (14 km) stretch, over which the river dropped 72 feet (22 m) altogether. It was given the name Priest Rapids by Alexander Ross of the Pacific Fur Company in 1811, for a native shaman. Ross wrote of his visit to the "strong and rocky rapid" where he met a man "called Haquilaugh, which signifies … priest." Haquilaugh was an influential Wanapum leader, for whom Ross gave the rapids its English name. At Priest Rapids the Columbia River narrowed and flowed quickly, making it an ideal salmon fishing site. There were several rapids and fishing sites, and a dozen or so Wanapum villages along the west bank of the Colu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priest Rapids Dam
Priest Rapids Dam is a hydroelectric, concrete gravity dam; located on the Columbia River, between the Yakima Firing Range and the Hanford Nuclear Reservation, and bridges Yakima County and Grant County, in the U.S. state of Washington. The dam is 24 miles south of the town of Vantage, and 47 miles northwest of the city of Richland. It is located at mile marker 397.1 from the mouth of the Columbia. It is owned by the Grant County Public Utility District (PUD). Priest Rapids, for which the dam was named, are now submerged beneath the dam's reservoir. Priest Rapids Dam is part of the Columbia River Basin system of dams. History After the disaster of 1949 Vanport Flood on the lower Columbia River, around Vancouver, Washington, and Portland, Oregon, the federal government established the Priest Rapids Project under the Flood Control Act of 1950 (Public Law 81-516; May 17, 1950). The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers decided the project would not be a top priority, so the Grant PUD beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tri-City Herald
The ''Tri-City Herald'' is a daily newspaper based in Kennewick, Washington, United States. Owned by The McClatchy Company, the newspaper serves southeastern Washington state, including the three cities of Kennewick, Pasco and Richland (which are collectively known as the Tri-Cities). The ''Herald'' also serves the smaller cities of Benton City, Connell, Prosser and West Richland. It is the only major English-language newspaper in Washington east of Yakima and south of Spokane, and includes local and national news, opinion columns, sports information, movie listings and comic strips among other features. The paper was founded in 1918 as the weekly ''Pasco Herald.'' In 1947, Glenn C. Lee and Robert Philip bought the paper, moved it to Kennewick and transformed it into the area's first daily paper, coining the name 'Tri-Cities' as part of the paper's name. Lee and Philip sold the paper to McClatchy in 1979. After over 30 years as an afternoon paper, it became a morning pape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beverly Railroad Bridge
The Beverly Railroad Bridge is a historic railroad bridge that now carries hikers, bicyclists, and pedestrians over the Columbia River near Beverly, Washington, United States. It was constructed by the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad (otherwise known as The Milwaukee Road) in 1909 during its Pacific Extension. In 1906, The Milwaukee Road began construction on its transcontinental rail line from Chicago, Illinois to Tacoma, Washington, which was completed three years later. The bridge was built on concrete piers above the Columbia River to provide clearance for any river traffic. The spans include 14 Warren deck trusses, one Parker through truss, and deck plate girders on the approaches. When the railroad electrified in the 1920s, supports for the catenary were added to the bridge. When the railroad ceased using electric locomotives in 1972, the catenary was removed, but the supports were kept in place. After the railroad went bankrupt in the mid-1970s and aban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington State Route 243
State Route 243 (SR 243) is a state highway in Grant County, Washington. It travels north–south along the Columbia River for , connecting SR 24 at the Vernita Bridge to SR 26 near Vantage. The highway travels through a predominantly rural and desert area, serving two hydroelectric dams and the communities of Desert Aire, Mattawa, and Beverly. The highway was established as a branch of Secondary State Highway 7C (SSH 7C) in 1957, to be built uphill from the reservoir of the new Priest Rapids Dam. Construction was completed in the early 1960s and it was re-designated as SR 243 during the 1964 state highway renumbering. Route description SR 243 begins at a junction with SR 24 at the north end of the Vernita Bridge, located in the Hanford Reach National Monument. Traffic continuing on SR 24 towards Othello is forced to turn east, while the highway continues northwest as SR 243. The highway turns west and follows the Colu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallula Gap
Wallula Gap () is a large water gap of the Columbia River in the northwest United States in southeast Washington. It cuts through the Horse Heaven Hills basalt anticlines in the Columbia River Basin, just south of the confluence of the Walla Walla and Columbia rivers. It has been recognized as a National Natural Landmark by the National Park Service as a site that provides an important illustration of the geological history of the United States. Geology Flood basalts In southeastern Washington, eastern Oregon, and southern Idaho, flood basalt flows of extremely fluid basaltic lava spread in all directions from long fissures, building broad fields of gently sloping lava that spread widely over great distances. Along the Snake River in Idaho, and the Columbia River in Washington and Oregon, these lava flows have been extensively exposed by erosion (with extensive displays of columnar basalt), and measure almost 2 km (1.24 mi) in total thickness. The basalts fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel Gap Ice Age Floods Features
Sentinel may refer to: Places Mountains * Mount Sentinel, a mountain next to the University of Montana in Missoula, Montana * Sentinel Buttress, a volcanic crag on James Ross Island, Antarctica * Sentinel Dome, a naturally occurring granite dome in Yosemite National Park, California * Sentinel Mountain (Montana), in Glacier National Park * Sentinel Peak (Alberta) * Sentinel Peak (Antarctica) * Sentinel Peak (Arizona), a peak in the Tucson Mountains * Sentinel Peak (British Columbia) * Sentinel Range, a mountain range in Antarctica * The Sentinel, Hout Bay * The Sentinel (Zion), a sandstone summit in Zion National Park, Utah Elsewhere * Sentinel, Arizona * Sentinel, California * Sentinel, Missouri * Sentinel, Oklahoma * Sentinel Island (other) Arts, entertainment, and media Artworks * ''Sentinel'' (sculpture), a 2000 sculpture by Tim Tolkien * ''Sentinels'' (Hudson), a 2005 public artwork by American artist Jon Barlow Hudson Comics * ''Sentinel'' (comic b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
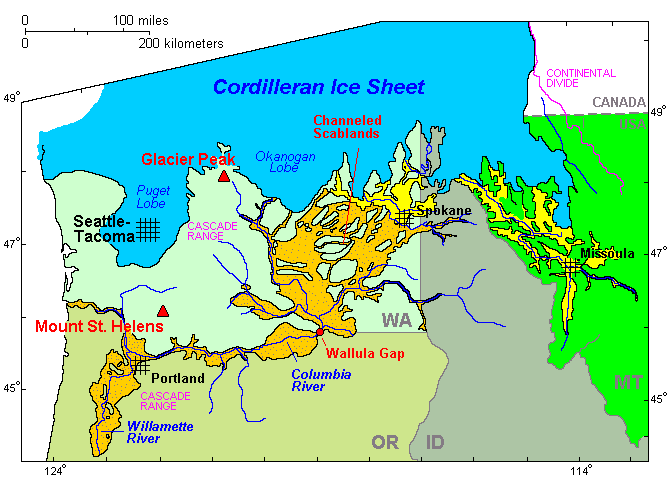
Channeled Scablands
The Channeled Scablands are a relatively barren and soil-free region of interconnected relict and dry flood channels, coulees and cataracts eroded into Palouse loess and the typically flat-lying basalt flows that remain after cataclysmic floods within the southeastern part of Washington.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl, Jr., and J.A. Jackson, eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. The Channeled Scablands were scoured by more than 40 cataclysmic floods during the Last Glacial Maximum and innumerable older cataclysmic floods over the last two million years. These floods were periodically unleashed whenever a large glacial lake broke through its ice dam and swept across eastern Washington and down the Columbia River Plateau during the Pleistocene epoch. The last of the cataclysmic floods occurred between 18,200 and 14,000 years ago.Balbas, A.M., Barth, A.M., Clark, P.U., Clark, J., Caffee, M., O'Connor, J., Baker, V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missoula Floods
The Missoula floods (also known as the Spokane floods or the Bretz floods or Bretz's floods) were cataclysmic glacial lake outburst floods that swept periodically across eastern Washington and down the Columbia River Gorge at the end of the last ice age. These floods were the result of periodic sudden ruptures of the ice dam on the Clark Fork River that created Glacial Lake Missoula. After each ice dam rupture, the waters of the lake would rush down the Clark Fork and the Columbia River, flooding much of eastern Washington and the Willamette Valley in western Oregon. After the lake drained, the ice would reform, creating Glacial Lake Missoula again. These floods have been researched since the 1920s. During the last deglaciation that followed the end of the Last Glacial Maximum, geologists estimate that a cycle of flooding and reformation of the lake lasted an average of 55 years and that the floods occurred several times over the 2,000-year period between 15,000 and 13,000 year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |