|
Sensory History
Sensory history is an area of academic study which examines the role the five senses have played in the past. It developed partly as a reaction to the lack of serious attention given to sensory experience in traditional history books, which often treat sensory experience as a writing technique rather than a serious avenue of enquiry. Works of sensory history try to convey a deeper understanding of the past through an emphasis on physical experiences. One of the most significant proponents of sensory history is the American historian Mark M. Smith. Anthropological approaches to sensory studies have had a notable influence on sensory history and there has been significant discussion and overlap between the two disciplines. The transient nature of sensory experience makes sensory history a difficult topic to study and write about. This challenge is reflected in debate within the field, such as what methods of presentation are appropriate for works of sensory history. History Karl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five People, Each Exercising One Of The Five Senses
5 is a number, numeral, and glyph. 5, five or number 5 may also refer to: * AD 5, the fifth year of the AD era * 5 BC, the fifth year before the AD era Literature * ''5'' (visual novel), a 2008 visual novel by Ram * ''5'' (comics), an award-winning comics anthology * ''No. 5'' (manga), a Japanese manga by Taiyō Matsumoto * The Famous Five (novel series), a series of children's adventure novels written by English author Enid Blyton Films * ''Five'' (1951 film), a post-apocalyptic film * ''Five'' (2003 film), an Iranian documentary by Abbas Kiarostami * ''Five'' (2011 film), a comedy-drama television film * ''Five'' (2016 film), a French comedy film * Number 5, the protagonist in the film ''Short Circuit'' (1986 film) Television and radio * 5 (TV channel), a television network in the Philippines (currently known as TV5 from 2008 to 2018 and again since 2020), owned by TV5 Network, Inc. * Channel 5 (British TV channel), British free-to-air television network sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interdisciplinarity
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several other fields like sociology, anthropology, psychology, economics, etc. It is about creating something by thinking across boundaries. It is related to an ''interdiscipline'' or an ''interdisciplinary field,'' which is an organizational unit that crosses traditional boundaries between academic disciplines or schools of thought, as new needs and professions emerge. Large engineering teams are usually interdisciplinary, as a power station or mobile phone or other project requires the melding of several specialties. However, the term "interdisciplinary" is sometimes confined to academic settings. The term ''interdisciplinary'' is applied within education and training pedagogies to describe studies that use methods and insights of several established disciplines or traditional fields of study. Interd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
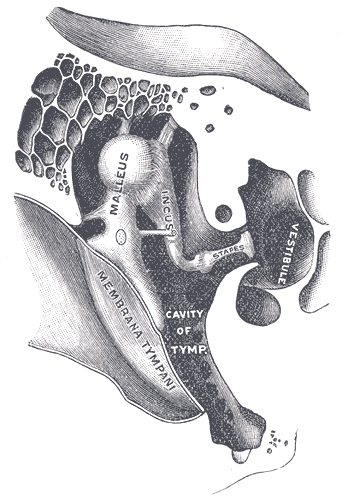
Hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid. In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the ... through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting Vibration, vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid, liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduction (physiology), transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Source
Historical source is an original source that contains important historical information. These sources are something that inform us about history at the most basic level, and are used as clues in order to study history. Historical sources can include coins, artefacts, monuments, literary sources, documents, artifacts, archaeological sites, features, oral transmissions, stone inscriptions, paintings, recorded sounds, images and oral history. Even ancient relics and ruins, broadly speaking, are historical sources. The types of sources include primary sources, secondary sources and tertiary sources. Types Primary source The natural morphological characters, the orographic and hydrographic structures, human interventions, buildings, infrastructures, archaeological finds, are "material sources that illustrate the uses and settlement forms of the past. The literary descriptions, the artistic images, the cartographic testimonies, are verbal or iconic sources able to provide othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Touch
The royal touch (also known as the king's touch) was a form of laying on of hands, whereby French and English monarchs touched their subjects, regardless of social classes, with the intent to cure them of various diseases and conditions. The thaumaturgic touch was most commonly applied to people suffering from tuberculous cervical lymphadenitis (better known as scrofula or the King's Evil), and exclusively to them from the 16th century onwards. The disease rarely resulted in death and often went into remission on its own, giving the impression that the monarch's touch cured it. The claimed power was most notably exercised by monarchs who sought to demonstrate the legitimacy of their reign and of their newly founded dynasties. Origins The kings and queens regnant of England and the kings of France were the only Christian rulers who claimed the divine gift (''divinitus'') to cure by touching or stroking the diseased. This special aptitude was thought to be evidence of God's hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern Britain
Early modern Britain is the history of the island of Great Britain roughly corresponding to the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries. Major historical events in early modern British history include numerous wars, especially with France, along with the English Renaissance, the English Reformation and Scottish Reformation, the English Civil War, the Restoration of Charles II, the Glorious Revolution, the Treaty of Union, the Scottish Enlightenment and the formation and the collapse of the First British Empire. England during the Tudor period (1486–1603) English Renaissance The term, "English Renaissance" is used by many historians to refer to a cultural movement in England in the 16th and 17th centuries that was heavily influenced by the Italian Renaissance. This movement is characterised by the flowering of English music (particularly the English adoption and development of the madrigal), notable achievements in drama (by William Shakespeare, Christopher Marlowe, and Ben Jon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Renaissance
The English Renaissance was a Cultural movement, cultural and Art movement, artistic movement in England from the early 16th century to the early 17th century. It is associated with the pan-European Renaissance that is usually regarded as beginning in Italy in the late 14th century. As in most of the rest of northern Europe, England saw little of these developments until more than a century later. Renaissance style and ideas, however, were slow to penetrate England, and the Elizabethan era in the second half of the 16th century is usually regarded as the height of the English Renaissance. However, many scholars see its beginnings in the early 16th century, during the reign of Henry VIII. The English Renaissance is different from the Italian Renaissance in several ways. The dominant art forms of the English Renaissance were literature and music. Visual arts in the English Renaissance were much less significant than in the Italian Renaissance. The English period began far later than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus is the Son of God, whose coming as the messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testament. Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century Hellenistic Judaism in the Roman province of Judea. Jesus' apostles and their followers spread around the Levant, Europe, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, the South Caucasus, Ancient Carthage, Egypt, and Ethiopia, despite significant initial persecution. It soon attracted gentile God-fearers, which led to a departure from Jewish customs, and, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Sexuality
The social construction of human sexuality and sexual behavior—along with its taboos, regulation, and social and political impact—has had a profound effect on the various cultures of the world since prehistoric times. The study of the history of human sexuality The work of Swiss jurist Johann Bachofen made a major impact on the study of the history of sexuality. Many authors, notably Lewis Henry Morgan and Friedrich Engels, were influenced by Bachofen, and criticized Bachofen's ideas on the subject, which were almost entirely drawn from a close reading of ancient mythology. In his 1861 book ''Mother Right: An Investigation of the Religious and Juridical Character of Matriarchy in the Ancient World'' Bachofen writes that in the beginning human sexuality was chaotic and promiscuous. This "aphroditic" stage was replaced by a matriarchal "demeteric" stage, which resulted from the mother being the only reliable way of establishing descendants. Only upon the switch to male-enfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racism
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagonism directed against other people because they are of a different race or ethnicity. Modern variants of racism are often based in social perceptions of biological differences between peoples. These views can take the form of social actions, practices or beliefs, or political systems in which different races are ranked as inherently superior or inferior to each other, based on presumed shared inheritable traits, abilities, or qualities. There have been attempts to legitimize racist beliefs through scientific means, such as scientific racism, which have been overwhelmingly shown to be unfounded. In terms of political systems (e.g. apartheid) that support the expression of prejudice or aversion in discriminatory practices or laws, racist ideology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorenz Oken
Lorenz Oken (1 August 1779 – 11 August 1851) was a German naturalist, botanist, biologist, and ornithologist. Oken was born Lorenz Okenfuss (german: Okenfuß) in Bohlsbach (now part of Offenburg), Ortenau, Baden, and studied natural history and medicine at the universities of Freiburg and Würzburg. He went on to the University of Göttingen, where he became a ''Privatdozent'' (unsalaried lecturer), and shortened his name to Oken. As Lorenz Oken, he published a small work entitled ''Grundriss der Naturphilosophie, der Theorie der Sinne, mit der darauf gegründeten Classification der Thiere'' (1802). This was the first of a series of works which established him as a leader of the movement of " Naturphilosophie" in Germany. In it he extended to physical science the philosophical principles which Immanuel Kant (1724–1804) had applied to epistemology and morality. Oken had been preceded in this by Johann Gottlieb Fichte (1762–1814), who, acknowledging that Kant had discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatosensory System
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch (haptic perception), as well as temperature (thermoception), body position (proprioception), and pain. It is a subset of the sensory nervous system, which also represents visual, auditory, olfactory, and gustatory stimuli. Somatosensation begins when mechano- and thermosensitive structures in the skin or internal organs sense physical stimuli such as pressure on the skin (see mechanotransduction, nociception). Activation of these structures, or receptors, leads to activation of peripheral sensory neurons that convey signals to the spinal cord as patterns of action potentials. Sensory information is then processed locally in the spinal cord to drive reflexes, and is also conveyed to the brain for conscious perception of touch and proprioception. Note, somatosensory information from the face and head enters the brain through periphera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |