|
Self-referential Encoding
Self-referential encoding is a method of organizing information in one's memory in which one interprets incoming information in relation to oneself, using one's self-concept as a background.Rogers, T. B., Kuiper, N. A., & Kirker, W. S. (1977). Self-reference and the encoding of personal information. ''Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 35''(9), 677–688. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.35.9.677 Examples include being able to attribute personality traits to oneself or to identify recollected episodes as being personal memories of the past.Benoit, R. G., Gilbert, S. J., Volle, E., & Burgess, P. W. (2010). When I think about me and simulate you: Medial rostral prefrontal cortex and self-referential processes. ''Neuroimage, 50''(3), 1340–1349. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.12.091 The implications of self-referential processing are evident in many psychological phenomena. For example, the "cocktail party effect" notes that people attend to the sound of their names even during other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Organization
Knowledge organization (KO), organization of knowledge, organization of information, or information organization is an intellectual discipline concerned with activities such as document description, indexing, and classification that serve to provide systems of representation and order for knowledge and information objects. According to ''The Organization of Information'' by Joudrey and Taylor, information organization: Issues related to knowledge sharing can be said to have been an important part of knowledge management for a long time. Knowledge sharing has received a lot of attention in research and business practice both within and outside organizations and its different levels. Sharing knowledge is not only about giving it to others, but it also includes searching, locating, and absorbing knowledge. Unawareness of the employees’ works and duties tend to provoke the repetition of mistakes, the waste of resources, and duplicating the same projects. It is important to mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recall (memory)
Recall in memory refers to the mental process of retrieval of information from the past. Along with encoding and storage, it is one of the three core processes of memory. There are three main types of recall: free recall, cued recall and serial recall. Psychologists test these forms of recall as a way to study the memory processes of humansrecall. (2010). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved March 04, 2010, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online: http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/493353/recal/ref> and animals. Two main theories of the process of recall are the two-stage theory and the theory of Encoding specificity principle, encoding specificity. Theories Two-stage theory The ''two-stage theory'' states that the process of recall begins with a search and retrieval process, and then a decision or recognition process where the correct information is chosen from what has been retrieved. In this theory, recognition only involves the latter of these two stages, or processes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulation Theory Of Empathy
The simulation theory of empathy holds that humans anticipate and make sense of the behavior of others by activating mental processes that, if they culminated in action, would produce similar behavior. This includes intentional behavior as well as the expression of emotions. The theory says that children use their own emotions to predict what others will do; we project our own mental states onto others. Simulation theory is not primarily a theory about empathy, but rather a theory of how people understand others—that they do so by way of a kind of empathetic response. This theory uses more biological evidence than other theories of mind, such as the theory-theory. Origin Simulation theory is based in philosophy of mind, a branch of philosophy that studies the nature of the mind and its relationship to the brain, especially the work of Alvin Goldman and Robert Gordon. The discovery of mirror neurons in macaque monkeys provides a physiological mechanism to explain the common cod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Cingulate Cortex
The posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) is the caudal part of the cingulate cortex, located posterior to the anterior cingulate cortex. This is the upper part of the "limbic lobe". The cingulate cortex is made up of an area around the midline of the brain. Surrounding areas include the retrosplenial cortex and the precuneus. Cytoarchitectonically the posterior cingulate cortex is associated with Brodmann areas 23 and 31. The PCC forms a central node in the default mode network of the brain. It has been shown to communicate with various brain networks simultaneously and is involved in diverse functions. Along with the precuneus, the PCC has been implicated as a neural substrate for human awareness in numerous studies of both the anesthesized and vegetative (coma) states. Imaging studies indicate a prominent role for the PCC in pain and episodic memory retrieval. Increased size of the ventral PCC is related to a decline in working memory performance. The PCC has also been strongly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cingulate Cortex
The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the cingulate sulcus. The cingulate cortex is usually considered part of the limbic lobe. It receives inputs from the thalamus and the neocortex, and projects to the entorhinal cortex via the cingulum. It is an integral part of the limbic system, which is involved with emotion formation and processing, learning, and memory. The combination of these three functions makes the cingulate gyrus highly influential in linking motivational outcomes to behavior (e.g. a certain action induced a positive emotional response, which results in learning). This role makes the cingulate cortex highly important in disorders such as depression and schizophrenia. It also plays a role in executive function and respiratory control. Etymology The term ''cingul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
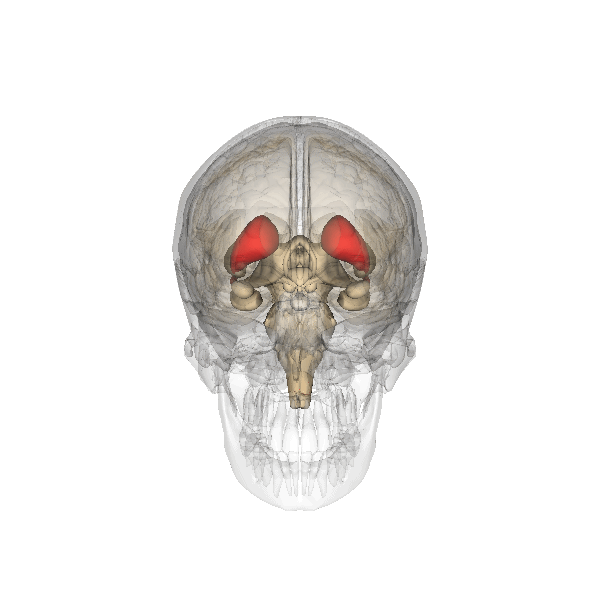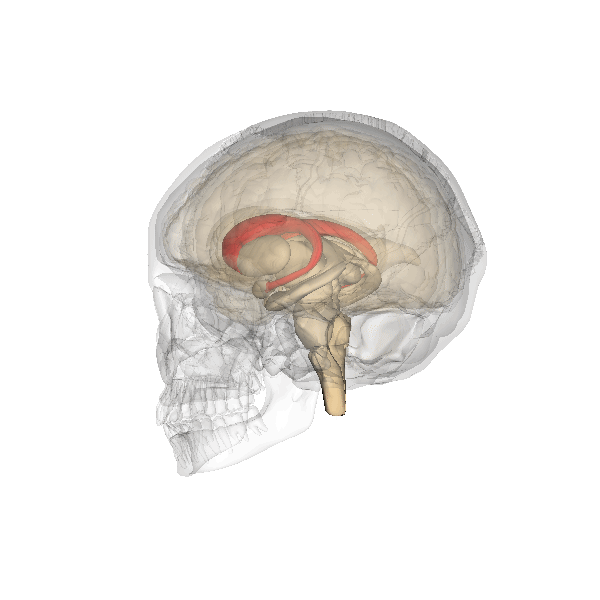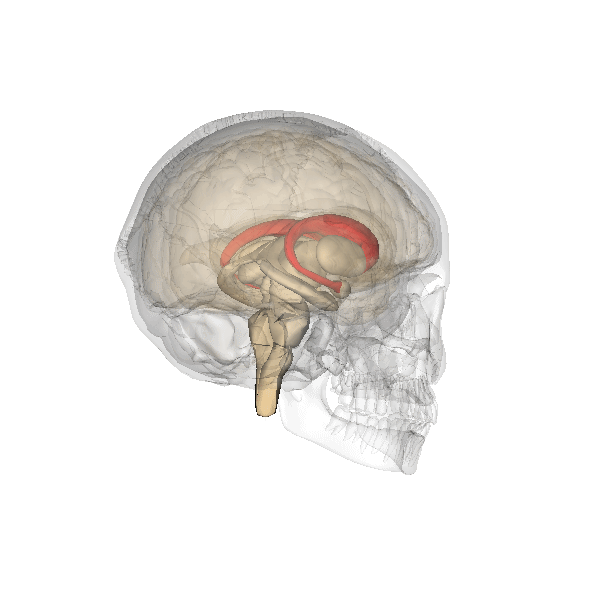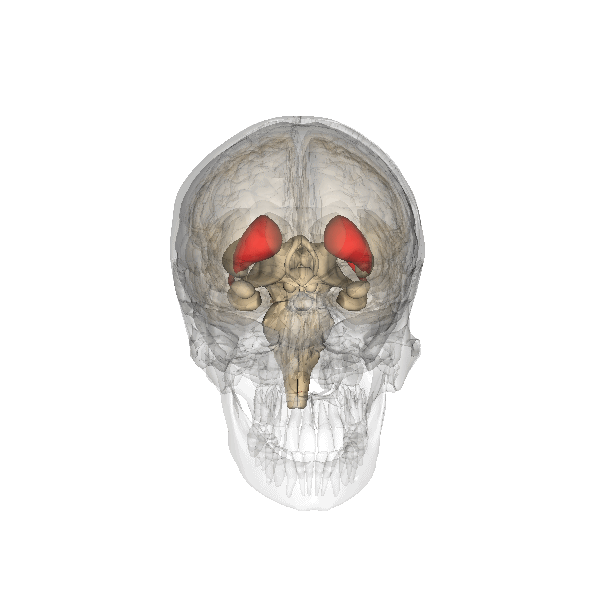
Caudate Nucleus
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatum, which is a component of the basal ganglia in the human brain. While the caudate nucleus has long been associated with motor processes due to its role in Parkinson's disease, it plays important roles in various other nonmotor functions as well, including procedural learning, associative learning and inhibitory control of action, among other functions. The caudate is also one of the brain structures which compose the reward system and functions as part of the cortico–basal ganglia– thalamic loop. Structure Together with the putamen, the caudate forms the dorsal striatum, which is considered a single functional structure; anatomically, it is separated by a large white matter tract, the internal capsule, so it is sometimes also referred to as two structures: the medial dorsal striatum (the caudate) and the lateral dorsal striatum (the putamen). In this vein, the two are functionally distinct not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefrontal Cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46, and BA47. The basic activity of this brain region is considered to be orchestration of thoughts and actions in accordance with internal goals. Many authors have indicated an integral link between a person's will to live, personality, and the functions of the prefrontal cortex. This brain region has been implicated in executive functions, such as planning, decision making, short-term memory, personality expression, moderating social behavior and controlling certain aspects of speech and language. Executive function relates to abilities to differentiate among conflicting thoughts, determine good and bad, better and best, same and different, future consequences of current activities, working toward a defined goal, prediction of outcomes, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbara Hayes-Roth
Barbara Hayes-Roth is an American computer scientist and psychologist whose research in artificial intelligence includes work on knowledge acquisition, automated planning and scheduling, spatial cognition, the blackboard system, adaptation, and intelligent behavior in interactive storytelling. She is a senior research scientist and lecturer in computer science at Stanford University. Education and career Hayes-Roth majored in psychology at Boston University, graduating magna cum laude in 1971. She went to the University of Michigan for graduate study in psychology, earning a master's degree in 1973 and completing her Ph.D. in 1974. Her dissertation, '' Interactions in the Acquisition and Utilization of Structured Knowledge'', was supervised by James Greeno. She became a researcher at Bell Laboratories from 1974 to 1976, and at the RAND Corporation from 1976 to 1982, also holding a position as consulting assistant professor in psychology at the University of California, Los Ang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meta-analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting measurements that are expected to have some degree of error. The aim then is to use approaches from statistics to derive a pooled estimate closest to the unknown common truth based on how this error is perceived. Meta-analytic results are considered the most trustworthy source of evidence by the evidence-based medicine literature.Herrera Ortiz AF., Cadavid Camacho E, Cubillos Rojas J, Cadavid Camacho T, Zoe Guevara S, Tatiana Rincón Cuenca N, Vásquez Perdomo A, Del Castillo Herazo V, & Giraldo Malo R. A Practical Guide to Perform a Systematic Literature Review and Meta-analysis. Principles and Practice of Clinical Research. 2022;7(4):47–57. https://doi.org/10.21801/ppcrj.2021.74.6 Not only can meta-analyses provide an estimate of the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association (psychology)
Association in psychology refers to a mental connection between concepts, events, or mental states that usually stems from specific experiences.Klein, Stephen (2012). ''Learning: Principles and Applications'' (6 ed.). SAGE Publications. . Associations are seen throughout several schools of thought in psychology including behaviorism, associationism, psychoanalysis, social psychology, and structuralism. The idea stems from Plato and Aristotle, especially with regard to the succession of memories, and it was carried on by philosophers such as John Locke, David Hume, David Hartley, and James Mill.Boring, E. G. (1950) It finds its place in modern psychology in such areas as memory, learning, and the study of neural pathways. Learned associations Associative learning is when a subject creates a relationship between stimuli (e.g. auditory or visual) or behavior and the original stimulus. The higher the concreteness of stimulus items, the more likely are they to evoke sensor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonemic
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language. For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-west of England, the sound patterns (''sin'') and (''sing'') are two separate words that are distinguished by the substitution of one phoneme, , for another phoneme, . Two words like this that differ in meaning through the contrast of a single phoneme form a ''minimal pair''. If, in another language, any two sequences differing only by pronunciation of the final sounds or are perceived as being the same in meaning, then these two sounds are interpreted as phonetic variants of a single phoneme in that language. Phonemes that are established by the use of minimal pairs, such as ''tap'' vs ''tab'' or ''pat'' vs ''bat'', are written between slashes: , . To show pronunciation, linguists use square brackets: (indicating an aspirated ''p'' in ''p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjectives
In linguistics, an adjective (abbreviated ) is a word that generally modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun. Traditionally, adjectives were considered one of the main parts of speech of the English language, although historically they were classed together with nouns. Nowadays, certain words that usually had been classified as adjectives, including ''the'', ''this'', ''my'', etc., typically are classed separately, as determiners. Here are some examples: * That's a funny idea. (attributive) * That idea is funny. ( predicative) * * The good, the bad, and the funny. ( substantive) Etymology ''Adjective'' comes from Latin ', a calque of grc, ἐπίθετον ὄνομα, epítheton ónoma, additional noun (whence also English '' epithet''). In the grammatical tradition of Latin and Greek, because adjectives were inflected for gender, number, and case like nouns (a process called declension), they we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |