|
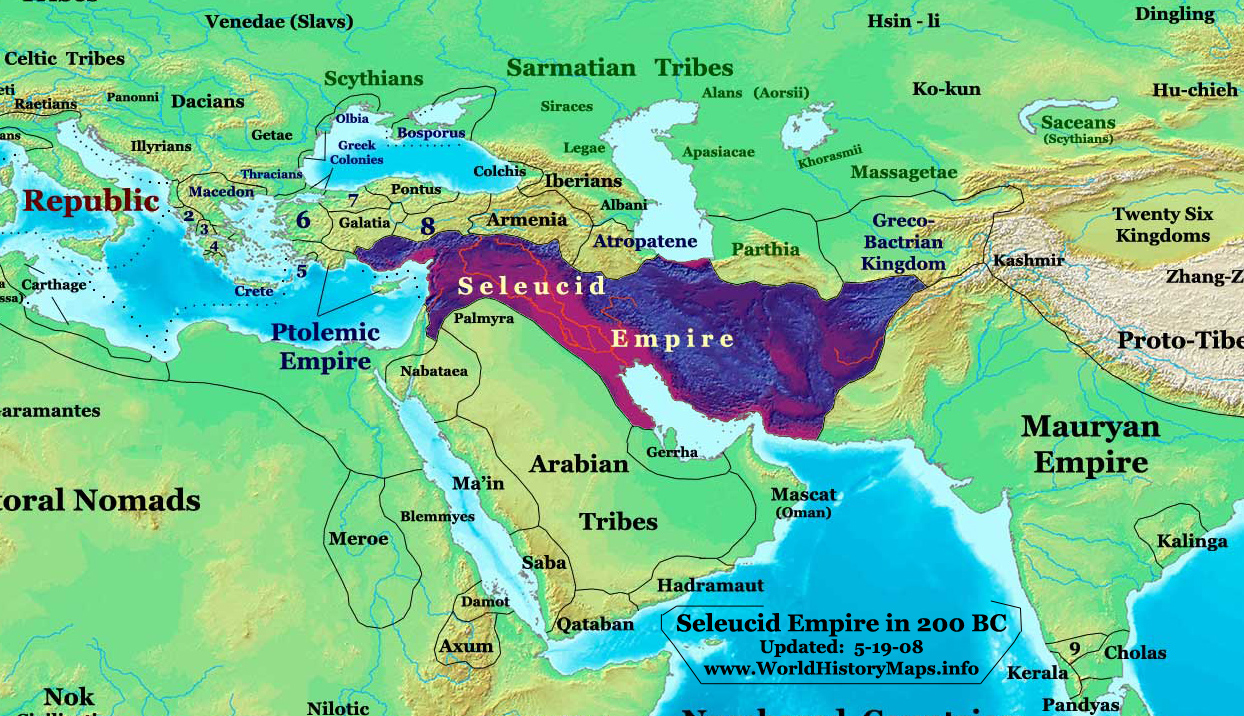
Seleucus IV
Seleucus IV Philopator (Ancient Greek, Greek: Σέλευκος Φιλοπάτωρ; c. 218 – 3 September 175 BC), ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire, reigned from 187 BC to 175 BC over a realm consisting of Coele-Syria, Syria (now including Cilicia and Judea), Mesopotamia, Babylonia and Nearer Iran (Media and Persia). Biography Birth and family He was the second son and successor of Antiochus III the Great and Laodice III. Seleucus IV wed his sister Laodice IV, by whom he had three children: two sons Demetrius I Soter, Antiochus (son of Seleucus IV), Antiochus and a daughter Laodice V. Seleucid conflict with Rome During the prelude to the Roman–Seleucid War, Roman-Seleucid War, Seleucus was put in charge of the re-established colony of Lysimachia (Thrace), Lysimacheia by his father. Upon the outbreak of war, Seleucus commanded his own force, unsuccessfully besieging Attalid dynasty, Pergamon, and taking the city of Phocaea before fighting in the Battle of Magnesia alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basileus
''Basileus'' ( el, ) is a Greek term and title that has signified various types of monarchs in history. In the English-speaking world it is perhaps most widely understood to mean "monarch", referring to either a "king" or an "emperor" and also by bishops of the Eastern orthodox church and Eastern Catholic Churches. The title was used by sovereigns and other persons of authority in ancient Greece, the Byzantine emperors, and the kings of modern Greece. The feminine forms are ''basileia'' (), ''basilis'' (), ''basilissa'' (), or the archaic '' basilinna'' (), meaning "queen" or "empress". Etymology The etymology of ''basileus'' is uncertain. The Mycenaean form was *''gʷasileus'' ( Linear B: , ''qa-si-re-u''), denoting some sort of court official or local chieftain, but not an actual king. Its hypothetical earlier Proto-Greek form would be *''gʷatileus''. Some linguists assume that it is a non-Greek word that was adopted by Bronze Age Greeks from a pre-existing linguistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman–Seleucid War
The Seleucid War (192–188 BC), also known as the War of Antiochos or the Syrian War, was a military conflict between two coalitions led by the Roman Republic and the Seleucid Empire. The fighting took place in modern day southern Greece, the Aegean Sea and Asia Minor. The war was the consequence of a "cold war" between both powers, which had started in 196 BC. In this period, the Romans and the Seleucids attempted to settle spheres of influence by forging alliances with the small Greek city-states. The fighting ended with a clear Roman victory. In the Treaty of Apamea, the Seleucids were forced to give up Asia Minor, which fell to Roman allies. As a main result of the war, the Roman Republic gained hegemony over the Greek city-states and Asia Minor and became the only remaining major power around the Mediterranean Sea. Prelude Antiochus III the Great, the Seleucid king, first became involved with Greece when he signed an alliance with King Philip V of Macedon in 203 BC.Green ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus IV Epiphanes
Antiochus IV Epiphanes (; grc, Ἀντίοχος ὁ Ἐπιφανής, ''Antíochos ho Epiphanḗs'', "God Manifest"; c. 215 BC – November/December 164 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king who ruled the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his death in 164 BC. He was a son of King Antiochus III the Great. Originally named Mithradates (alternative form '' Mithridates''), he assumed the name Antiochus after he ascended the throne. Notable events during Antiochus's reign include his near-conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt, his persecution of the Jews of Judea and Samaria, and the rebellion of the Jewish Maccabees. Antiochus's accession to the throne was controversial, and he was seen as a usurper by some. After the death of his brother Seleucus IV Philopator in 175 BC, the "true" heir should have been Seleucus's son Demetrius I. However, Demetrius I was very young and a hostage in Rome at the time, and Antiochus seized the opportunity to declare himself king instead, successfully rall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace (cf. Tylis), who settled here and became a small transient foreign tribe in the 3rd century BC, following the Gallic invasion of the Balkans in 279 BC. It has been called the "Gallia" of the East. Geography Galatia was bounded on the north by Bithynia and Paphlagonia, on the east by Pontus and Cappadocia, on the south by Cilicia and Lycaonia, and on the west by Phrygia. Its capital was Ancyra (i.e. Ankara, today the capital of modern Turkey). Celtic Galatia The terms "Galatians" came to be used by the Greeks for the three Celtic peoples of Anatolia: the Tectosages, the Trocmii, and the Tolistobogii. By the 1st century BC, the Celts had become so Hellenized that some Greek writers called them ''Hellenogalatai'' (Ἑλληνογαλάτ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharnaces I Of Pontus
Pharnaces I ( el, Φαρνάκης; lived 2nd century BC), fifth king of Pontus, was of Persian and Greek ancestry. He was the son of King Mithridates III of Pontus and his wife Laodice, whom he succeeded on the throne. Pharnaces had two siblings: a brother called Mithridates IV of Pontus and a sister called Laodice who both succeeded Pharnaces. He was born and raised in the Kingdom of Pontus. Life The date of his accession cannot be fixed with certainty; but it is certain, at least, that he was on the throne before 183 BC, in which year he succeeded in reducing the important city of Sinope, which had been long an object of ambition to the Kings of Pontus. The Rhodians sent an embassy to Rome to complain of this aggression, but without effect. About the same time Pharnaces became involved in disputes with his neighbour, King of Pergamon, Eumenes II, which led to repeated embassies from both monarchs to Rome, as well as to partial hostilities. But in the spring of 181 BC, witho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaean League
The Achaean League (Greek: , ''Koinon ton Akhaion'' "League of Achaeans") was a Hellenistic-era confederation of Greek city states on the northern and central Peloponnese. The league was named after the region of Achaea in the northwestern Peloponnese, which formed its original core. The first league was formed in the fifth century BC. The second Achaean League was established in 280 BC. As a rival of Antigonid Macedon and an ally of Rome, the league played a major role in the expansion of the Roman Republic into Greece. This process eventually led to the League's conquest and dissolution by the Romans in 146 BC. The League represents the most successful attempt by the Greek city states to develop a form of federalism, which balanced the need for collective action with the desire for local autonomy. Through the writings of the Achaean statesman Polybius, this structure has had an influence on the constitution of the United States and other modern federal states. History Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elymais
Elymais or Elamais (Ἐλυμαΐς, Hellenic form of the more ancient name, Elam) was an autonomous state of the 2nd century BC to the early 3rd century AD, frequently a vassal under Parthian control. It was located at the head of the Persian Gulf in Susiana (the present-day region of Khuzestan, Iran). Most of the population probably descended from the ancient Elamites, who once had control of that area. General information The Elymaeans were reputed to be skilled archers. In 187 BC, they killed Antiochus III the Great after he had pillaged their temple of Bel. Nothing is known of their language, even though Elamite was still used by the Achaemenid Empire 250 years before the kingdom of Elymais came into existence. A number of Aramaic inscriptions are found in Elymais. The region's "wealth in silver and gold" is referred to in the deutero-canonical work 1 Maccabees, which refers to Elymais as a "city" of interest to Antiochus IV Epiphanes: the narrative there states that " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bel (mythology)
Bêl (; from akk, bēlu) is a title signifying "lord" or "master" applied to various gods in the Mesopotamian religion of Akkad, Assyria, and Babylonia. The feminine form is ''Bêlit'' ('Lady, Mistress') in Akkadian. ''Bel'' is represented in Greek as Belos and in Latin as Belus. ''Belit'' appears in Greek form as Beltis (Βελτις). Linguistically, ''Bel'' is an East Semitic form cognate with the Northwest Semitic Baal with the same meaning. ''Bel'' was especially used for the Babylonian god Marduk in Assyrian and neo-Babylonian personal names or mentioned in inscriptions in a Mesopotamian context. Similarly, ''Bêlit'' mostly refers to Marduk's spouse Sarpanit. Marduk's mother, the Sumerian religion, Sumerian goddess often referred to in the Sumerian language as Ninhursag, Damgalnuna, Damkina, and Ninmah, was often known as ''Belit-ili'' ("Lady of the Gods") in Akkadian. Other gods called "Lord" were sometimes identified totally or in part with Bel Marduk. The god Malak-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galatian War
The Galatian War was a war between the Galatian Gauls and the Roman Republic supported by their allies Pergamum in 189 BC. The war was fought in Galatia in central Asia Minor, in present-day Turkey. The Romans had just defeated the Seleucids in the Roman-Syrian War and had forced them to thereby sue for peace. Following their recently successful operation in Syria, the Romans then turned their attention towards the Gallic tribes of Galatia who had emigrated to Asia Minor almost 100 years prior to the ensuing military engagement. Gnaeus Manlius Vulso, the consul, excused the invasion by saying that it was in retaliation for the Galatians supplying troops to the Seleucids during the war. Vulso embarked on this campaign without the permission of the Roman Senate. Joined by Pergamum, the Romans marched inland and attacked the Galatians. They defeated the Galatians in a battle on Mount Olympus and followed up the victory by defeating a larger army near Ancyra (modern Ankara, Turkey). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period—from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. Roman society under the Republic was primarily a cultural mix of Latin and Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Roman Pantheon. Its political organization developed, at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by a senate. The top magistrates were the two consuls, who had an extensive range of executive, legislative, judicial, military, and religious powers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Apamea
The Treaty of Apamea was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman–Seleucid War. The treaty took place after Roman victories at the Battle of Thermopylae (in 191 BC), the Battle of Magnesia (in 190 BC), and after Roman and Rhodian naval victories over the Seleucid navy. Terms of the treaty The treaty, according to Appian, obliged Antiochus III to abandon Europe altogether and all of Asia west of the Taurus Mountains. He had to surrender all the war elephants in his possession and was limited to twelve warships for the purpose of keeping his subjects under control, but he was allowed to build more if he was attacked. Antiochus was barred from recruiting mercenaries "north of the Taurus" (that is, from territory just ceded to Roman allies Pergamon and Rhodes) and entertaining fugitives from the same. Antiochus had to give twenty hostages, whom the Roman consul would select. The hostages should ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of Pergamon under Eumenes II against a Seleucid army of Antiochus III the Great. The two armies initially camped north-east of Magnesia ad Sipylum in Asia Minor (modern-day Manisa, Turkey), attempting to provoke each other into a battle on favorable terrain for several days. When the battle finally began, Eumenes managed to throw the Seleucid left flank into disarray. While Antiochus' cavalry overpowered his adversaries on the right flank of the battlefield, his army's center collapsed before he could reinforce it. Modern estimates give 10,000 dead for the Seleucids and 5,000 killed for the Romans. The battle resulted in a decisive Roman-Pergamene victory, which led to the Treaty of Apamea that ended Seleucid domination in Asia Minor. Backgrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |