|
Seismic Tomography
Seismic tomography or seismotomography is a technique for imaging the subsurface of the Earth with seismic waves produced by earthquakes or explosions. P-, S-, and surface waves can be used for tomographic models of different resolutions based on seismic wavelength, wave source distance, and the seismograph array coverage. The data received at seismometers are used to solve an inverse problem, wherein the locations of reflection and refraction of the wave paths are determined. This solution can be used to create 3D images of velocity anomalies which may be interpreted as structural, thermal, or compositional variations. Geoscientists use these images to better understand core, mantle, and plate tectonic processes. Theory Tomography is solved as an inverse problem. Seismic travel time data are compared to an initial Earth model and the model is modified until the best possible fit between the model predictions and observed data is found. Seismic waves would travel in straight lines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-wave
A P wave (primary wave or pressure wave) is one of the two main types of elastic body waves, called seismic waves in seismology. P waves travel faster than other seismic waves and hence are the first signal from an earthquake to arrive at any affected location or at a seismograph. P waves may be transmitted through gases, liquids, or solids. Nomenclature The name ''P wave'' can stand for either pressure wave (as it is formed from alternating compressions and rarefactions) or primary wave (as it has high velocity and is therefore the first wave to be recorded by a seismograph). The name '' S wave'' represents another seismic wave propagation mode, standing for secondary or shear wave. Seismic waves in the Earth Primary and secondary waves are body waves that travel within the Earth. The motion and behavior of both P and S waves in the Earth are monitored to probe the interior structure of the Earth. Discontinuities in velocity as a function of depth are indicative of cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismograph
A seismometer is an instrument that responds to ground noises and shaking such as caused by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and explosions. They are usually combined with a timing device and a recording device to form a seismograph. The output of such a device—formerly recorded on paper (see picture) or film, now recorded and processed digitally—is a seismogram. Such data is used to locate and characterize earthquakes, and to study the Earth's internal structure. Basic principles A simple seismometer, sensitive to up-down motions of the Earth, is like a weight hanging from a spring, both suspended from a frame that moves along with any motion detected. The relative motion between the weight (called the mass) and the frame provides a measurement of the vertical ground motion. A rotating drum is attached to the frame and a pen is attached to the weight, thus recording any ground motion in a seismogram. Any movement from the ground moves the frame. The mass tends not to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake River Plain
image:Snake River view near Twin Falls, Idaho.jpg, The Snake River cutting through the plain leaves many canyons and Canyon#List of gorges, gorges, such as this one near Twin Falls, Idaho The Snake River Plain is a geology, geologic feature located primarily within the U.S. state of Idaho. It stretches about westward from northwest of the state of Wyoming to the Idaho-Oregon border. The plain is a wide, flat bow-shaped depression and covers about a quarter of Idaho. Three major volcanic buttes dot the plain east of Arco, Idaho, Arco, the largest being Big Southern Butte. Most of Idaho's major cities are in the Snake River Plain, as is much of its agricultural land. Geology The Snake River Plain can be divided into three sections: western, central, and eastern. The western Snake River Plain is a large tectonic graben or rift valley filled with several kilometers of lacustrine (lake) sediments; the sediments are underlain by rhyolite and basalt, and overlain by basalt. The w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowstone Caldera
The Yellowstone Caldera, sometimes referred to as the Yellowstone Supervolcano, is a volcanic caldera and supervolcano in Yellowstone National Park in the Western United States. The caldera and most of the park are located in the northwest corner of Wyoming. The caldera measures , and postcaldera lavas spill out a significant distance beyond the caldera proper. The caldera formed during the last of three supereruptions over the past 2.1 million years: the Huckleberry Ridge eruption 2.1 million years ago (which created the Island Park Caldera and the Huckleberry Ridge Tuff), the Mesa Falls eruption 1.3 million years ago (which created the Henry's Fork Caldera and the Mesa Falls Tuff), and the Lava Creek eruption approximately 640,000 years ago (which created the Yellowstone Caldera and the Lava Creek Tuff). Volcanoes at Yellowstone Volcanism at Yellowstone is relatively recent, with calderas created by large eruptions that took place 2.1 million, 1.3 million, and 640,000 y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowstone Hotspot
The Yellowstone hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in the United States responsible for large scale volcanism in Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Oregon, and Wyoming, formed as the North American tectonic plate moved over it. It formed the eastern Snake River Plain through a succession of caldera-forming eruptions. The resulting calderas include the Island Park Caldera, Henry's Fork Caldera, and the Bruneau-Jarbidge caldera. The hotspot currently lies under the Yellowstone Caldera. The hotspot's most recent caldera-forming supereruption, known as the Lava Creek Eruption, took place 640,000 years ago and created the Lava Creek Tuff, and the most recent Yellowstone Caldera. The Yellowstone hotspot is one of a few volcanic hotspots underlying the North American tectonic plate; another example is the Anahim hotspot. Snake River Plain The eastern Snake River Plain is a topographic depression that cuts across Basin and Range Mountain structures, more or less parallel to North American plate mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diapir
A diapir (; , ) is a type of igneous intrusion in which a more mobile and ductily deformable material is forced into brittle overlying rocks. Depending on the tectonic environment, diapirs can range from idealized mushroom-shaped Rayleigh–Taylor-instability-type structures in regions with low tectonic stress such as in the Gulf of Mexico to narrow dikes of material that move along tectonically induced fractures in surrounding rock. The term was introduced by the Romanian geologist Ludovic Mrazek, who was the first to understand the principle of salt tectonics and plasticity. The term ''diapir'' may be applied to igneous structures, but it is more commonly applied to non-igneous, relatively cold materials, such as salt domes and mud diapirs. Occurrence Differential loading causes salt deposits covered by overburden (sediment) to rise upward toward the surface and pierce the overburden, forming diapirs (including salt domes), pillars, sheets, or other geological structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
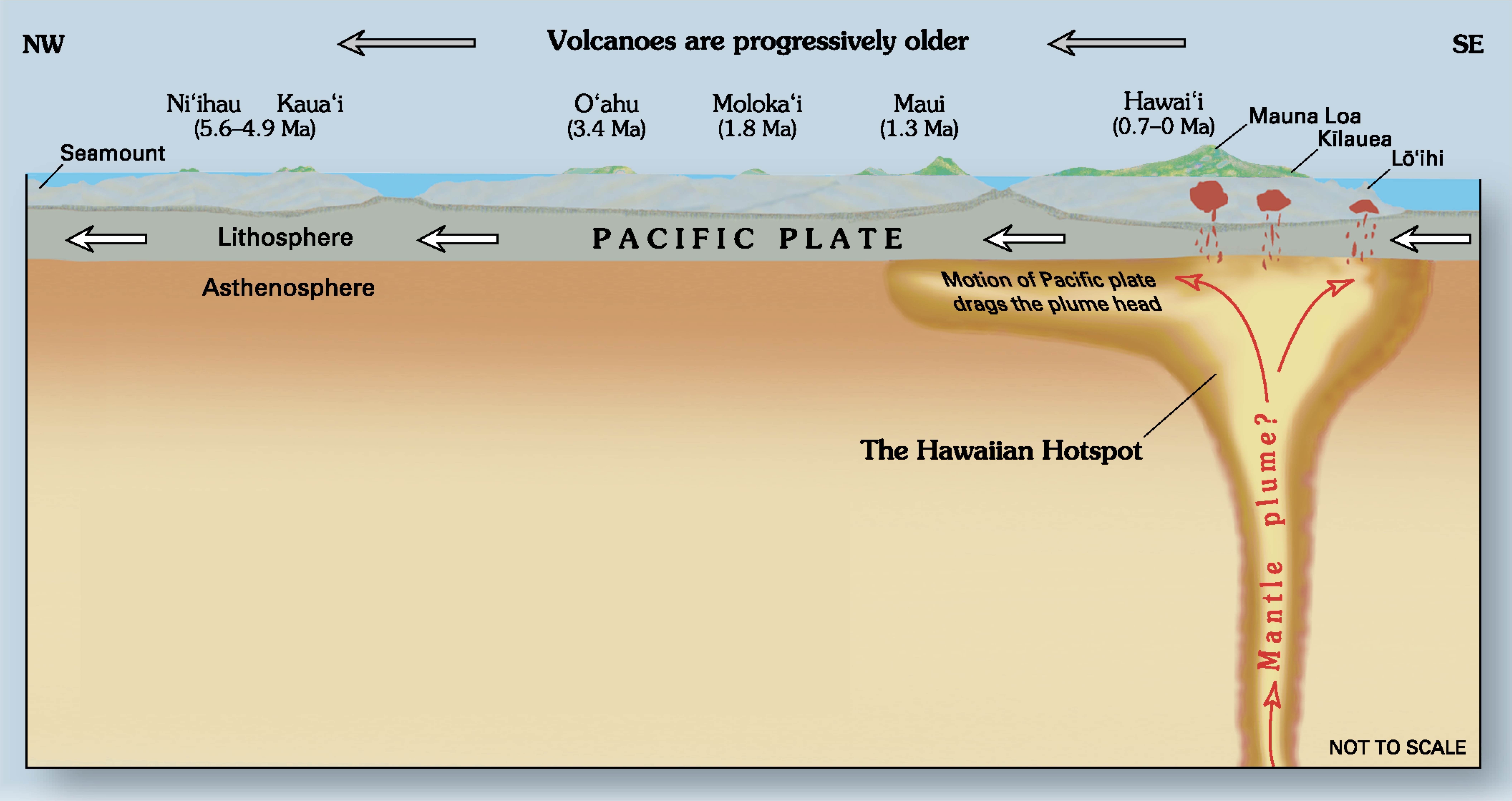
Hotspot (geology)
In geology, hotspots (or hot spots) are volcanic locales thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Examples include the Hawaii, Iceland, and Yellowstone hotspots. A hotspot's position on the Earth's surface is independent of tectonic plate boundaries, and so hotspots may create a chain of volcanoes as the plates move above them. There are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins. One suggests that hotspots are due to mantle plumes that rise as thermal diapirs from the core–mantle boundary. The alternative plate theory is that the mantle source beneath a hotspot is not anomalously hot, rather the crust above is unusually weak or thin, so that lithospheric extension permits the passive rising of melt from shallow depths. Origin The origins of the concept of hotspots lie in the work of J. Tuzo Wilson, who postulated in 1963 that the formation of the Hawaiian Islands resulted from the slow movement of a tecton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartoon Of African LLSVP
A cartoon is a type of visual art that is typically drawn, frequently animated, in an unrealistic or semi-realistic style. The specific meaning has evolved over time, but the modern usage usually refers to either: an image or series of images intended for satire, caricature, or humor; or a motion picture that relies on a sequence of illustrations for its animation. Someone who creates cartoons in the first sense is called a ''cartoonist'', and in the second sense they are usually called an ''animator''. The concept originated in the Middle Ages, and first described a preparatory drawing for a piece of art, such as a painting, fresco, tapestry, or stained glass window. In the 19th century, beginning in ''Punch'' magazine in 1843, cartoon came to refer – ironically at first – to humorous artworks in magazines and newspapers. Then it also was used for political cartoons and comic strips. When the medium developed, in the early 20th century, it began to refer to animated films ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-ocean Ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting ocean basis but regardless, are traditionally called mid-ocean rid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shield (geology)
A shield is a large area of exposed Precambrian crystalline igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks that form tectonically stable areas. These rocks are older than 570 million years and sometimes date back to around 2 to 3.5 billion years. They have been little affected by tectonic events following the end of the Precambrian, and are relatively flat regions where mountain building, faulting, and other tectonic processes are minor, compared with the activity at their margins and between tectonic plates. Shields occur on all continents. Terminology The term shield cannot be used interchangeably with the term craton. However, shield can be used interchangeably with the term basement. The difference is that a craton describes a basement overlayed by a sedimentary platform while shield only describes the basement. The term ''shield'', used to describe this type of geographic region, appears in the 1901 English translation of ''Eduard Suess's Face of Earth'' by H. B. C. Sollas, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banana Doughnut Theory
The Banana Doughnut theory - also sometimes known as Born-Fréchet kernel theory, or Finite-frequency theory - is a model in seismic tomography that describes the shape of the Fresnel zone along the entire ray path of a body wave. This theory suggests that the area that influences the ray velocity is the surrounding material and not the infinitesimally small ray path. This surrounding material forms a tube enclosing the ray, but does not incorporate the ray path itself. The name was coined by Princeton University postdoc Henk Marquering. This theory gets the name "banana" because the tube of influence along the entire ray path from source to receiver is an arc resembling the fruit. The "doughnut A doughnut or donut () is a type of food made from leavened fried dough. It is popular in many countries and is prepared in various forms as a sweet snack that can be homemade or purchased in bakeries, supermarkets, food stalls, and franc ..." part of the name comes from the ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveform
In electronics, acoustics, and related fields, the waveform of a signal is the shape of its graph as a function of time, independent of its time and magnitude scales and of any displacement in time.David Crecraft, David Gorham, ''Electronics'', 2nd ed., , CRC Press, 2002, p. 62 In electronics, the term is usually applied to periodically varying voltages, currents, or electromagnetic fields. In acoustics, it is usually applied to steady periodic sounds—variations of pressure in air or other media. In these cases, the waveform is an attribute that is independent of the frequency, amplitude, or phase shift of the signal. The term can also be used for non-periodic signals, like chirps and pulses. The waveform of an electrical signal can be visualized in an oscilloscope or any other device that can capture and plot its value at various times, with a suitable scales in the time and value axes. The electrocardiograph is a medical device to record the waveform of the ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |