|
Season Extension
Season extension in agriculture is any method that allows a crop to be grown beyond its normal outdoor growing season and harvesting time frame, or the extra time thus achieved. To extend the growing season into the colder months, one can use unheated techniques such as floating row covers, low tunnels, caterpillar tunnels, or hoophouses. However, even if colder temperatures are mitigated, most crops will stop growing when the days become shorter than 10 hours, and resume after winter as the daylight increases above 10 hours. A hothouse — a greenhouse which is heated and illuminated — creates an environment where plants are fooled into thinking it is their normal growing season. Though this ''is'' a form of season extension for the grower, it is not the usual meaning of the term. Season extension can apply to other climates, where conditions other than cold and shortened period of sunlight end the growing year (e.g. a rainy season). Structures * Unheated greenhouses (also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Frame
In agriculture and gardening, a cold frame is a transparent-roofed enclosure, built low to the ground, used to protect plants from adverse weather, primarily excessive cold or wet. The transparent top admits sunlight and prevents heat escape via convection that would otherwise occur, particularly at night. Essentially, a cold frame functions as a miniature greenhouse to extend the growing season. Historically, cold frames were built to be used in addition to a heated greenhouse. The name itself exemplifies the distinction between the warm greenhouse and the unheated cold frame. They were frequently built as part of the greenhouse's foundation brickwork along the southern wall (in northern latitudes). This allowed seeds to be germinated in the greenhouse and then easily moved to the attached cold frame to be "hardened-off" before final planting outside. Cold frames are similar to some enclosed hotbeds, also called hotboxes. The difference is in the amount of heat generated inside. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. The history of agriculture began thousands of years ago. After gathering wild grains beginning at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers began to plant them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs and cattle were domesticated over 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. Industrial agriculture based on large-scale monoculture in the twentieth century came to dominate agricultural output, though about 2 billion people still depended on subsistence agriculture. The major agricultural products can be broadly grouped into foods, fibers, fuels, and raw materials (such as rubber). Food classes include cereals (grains), vegetables, fruits, cooking oils, meat, milk, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
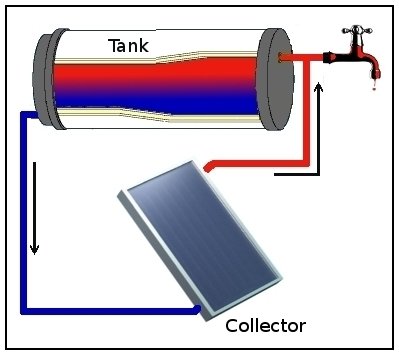
Thermosiphon
Thermosiphon (or thermosyphon) is a method of passive heat exchange, based on natural convection, which circulates a fluid without the necessity of a mechanical pump. Thermosiphoning is used for circulation of liquids and volatile gases in heating and cooling applications such as heat pumps, water heaters, boilers and furnaces. Thermosiphoning also occurs across air temperature gradients such as those utilized in a wood fire chimney or solar chimney. This circulation can either be open-loop, as when the substance in a holding tank is passed in one direction via a heated transfer tube mounted at the bottom of the tank to a distribution point—even one mounted above the originating tank—or it can be a vertical closed-loop circuit with return to the original container. Its purpose is to simplify the transfer of liquid or gas while avoiding the cost and complexity of a conventional pump. Simple thermosiphon Natural convection of the liquid starts when heat transfer to the liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coliform Bacteria
Coliform bacteria are defined as either motile or non-motile Gram-negative non- spore forming Bacilli that possess β-galactosidase to produce acids and gases under their optimal growth temperature of 35-37°C. They can be aerobes or facultative aerobes, and are a commonly used indicator of low sanitary quality of foods, milk, and water. Coliforms can be found in the aquatic environment, in soil and on vegetation; they are universally present in large numbers in the feces of warm-blooded animals as they are known to inhabit the gastrointestinal system. While coliform bacteria are not normally causes of serious illness, they are easy to culture, and their presence is used to infer that other pathogenic organisms of fecal origin may be present in a sample, or that said sample is not safe to consume. Such pathogens include disease-causing bacteria, viruses, or protozoa and many multicellular parasites. Genera Typical genera include: * '' Citrobacter ''are peritrichous facultative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic Mulch
Plastic mulch is a product used in plasticulture in a similar fashion to mulch, to suppress weeds and conserve water in crop production and landscaping. Certain plastic mulches also act as a barrier to keep methyl bromide, both a powerful fumigant and ozone depleter, in the soil. Crops grow through slits or holes in thin plastic sheeting. Plastic mulch is often used in conjunction with drip irrigation. Some research has been done using different colors of mulch to affect crop growth. Use of plastic mulch is predominant in large-scale vegetable growing, with millions of acres cultivated under plastic mulch worldwide each year. Disposal of plastic mulch is an environmental problem. Technologies exist to provide for the recycling of used/disposed plastic mulch into viable plastic resins for re-use in the plastics manufacturing industry. However these methods are not very effective due to contamination by agrochemicals of the plastic. Other concerns include residual microplastics in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mulch
A mulch is a layer of material applied to the surface of soil. Reasons for applying mulch include conservation of soil moisture, improving fertility and health of the soil, reducing weed growth and enhancing the visual appeal of the area. A mulch is usually, but not exclusively, organic in nature. It may be permanent (e.g. plastic sheeting) or temporary (e.g. bark chips). It may be applied to bare soil or around existing plants. Mulches of manure or compost will be incorporated naturally into the soil by the activity of worms and other organisms. The process is used both in commercial crop production and in gardening, and when applied correctly, can improve soil productivity. Living mulches include moss lawns and other ground covers. Uses Many materials are used as mulches, which are used to retain soil moisture, regulate soil temperature, suppress weed growth, and for aesthetics. They are applied to the soil surface, around trees, paths, flower beds, to prevent soil erosio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compost
Compost is a mixture of ingredients used as plant fertilizer and to improve soil's physical, chemical and biological properties. It is commonly prepared by decomposing plant, food waste, recycling organic materials and manure. The resulting mixture is rich in plant nutrients and beneficial organisms, such as bacteria, protozoa, nematodes and fungi. Compost improves soil fertility in gardens, landscaping, horticulture, urban agriculture, and organic farming, reducing dependency on commercial chemical fertilizers. The benefits of compost include providing nutrients to crops as fertilizer, acting as a soil conditioner, increasing the humus or humic acid contents of the soil, and introducing beneficial microbes that help to suppress pathogens in the soil and reduce soil-borne diseases. At the simplest level, composting requires gathering a mix of 'greens' (green waste) and 'browns' (brown waste). Greens are materials rich in nitrogen such as leaves, grass, and food scraps. Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotbed
A hotbed is a biological term for an area of decaying organic matter that is warmer than its surroundings. The heat gradient is generated by the decomposition of organic substituents within the pile by microorganism metabolization. A hotbed covered with a small glass cover (also called a hotbox) is used as a small version of a hothouse (heated greenhouse or cold frame). Oftentimes, this bed is made of manure from animals such as horses, which pass undigested plant cellulose in their droppings, creating a good environment for microorganisms to come and break down the cellulose and create a hotbed. (The digestive systems of ruminants Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The ... such as cattle and sheep destroy and use all cellulose in their food, and their droppings remain col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloche (agriculture)
In agriculture and gardening, a cloche (from French, ''cloche'' for "bell") is a covering for protecting plants from cold temperatures. The original form of a cloche is a bell-shaped glass cover that is placed over an individual plant; modern cloches are usually made from plastic. The use of cloches is traced back to market gardens in 19th century France, where entire fields of plants would be protected with cloches. In commercial growing, cloches have largely been replaced by row cover, and nowadays are mainly found in smaller gardens. History Parisian market gardens in the 1800s used 18-inch diameter bell-shaped glass jars (cloches) to protect plants in cold weather. They were used to protect everything from young seedlings to mature plants. Notched wooden sticks were used to prop up and vent the jars on sunny days, and were placed back down on the soil before nightfall. "Chase barn cloches", introduced in the early twentieth century by Major L.H. Chase, are constructed wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transpiration
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers. Water is necessary for plants but only a small amount of water taken up by the roots is used for growth and metabolism. The remaining 97–99.5% is lost by transpiration and guttation. Leaf surfaces are dotted with pores called stomata (singular "stoma"), and in most plants they are more numerous on the undersides of the foliage. The stomata are bordered by guard cells and their stomatal accessory cells (together known as stomatal complex) that open and close the pore. Transpiration occurs through the stomatal apertures, and can be thought of as a necessary "cost" associated with the opening of the stomata to allow the diffusion of carbon dioxide gas from the air for photosynthesis. Transpiration also cools plants, changes osmotic pressure of cells, and enables mass flow of mineral nutrients and water from roots to shoots. Two major factors i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Row Cover
In agriculture and gardening, row cover is any transparent or semi-transparent flexible material, like fabric or plastic sheeting, used as a protective covering for plants, usually vegetables. Covers are used to extend growing seasons, and reduce undesirable effects of cold, wind and insects. Article marked reviewed by publisher in 2012. Row covers can reduce the drying effect of wind, and can provide a small amount of warming in a similar way to unheated cold frames, greenhouses and polytunnels, creating a microclimate for the plants. The first commercial-scale use of polyethylene row covers in the US was in the 1950s, and by the 1980s their use was widespread. Row cover is a lightweight synthetic, such as clear plastic (polyethylene) or spunbonded polyester called horticultural fleece. Plastic covers are elevated above plants on a supporting framework such as wire hoops to form a low tunnel. (Plastic placed directly on the ground is mulch.) Fleece covers can be placed directl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Chimney
:''This article refers to a device for ventilation. For the power generation technology, see Solar updraft tower.'' A solar chimney often referred to as a thermal chimney is a way of improving the natural ventilation of buildings by using convection of air heated by passive solar energy. A simple description of a solar chimney is that of a vertical shaft utilizing solar energy to enhance the natural stack ventilation through a building. The solar chimney has been in use for centuries, particularly in the Middle East and Near East by the Persians, as well as in Europe by the Romans. Description In its simplest form, the solar chimney consists of a black-painted chimney. During the day solar energy heats the chimney and the air within it, creating an updraft of air in the chimney. The suction created at the chimney's base can be used to ventilate and cool the building below. In most parts of the world it is easier to harness wind power for such ventilation as with a windcatcher, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |