|
Seal Of Solomon
The Seal of Solomon or Ring of Solomon ( he, חותם שלמה, '; ar, خاتم سليمان, ') is the legendary signet ring attributed to the Israelite king Solomon in medieval mystical traditions, from which it developed in parallel within Jewish mysticism, Islamic mysticism and Western occultism. It is the predecessor to the Star of David, the contemporary cultural and religious symbol of the Jewish people. It was often depicted in the shape of either a pentagram or a hexagram. In religious lore, the ring is variously described as having given Solomon the power to command the supernatural, including ' and ', and also the ability to speak with animals. Due to the proverbial wisdom of Solomon, it came to be seen as an amulet or talisman, or a symbol or character in medieval magic and Renaissance magic, occultism, and alchemy. Name The varied traditions refer to a seal, stamp or die, utilized to mark an impression often or most frequently by means of a signet ring own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talismanic Scroll At The Met
Talismanic (foaled February 28, 2013) is a retired British-bred, French-trained Thoroughbred racehorse who achieved his greatest success in America in the 2017 Breeders' Cup Turf. Background Talismanic is a "photogenic" dark bay horse with a large white blaze and four white stockings. He was bred by Darley Stud, which purchased his sire Medaglia d'Oro in 2009. Medaglia d'Oro was the most successful performer on the dirt of El Prado, a son of Sadler's Wells, with major wins including the Travers Stakes, Whitney Handicap and Donn Handicap. As a sire, Medaglia d'Oro is best known for his American runners on the dirt, including champions Rachel Alexandra and Songbird, but has also had success with turf performers in Australia and Europe. Talismanic's dam Magic Mission is a stakes-winning daughter of Machiavellian. She descends from the outstanding mare Highclere, winner of the 1000 Guineas and Prix de Diane. Other members of this family include Deep Impact, Nayef, Nashwan and Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance Magic
Renaissance magic was a resurgence in Hermeticism and Neo-Platonic varieties of the Magic (supernatural), magical arts which arose along with Renaissance humanism in the 15th and 16th centuries CE. These magical arts (called ''#Artes magicae, artes magicae'') were divided into seven types. There was great uncertainty in distinguishing practices of superstition, occultism, and perfectly sound scholarly knowledge or pious ritual. The intellectual and spiritual tensions erupted in the Early Modern witch-hunt, witch craze, further reinforced by the turmoil of the Protestant Reformation, especially in Germany, England, and Scotland. Artes magicae The seven ''artes magicae'' or ''artes prohibitae'', arts prohibited by canon law, as expounded by Johannes Hartlieb in 1456, their sevenfold partition reflecting that of the artes liberales and artes mechanicae, were: #nigromancy ('black magic', demonolatry) #geomancy #hydromancy #aeromancy #pyromancy #chiromancy #scapulimancy The divisio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gittin
Gittin (Hebrew: ) is a tractate of the Mishnah and the Talmud, and is part of the order of Nashim. The content of the tractate primarily deals with the legal provisions related to halakhic divorce, in particular, the laws relating to the ''Get'' (divorce document), although the tractate contains a number of other social provisions which are only vaguely related to that subject, but which offer numerous historical references related to the time of the Jewish uprising. The laws of the divorce itself, including when a divorce is permitted or even required, are discussed in other tractates, namely Ketubot. The word ''get'' (Hebrew: ) is thought to be an Akkadian word and generally refers to a written document.The Recent Study of Hebrew: A Survey of the Literature with Selected Bibliography, Nahum M. Waldman, Eisenbrauns, 1989 See also * Get (divorce document) A or ''gett'' (; , plural ) is a document in Jewish religious law which effectuates a divorce between a Jewish cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggadic
Aggadah ( he, ''ʾAggāḏā'' or ''Haggāḏā''; Jewish Babylonian Aramaic: אַגָּדְתָא ''ʾAggāḏəṯāʾ''; "tales, fairytale, lore") is the non-legalistic exegesis which appears in the classical rabbinic literature of Judaism, particularly the Talmud and Midrash. In general, Aggadah is a compendium of rabbinic texts that incorporates folklore, historical anecdotes, moral exhortations, and practical advice in various spheres, from business to medicine. Etymology The Hebrew word ''haggadah'' (הַגָּדָה) is derived from the Hebrew root נגד, meaning "declare, make known, expound", also known from the common Hebrew verb להגיד.Berachyahu Lifshitz, "Aggadah Versus Haggadah : Towards a More Precise Understanding of the Distinction", ''Diné Yisrael'' 24 (2007): page 23 (English section). The majority scholarly opinion is that the Hebrew word ''aggadah'' (אַגָּדָה) and corresponding Aramaic ''aggadta'' (אַגָּדְתָא) are variants of ''h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sefer HaRazim
''Sefer HaRazim'' ( he, ספר הרזים; "Book of Secrets") is a Jewish magical text supposedly given to Noah by the angel Raziel, and passed down throughout Biblical history until it ended up in the possession of Solomon, for whom it was a great source of his wisdom and purported magical powers. Note that this is not the same work as the ''Sefer Raziel HaMalakh'', which was given to Adam by the same angel, although both works stem from the same tradition, and large parts of ''Sefer HaRazim'' were incorporated into the ''Sefer Raziel'' under its original title. It is thought to be a sourcebook for Jewish magic, calling upon angels rather than God to perform supernatural feats. Discovery The text was rediscovered in the 20th century by Mordecai Margalioth, a Jewish scholar visiting Oxford in 1963, using fragments found in the Cairo Geniza. He hypothesised that several fragments of Jewish magical literature shared a common source and was certain that he could reconstruct this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiquitates Judaicae
''Antiquities of the Jews'' ( la, Antiquitates Iudaicae; el, Ἰουδαϊκὴ ἀρχαιολογία, ''Ioudaikē archaiologia'') is a 20-volume historiographical work, written in Greek, by historian Flavius Josephus in the 13th year of the reign of Roman emperor Flavius Domitian which was around AD 93 or 94.Freedman, David Noel, ed., ''The Anchor Bible Dictionary'', (New York: Doubleday, 1997, 1992). ''Antiquities of the Jews'' contains an account of the history of the Jewish people for Josephus' gentile patrons. In the first ten volumes, Josephus follows the events of the Hebrew Bible beginning with the creation of Adam and Eve. The second ten volumes continues the history of the Jewish people beyond the biblical text and up to the Jewish War, or the First Jewish–Roman War, 66 to 73 CE. This work, along with Josephus's other major work, ''The Jewish War'' (''De Bello Iudaico''), provides valuable background material for historians wishing to understand 1st-century AD Jud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for ''The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly descent and a mother who claimed royal ancestry. He initially fought against the Romans during the First Jewish–Roman War as head of Jewish forces in Galilee, until surrendering in 67 AD to Roman forces led by Vespasian after the six-week siege of Yodfat. Josephus claimed the Jewish Messianic prophecies that initiated the First Jewish–Roman War made reference to Vespasian becoming Emperor of Rome. In response, Vespasian decided to keep Josephus as a slave and presumably interpreter. After Vespasian became Emperor in 69 AD, he granted Josephus his freedom, at which time Josephus assumed the emperor's family name of Flavius.Simon Claude Mimouni, ''Le Judaïsme ancien du VIe siècle avant notre ère au IIIe siècle de notre ère : Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
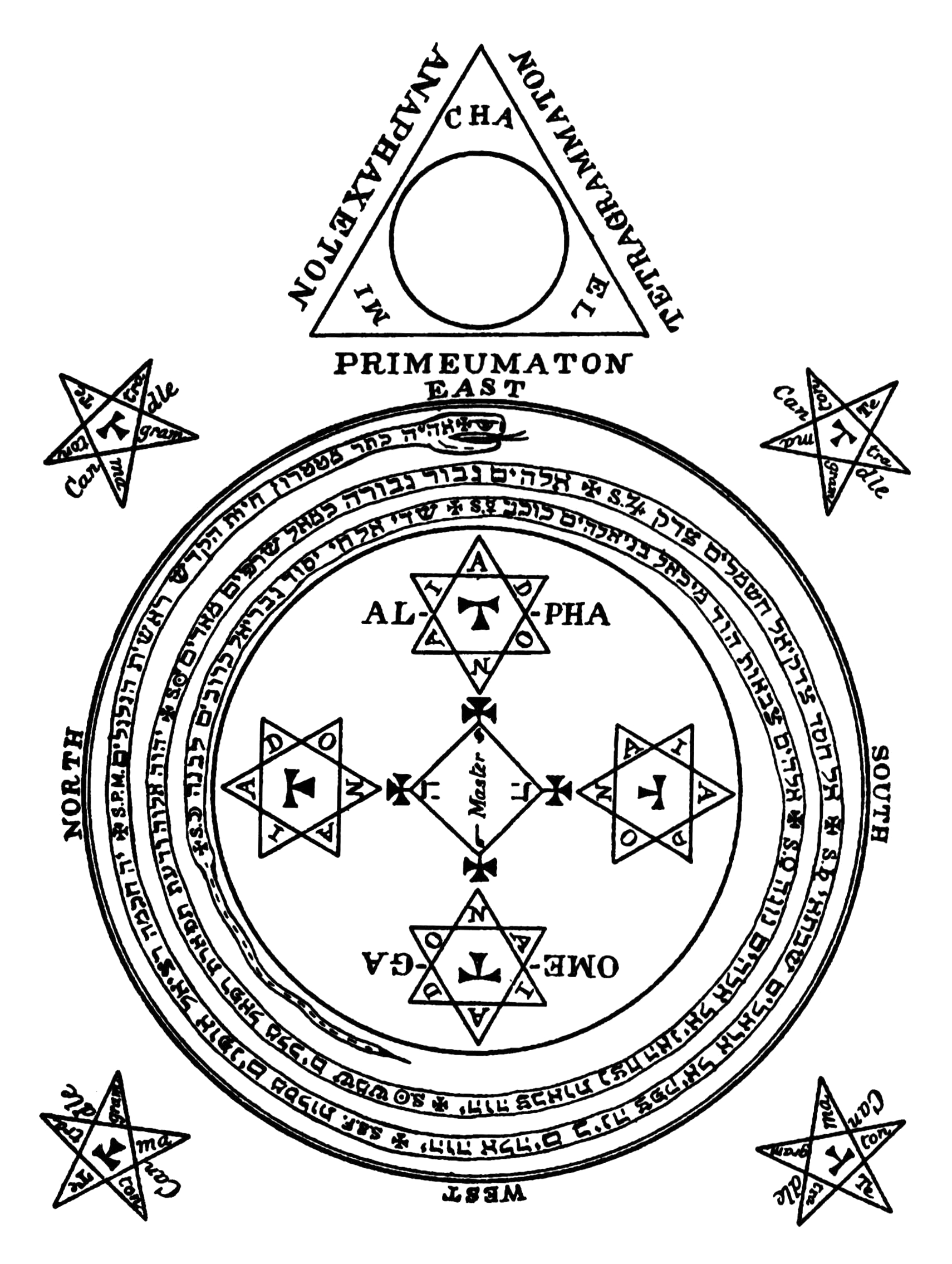
Goetia Seal Of Solomon
''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', also known as ''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis'' or simply ''Lemegeton'', is an anonymous grimoire on demonology. It was compiled in the mid-17th century, mostly from materials a couple of centuries older.''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis: The Lesser Key of Solomon, Detailing the Ceremonial Art of Commanding Spirits Both Good and Evil''; ed. Joseph H. Peterson; Weiser Books Maine; 2001. pp. xi–xvii.''The Goetia of Dr Rudd''; Thomas Rudd, Eds. Stephen Skinner & David Rankine; 2007, Golden Hoard Press. p. 399. It is divided into five books—the ''Ars Goetia'', ''Ars Theurgia-Goetia'', ''Ars Paulina'', ''Ars Almadel'', and ''Ars Notoria''. ''Ars Goetia'' Etymology The text is more properly called "Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis, or, The little Key of Solomon". The title most commonly used, "The Lesser Key of Solomon," does not in fact occur in the manuscripts. A.E. Waite, in his 1898 ''Book of Black Magic and of Pacts'' does use the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moroccan 4 Falus Coin (AH 1290)
Moroccan may refer to: * Something or someone from, or related to the country of Morocco * Moroccan people * Moroccan Arabic, spoken in Morocco * Moroccan Jews See also * Morocco leather Morocco leather (also known as Levant, the French Maroquin, or German Saffian from Safi, Morocco, Safi, a Moroccan town famous for leather) is a Vegetable tanning, vegetable-tanned leather known for its softness, pliability, and ability to take c ... * * {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harun Al-Rashid
Abu Ja'far Harun ibn Muhammad al-Mahdi ( ar , أبو جعفر هارون ابن محمد المهدي) or Harun ibn al-Mahdi (; or 766 – 24 March 809), famously known as Harun al-Rashid ( ar, هَارُون الرَشِيد, translit=Hārūn al-Rashīd) was the fifth Abbasid caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate, reigning from September 786 until his death. His reign is traditionally regarded to be the beginning of the Islamic Golden Age. His epithet "al-Rashid" translates to "the Orthodox", "the Just", "the Upright", or "the Rightly-Guided". Harun established the legendary library Bayt al-Hikma ("House of Wisdom") in Baghdad in present-day Iraq, and during his rule Baghdad began to flourish as a world center of knowledge, culture and trade. During his rule, the family of Barmakids, which played a deciding role in establishing the Abbasid Caliphate, declined gradually. In 796, he moved his court and government to Raqqa in present-day Syria. A Frankish mission came to offer H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindbad
Sinbad the Sailor (; ar, سندباد البحري, Sindibādu al-Bahriyy; fa, سُنباد بحری, Sonbād-e Bahri or Sindbad) is a fictional mariner and the hero of a story-cycle of Persian origin. He is described as hailing from Baghdad during the early Abbasid Caliphate (8th and 9th centuries A.D.). In the course of seven voyages throughout the seas east of Africa and south of Asia, he has fantastic adventures in magical realms, encountering monsters and witnessing supernatural phenomena. Origins and sources The tales of Sinbad are a relatively late addition to the ''One Thousand and One Nights'' – they do not feature in the earliest 14th-century manuscript, and they appear as an independent cycle in 18th- and 19th-century collections. The tale reflects the trend within the Abbasid realm of Arab and Muslim sailors exploring the world. The stories display the folk and themes present in works of that time. The Abbasid reign was known as a period of great economic and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Nights
''One Thousand and One Nights'' ( ar, أَلْفُ لَيْلَةٍ وَلَيْلَةٌ, italic=yes, ) is a collection of Middle Eastern folk tales compiled in Arabic during the Islamic Golden Age. It is often known in English as the ''Arabian Nights'', from the first English-language edition (), which rendered the title as ''The Arabian Nights' Entertainment''. The work was collected over many centuries by various authors, translators, and scholars across West, Central and South Asia, and North Africa. Some tales trace their roots back to ancient and medieval Arabic, Egyptian, Sanskrit, Persian, and Mesopotamian literature. Many tales were originally folk stories from the Abbasid and Mamluk eras, while others, especially the frame story, are most probably drawn from the Pahlavi Persian work ( fa, هزار افسان, lit. ''A Thousand Tales''), which in turn relied partly on Indian elements. Common to all the editions of the ''Nights'' is the framing device of the story o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)