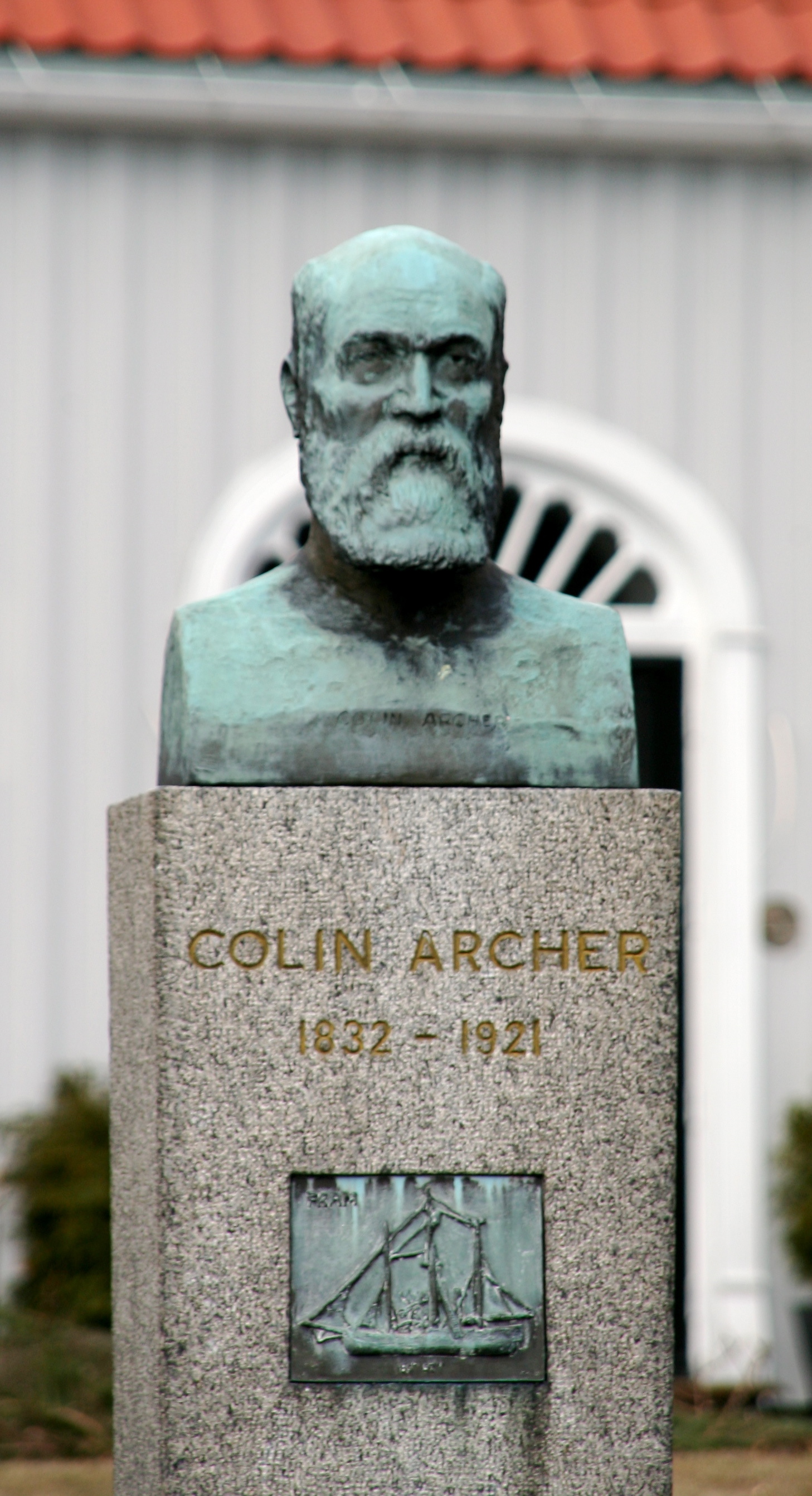|
Scotia (barque)
''Scotia'' was a barque that was built in 1872 as the Norwegian whaler ''Hekla''. She was purchased in 1902 by William Speirs Bruce and refitted as a research vessel for use by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition. After the expedition, she served as a sealer, patrol vessel and collier. She was destroyed by fire in January 1916. Description The ship was , with a beam of . She had a draught of . The ship was assessed at . History ''Hekla'' was built as a barque in 1872 by Jørgensen & Knudsen, Drammen for S. S. Svendsen of Sandefjord. She was used as a sealer, making voyages to the east coast of Greenland from 1872 to 1882 and to Scoresby Sound in 1892. In 1896, she was sold to N. Bugge, Tønsberg. She was sold in 1898 to A/S Sæl- og Hvalfangerskib Hekla, Christiania and was placed under the management of M. C. Tvethe. ''Hekla'' was sold in 1900 to A/S Hecla, Sandefjord, operated under the management of Anders Marcussen. In 1902, she was purchased by William Speirs Bru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barque
A barque, barc, or bark is a type of sailing ship, sailing vessel with three or more mast (sailing), masts having the fore- and mainmasts Square rig, rigged square and only the mizzen (the aftmost mast) Fore-and-aft rig, rigged fore and aft. Sometimes, the mizzen is only partly fore-and-aft rigged, bearing a square-rigged sail above. Etymology The word "barque" entered English via the French term, which in turn came from the Latin language, Latin ''barca'' by way of Occitan language, Occitan, Catalan language, Catalan, Spanish, or Italian. The Latin ''barca'' may stem from Celtic language, Celtic ''barc'' (per Rudolf Thurneysen, Thurneysen) or Greek ''baris'' (per Friedrich Christian Diez, Diez), a term for an Egyptian boat. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'', however, considers the latter improbable. The word ''barc'' appears to have come from Celtic languages. The form adopted by English, perhaps from Irish language, Irish, was "bark", while that adopted by Latin as ''barca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colin Archer
Colin Archer (22 July 1832 – 8 February 1921) was a Norwegian naval architect and shipbuilder known for his seaworthy pilot and rescue boats and the larger sailing and polar ships. His most famous ship is the ''Fram'', used on both in Fridtjof Nansen's and Roald Amundsen's polar expeditions. He was born at Tollerodden in Larvik, Norway, where he also had his own house built and his boatyard. Early life Colin Archer was born in Larvik in southern Norway as the 12th of 13 children to parents who immigrated to Norway from Scotland in 1825. Before his career in naval architecture, he spent time as a farmer and administrator in Queensland, Australia with several of his brothers, including David who first arrived in Sydney in 1834. During his time as an administrator he was contracted to produce a map of the Fitzroy River. Their settlement is now known as Gracemere Homestead. In 1861, Archer returned to Larvik and undertook the study of practical and theoretical shipbuildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayrshire
Ayrshire ( gd, Siorrachd Inbhir Àir, ) is a historic county and registration county in south-west Scotland, located on the shores of the Firth of Clyde. Its principal towns include Ayr, Kilmarnock and Irvine and it borders the counties of Renfrewshire and Lanarkshire to the north-east, Dumfriesshire to the south-east, and Kirkcudbrightshire and Wigtownshire to the south. Like many other counties of Scotland it currently has no administrative function, instead being sub-divided into the council areas of North Ayrshire, South Ayrshire and East Ayrshire. It has a population of approximately 366,800. The electoral and valuation area named Ayrshire covers the three council areas of South Ayrshire, East Ayrshire and North Ayrshire, therefore including the Isle of Arran, Great Cumbrae and Little Cumbrae. These three islands are part of the historic County of Bute and are sometimes included when the term ''Ayrshire'' is applied to the region. The same area is known as ''Ayrshire a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millport, Cumbrae
Millport (Scottish Gaelic: Port a' Mhuilinn) is the only town on the island of Great Cumbrae in the Firth of Clyde off the coast of mainland Britain, in the council area of North Ayrshire. The town is south of the ferry terminal that links the island to the Scottish mainland. Due to its small size, the island and its town are often linked in the minds of visitors and residents and Cumbrae is often referred to as Millport. The island offers views across to the Isle of Arran as well as of its smaller neighbour which lies barely a kilometre away, called Little Cumbrae. The Cumbraes are referred to as the ''Kumreyiar'' in the medieval Norse '' Saga of Haakon Haakonarson''. Etymology The Gaelic name ''Cumaradh'' means "place of the Cymric people", referring to the Brittonic-speaking inhabitants of the Kingdom of Strathclyde. Alternatively, the name Cumbrae may derive from ''Kil Maura'' meaning "cell or church of a female saint". History The Garrison House in the centre of town, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Helena
Saint Helena () is a British overseas territory located in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote volcanic tropical island west of the coast of south-western Africa, and east of Rio de Janeiro in South America. It is one of three constituent parts of the British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. Saint Helena measures about and has a population of 4,439 per the 2021 census. It was named after Helena, mother of Constantine I. It is one of the most remote islands in the world and was uninhabited when discovered by the Portuguese enroute to the Indian subcontinent in 1502. For about four centuries the island was an important stopover for ships from Europe to Asia and back, while sailing around the African continent, until the opening of the Suez canal. St Helena is the United Kingdom's second-oldest overseas territory after Bermuda. Saint Helena is known for being the site of Napoleon's second exile, following his final defeat in 1815. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weddell Sea
The Weddell Sea is part of the Southern Ocean and contains the Weddell Gyre. Its land boundaries are defined by the bay formed from the coasts of Coats Land and the Antarctic Peninsula. The easternmost point is Cape Norvegia at Princess Martha Coast, Queen Maud Land. To the east of Cape Norvegia is the King Haakon VII Sea. Much of the southern part of the sea is covered by a permanent, massive ice shelf field, the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf. The sea is contained within the two overlapping Antarctic territorial claims of Argentine Antarctica, the British Antarctic Territory, and also resides partially within the Antarctic Chilean Territory. At its widest the sea is around across, and its area is around . Various ice shelves, including the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf, fringe the Weddell sea. Some of the ice shelves on the east side of the Antarctic Peninsula, which formerly covered roughly of the Weddell Sea, had completely disappeared by 2002. The Weddell Sea has been deemed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South America's southeastern coast. "Buenos Aires" can be translated as "fair winds" or "good airs", but the former was the meaning intended by the founders in the 16th century, by the use of the original name "Real de Nuestra Señora Santa María del Buen Ayre", named after the Madonna of Bonaria in Sardinia, Italy. Buenos Aires is classified as an alpha global city, according to the Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) 2020 ranking. The city of Buenos Aires is neither part of Buenos Aires Province nor the Province's capital; rather, it is an autonomous district. In 1880, after decades of political infighting, Buenos Aires was federalized and removed from Buenos Aires Province. The city limits were enlarged to include t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotia Bay
Scotia Bay is a bay wide, lying immediately east of Mossman Peninsula on the south side of Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It was discovered and roughly charted in the course of the joint cruise by Captain George Powell and Captain Nathaniel Palmer in 1821. It was surveyed in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under William Speirs Bruce who named it for the expedition ship . Historic site An area of the bay contains a stone hut built in 1903 by the Scottish expedition and known as Ormond House; an Argentine meteorological hut and magnetic observatory, built in 1905 and known as Moneta House; and a graveyard with twelve graves, the oldest dating from 1903. These have been designated a Historic Site or Monument (HSM 42), following a proposal by Argentina to the Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Orkney Islands
The South Orkney Islands are a group of islands in the Southern Ocean, about north-east of the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula''Antarctica: Secrets of the Southern Continent'' p. 122 David McGonigal, 2009 and south-west of . They have a total area of about . The islands are claimed both by Britain (as part of the since 1962, previously as a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurie Island
Laurie Island is the second largest of the South Orkney Islands. The island is claimed by both Argentina as part of Argentine Antarctica, and the United Kingdom as part of the British Antarctic Territory. However, under the Antarctic Treaty System all sovereignty claims are frozen, as the island lies south of the parallel 60°. Buchanan Point at the north-eastern end of the island, with Cape Whitson on its south coast, are Important Bird Areas. History Laurie Island was discovered by Captains George Powell and Nathaniel Palmer in the course of their 1821 expedition to the South Atlantic. Richard Holmes Laurie used Powell's observations to create a map of the island, and subsequently, the island was named after him. Two years later, James Weddell mapped the island for the second time, though his charts turned out to be much less accurate than Powell's charts. Weddell attempted to rename the island to Melville Island for the 2nd Viscount Melville, but the name failed to stick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; es, Islas Malvinas, link=no ) is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about from Cape Dubouzet at the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, at a latitude of about 52°S. The archipelago, with an area of , comprises East Falkland, West Falkland, and 776 smaller islands. As a British overseas territory, the Falklands have internal self-governance, but the United Kingdom takes responsibility for their defence and foreign affairs. The capital and largest settlement is Stanley on East Falkland. Controversy exists over the Falklands' discovery and subsequent colonisation by Europeans. At various times, the islands have had French, British, Spanish, and Argentine settlements. Britain reasserted its rule in 1833, but Argentina maintains its claim to the islands. In April 1982, Argentine military forces invaded the islands. British a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic
The Antarctic ( or , American English also or ; commonly ) is a polar region around Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau and other island territories located on the Antarctic Plate or south of the Antarctic Convergence. The Antarctic region includes the ice shelves, waters, and all the island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence, a zone approximately wide varying in latitude seasonally. The region covers some 20 percent of the Southern Hemisphere, of which 5.5 percent (14 million km2) is the surface area of the Antarctica continent itself. All of the land and ice shelves south of 60°S latitude are administered under the Antarctic Treaty System. Biogeographically, the Antarctic realm is one of eight biogeographic realms of Earth's land surface. Geography As defined by the Antarctic Treaty System, the Antarctic r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |