|
Scoresby Land Group
The Scoresby Land Group is a geologic group found in the Jameson Land Basin, Scoresby Land, East Greenland. It preserves fossils dating back to the Triassic period. It comprises the Wordie Creek Formation (Lower Triassic), Pingo Dal Formation (?Lower Triassic), Gipsdalen Formation ( Middle to Upper Triassic) and the Fleming Fjord Formation (Upper Triassic). It is underlain by Upper Permian beds of the Schuchert Dal Formation and overlain by Rhaetian beds of the Kap Stewart Group. See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Greenland This is a list of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Greenland. List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Antarctica * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in North America * ... References Geologic groups of Europe Geologic groups of North America Geologic formations of Greenland Triassic Greenland {{Triassic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group (stratigraphy)
In geology, a group is a lithostratigraphic unit consisting of a series of related formations that have been classified together to form a group. Formations are the fundamental unit of stratigraphy. Groups may sometimes be combined into supergroups. Groups are useful for showing relationships between formations, and they are also useful for small-scale mapping or for studying the stratigraphy of large regions. Geologists exploring a new area have sometimes defined groups when they believe the strata within the groups can be divided into formations during subsequent investigations of the area. It is possible for only some of the strata making up a group to be divided into formations. An example of a group is the Glen Canyon Group, which includes (in ascending order) the Wingate Sandstone, the Moenave Formation, the Kayenta Formation, and the Navajo Sandstone. Each of the formations can be distinguished from its neighbor by its lithology, but all were deposited in the same vast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pingo Dal Formation
Pingos are intrapermafrost ice-cored hills, high and in diameter. They are typically conical in shape and grow and persist only in permafrost environments, such as the Arctic and subarctic. A pingo is a Periglaciation, periglacial landform, which is defined as a non-glacial landform or process linked to colder climates. It is estimated that there are more than 11,000 pingos on Earth. The Tuktoyaktuk peninsula area has the greatest concentration of pingos in the world with a total of 1,350 pingos. There is currently remarkably limited data on pingos. History In 1825, John Franklin made the earliest description of a pingo when he climbed a small pingo on Ellice Island in the Mackenzie River, Mackenzie Delta. However, it was in 1938 that the term ''pingo'' was first borrowed from the Inuvialuit by the Arctic botanist Erling Porsild, Alf Erling Porsild in his paper on Earth mounds of the western Arctic coast of Canada and Alaska. Porsild Pingo in Tuktoyaktuk is named in his h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Groups Of North America
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Groups Of Europe
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fossiliferous Stratigraphic Units In Greenland
This is a list of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Greenland. List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Antarctica * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in North America ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in the Northwest Territories ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Nunavut ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Newfoundland and Labrador * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Europe ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Iceland ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Norway ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Russia ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Svalbard References Bibliography * * * * Further reading * C. B. Skovsted and J. S. Peel. 2011. ''Hyolithellus'' in life position from the Lower Cambrian of north Greenland. Journal of Paleontology 85(1):37-47 * A. C. Daley and J. S. Peel. 2010. A Possible Ano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
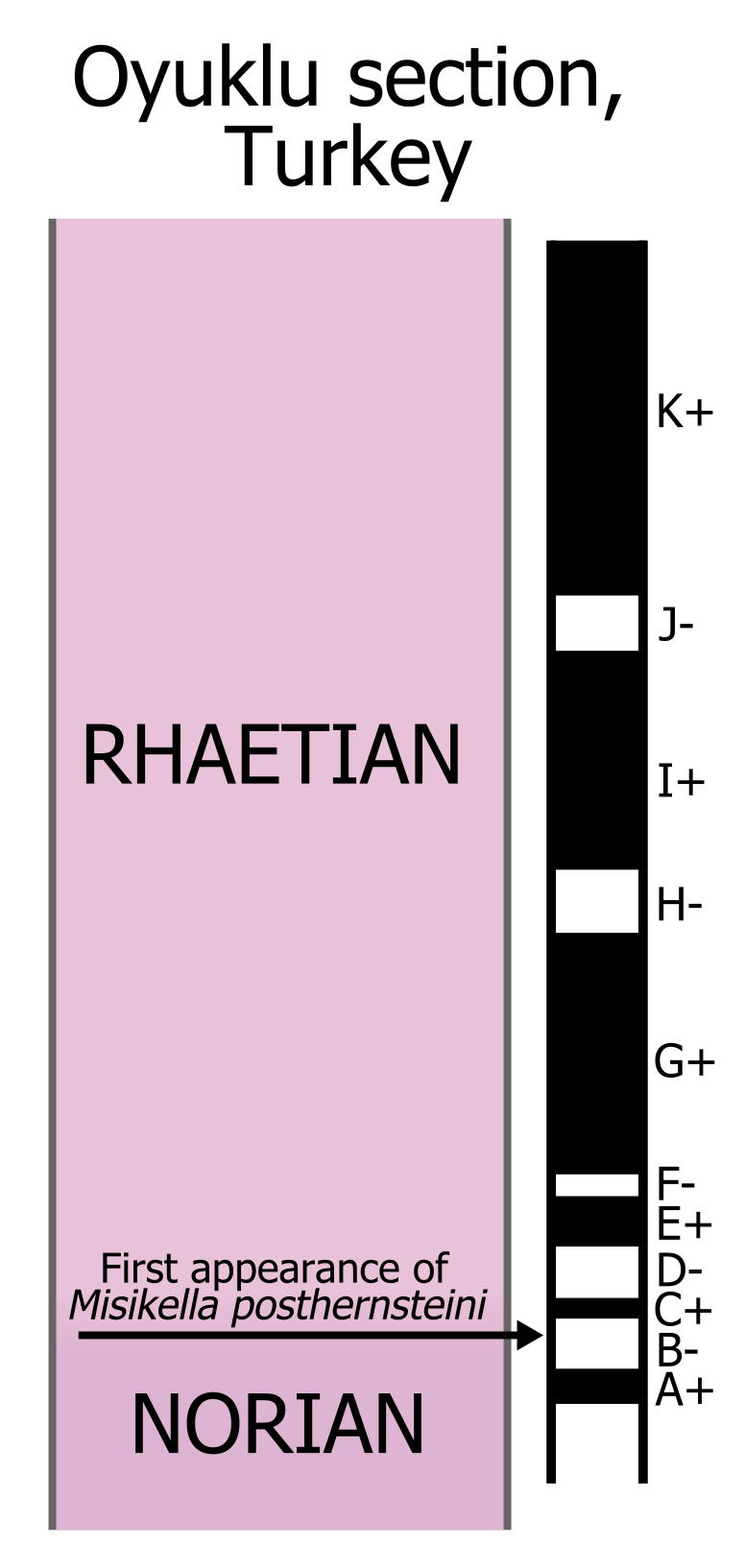
Rhaetian
The Rhaetian is the latest age of the Triassic Period (in geochronology) or the uppermost stage of the Triassic System (in chronostratigraphy). It was preceded by the Norian and succeeded by the Hettangian (the lowermost stage or earliest age of the Jurassic). The base of the Rhaetian lacks a formal GSSP, though candidate sections include Steinbergkogel in Austria (since 2007) and Pignola-Abriola in Italy (since 2016). The end of the Rhaetian (and the base of the overlying Hettangian Stage) is more well-defined. According to the current ICS (International Commission on Stratigraphy) system, the Rhaetian ended ± 0.2 Ma (million years ago). In 2010, the base of the Rhaetian (i.e. the Norian-Rhaetian boundary) was voted to be defined based on the first appearance of '' Misikella posthernsteini'', a marine conodont. However, there is still much debate over the age of this boundary, as well as the evolution of ''M. posthernsteini''. The most comprehensive source of precise age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids (reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their amp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleming Fjord Formation
The Fleming Fjord Formation, alternatively called the Fleming Fjord Group is an Upper Triassic geological formation in the northeastern coast of Jameson Land, Greenland. It consists of terrestrial sediments and is known for its fossil content. Description It is of Norian to Rhaetian age and is subdivided into three members; at the base the Edderfugledal Member, followed by the Malmros Klint Member with the Ørsted Dal Member at the top. It was deposited in a large shallow to ephemeral lake. Paleobiota The fauna of Fleming Fjord is diverse, including sauropodomorph dinosaurs, pterosaurs, temnospondyls, mammaliaforms, aetosaurs, and other taxa. Freshwater unionid bivalves and conchostracans have been reported from the Malmros Klint Member. Fish Lungfish, actinopterygian, and chondrichthyan teeth have been reported from the Malmros Klint Member. Amphibians Reptiles Besides the forms described below, a diverse ichnofauna of small and large tracks has also been reported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch of the Triassic Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone'')'', the middle Muschelkalk (shell-bearing limestone) and the upper Keuper (coloured clay). The Late Triassic Series co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epochs of the Triassic period or the middle of three series in which the Triassic system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Early Triassic Epoch and followed by the Late Triassic Epoch. The Middle Triassic is divided into the Anisian and Ladinian ages or stages. Formerly the middle series in the Triassic was also known as Muschelkalk. This name is now only used for a specific unit of rock strata with approximately Middle Triassic age, found in western Europe. Middle Triassic fauna Following the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the most devastating of all mass-extinctions, life recovered slowly. In the Middle Triassic, many groups of organisms reached higher diversity again, such as the marine reptiles (e.g. ichthyosaurs, sauropterygians, thallatosaurs), ray-finned fish and many invertebrate groups like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gipsdalen Formation
Gipsdalen is a valley in Bünsow Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It has a length of about 22 kilometers. The river Gipsdalselva flows through the valley and debouches into Gipsvika in Sassenfjorden. At the western side of the valley are Norströmfjellet, Meakinsfjellet, Grahamkammen, Usherfjellet and Gipshuken. References Valleys of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Triassic span the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |