|
Schwinger Effect
The Schwinger effect is a predicted physical phenomenon whereby matter is created by a strong electric field. It is also referred to as the Sauter–Schwinger effect, Schwinger mechanism, or Schwinger pair production. It is a prediction of quantum electrodynamics (QED) in which electron– positron pairs are spontaneously created in the presence of an electric field, thereby causing the decay of the electric field. The effect was originally proposed by Fritz Sauter in 1931 and further important work was carried out by Werner Heisenberg and Hans Heinrich Euler in 1936, though it was not until 1951 that Julian Schwinger gave a complete theoretical description. The Schwinger effect can be thought of as vacuum decay in the presence of an electric field. Although the notion of vacuum decay suggests that something is created out of nothing, physical conservation laws are nevertheless obeyed. To understand this, note that electrons and positrons are each other's antiparticles, with iden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwinger Pair Production
The Schwinger effect is a predicted physical phenomenon whereby matter is created by a strong electric field. It is also referred to as the Sauter–Schwinger effect, Schwinger mechanism, or Schwinger pair production. It is a prediction of quantum electrodynamics (QED) in which electron–positron pairs are spontaneously created in the presence of an electric field, thereby causing the decay of the electric field. The effect was originally proposed by Fritz Sauter in 1931 and further important work was carried out by Werner Heisenberg and Hans Heinrich Euler in 1936, though it was not until 1951 that Julian Schwinger gave a complete theoretical description. The Schwinger effect can be thought of as vacuum decay in the presence of an electric field. Although the notion of vacuum decay suggests that something is created out of nothing, physical conservation laws are nevertheless obeyed. To understand this, note that electrons and positrons are each other's antiparticles, with identic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perturbation Theory (quantum Mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, perturbation theory is a set of approximation schemes directly related to mathematical perturbation for describing a complicated quantum system in terms of a simpler one. The idea is to start with a simple system for which a mathematical solution is known, and add an additional "perturbing" Hamiltonian representing a weak disturbance to the system. If the disturbance is not too large, the various physical quantities associated with the perturbed system (e.g. its energy levels and eigenstates) can be expressed as "corrections" to those of the simple system. These corrections, being small compared to the size of the quantities themselves, can be calculated using approximate methods such as asymptotic series. The complicated system can therefore be studied based on knowledge of the simpler one. In effect, it is describing a complicated unsolved system using a simple, solvable system. Approximate Hamiltonians Perturbation theory is an important tool for de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
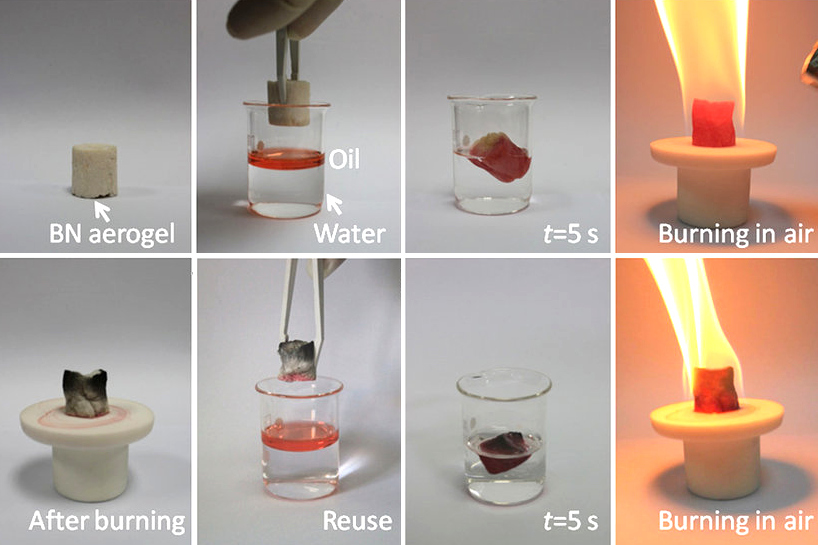
Boron Nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula BN. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal form corresponding to graphite is the most stable and soft among BN polymorphs, and is therefore used as a lubricant and an additive to cosmetic products. The cubic ( zincblende aka sphalerite structure) variety analogous to diamond is called c-BN; it is softer than diamond, but its thermal and chemical stability is superior. The rare wurtzite BN modification is similar to lonsdaleite but slightly softer than the cubic form. Because of excellent thermal and chemical stability, boron nitride ceramics are used in high-temperature equipment and metal casting. Boron nitride has potential use in nanotechnology. Structure Boron nitride exists in multiple forms that differ in the arrangement of the boron and nitrogen atoms, giving rise to varyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superlattice
A superlattice is a periodic structure of layers of two (or more) materials. Typically, the thickness of one layer is several nanometers. It can also refer to a lower-dimensional structure such as an array of quantum dots or quantum wells. Discovery Superlattices were discovered early in 1925 by Johansson and Linde after the studies on gold-copper and palladium-copper systems through their special X-ray diffraction patterns. Further experimental observations and theoretical modifications on the field were done by Bradley and Jay, Gorsky, Borelius, Dehlinger and Graf, Bragg and Williams and Bethe. Theories were based on the transition of arrangement of atoms in crystal lattices from disordered state to an ordered state. Mechanical properties J.S. Koehler theoretically predicted that by using alternate (nano-)layers of materials with high and low elastic constants, shearing resistance is improved by up to 100 times as the Frank–Read source of dislocations cannot operate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirac Point
Dirac cones, named after Paul Dirac, are features that occur in some electronic band structures that describe unusual electron transport properties of materials like graphene and topological insulators. In these materials, at energies near the Fermi level, the valence band and conduction band take the shape of the upper and lower halves of a conical surface, meeting at what are called Dirac points. Description In quantum mechanics, Dirac cones are a kind of crossing-point which electrons avoid, where the energy of the valence and conduction bands are not equal anywhere in two dimensional lattice -space, except at the zero dimensional Dirac points. As a result of the cones, electrical conduction can be described by the movement of charge carriers which are massless fermions, a situation which is handled theoretically by the relativistic Dirac equation. The massless fermions lead to various quantum Hall effects, magnetoelectric effects in topological materials, and ultr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Hole
In physics, chemistry, and electronic engineering, an electron hole (often simply called a hole) is a quasiparticle which is the lack of an electron at a position where one could exist in an atom or atomic lattice. Since in a normal atom or crystal lattice the negative charge of the electrons is balanced by the positive charge of the atomic nuclei, the absence of an electron leaves a net positive charge at the hole's location. Holes in a metal or semiconductor crystal lattice can move through the lattice as electrons can, and act similarly to positively-charged particles. They play an important role in the operation of semiconductor devices such as transistors, diodes and integrated circuits. If an electron is excited into a higher state it leaves a hole in its old state. This meaning is used in Auger electron spectroscopy (and other x-ray techniques), in computational chemistry, and to explain the low electron-electron scattering-rate in crystals (metals, semiconduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andre Geim
, birth_date = , birth_place = Sochi, Russian SFSR, Soviet Union , death_date = , death_place = , workplaces = , nationality = Dutch and British , fields = Condensed matter physics , doctoral_students = , doctoral_advisor = Victor Petrashov , thesis_title = Investigation of mechanisms of transport relaxation in metals by a helicon resonance method , thesis_year = 1987 , alma_mater = Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology , known_for = , awards = , signature = , signature_alt = , footnotes = , spouse = Irina Grigorieva , website = Sir Andre Konstantin Geim (russian: Андре́й Константи́нович Гейм; born 21 October 1958; IPA1 pronunciation: ɑːndreɪ gaɪm) is a Russian-born Dutch-British physicist working in England in the School of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Manchester. Gei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Graphene Institute
The National Graphene Institute is a research institute and building at the University of Manchester that is focused on the research of graphene. Construction of the building to house the institute started in 2013 and finished in 2015. Institute The creation of the institute, including the construction of the building, cost £61 million. Funded by the Government of the United Kingdom, UK Government (£38m) and the European Union's European Regional Development Fund (£23m), the building is the national centre for graphene research in the UK. It provides facilities for industry and university academics to collaborate on graphene applications and the commercialisation of graphene. The building was opened on 20 March 2015 by George Osborne. Building The five-story glass-fronted building provides of research space. This includes 1,500 square metres (16,000 sq ft) of class 100 and class 1000 clean rooms, one of which occupies the entire lower ground floor (in order to min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Hadron Collider
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world's largest and highest-energy particle collider. It was built by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) between 1998 and 2008 in collaboration with over 10,000 scientists and hundreds of universities and laboratories, as well as more than 100 countries. It lies in a tunnel in circumference and as deep as beneath the France–Switzerland border near Geneva. The first collisions were achieved in 2010 at an energy of 3.5 teraelectronvolts (TeV) per beam, about four times the previous world record. After upgrades it reached 6.5 TeV per beam (13 TeV total collision energy). At the end of 2018, it was shut down for three years for further upgrades. The collider has four crossing points where the accelerated particles collide. Seven detectors, each designed to detect different phenomena, are positioned around the crossing points. The LHC primarily collides proton beams, but it can also accelerate beams of heavy ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Monopole
In particle physics, a magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). A magnetic monopole would have a net north or south "magnetic charge". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence. The known elementary particles that have electric charge are electric monopoles. Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets is not caused by magnetic monopoles, and indeed, there is no known experimental or observational evidence that magnetic monopoles exist. Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles. Historical background Early science and classical physics Many early scientists attributed the magnetism of lodestones to two different "magnetic fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Dual
In physics, the electromagnetic dual concept is based on the idea that, in the static case, electromagnetism has two separate facets: electric fields and magnetic fields. Expressions in one of these will have a directly analogous, or dual, expression in the other. The reason for this can ultimately be traced to special relativity where applying the Lorentz transformation to the electric field will transform it into a magnetic field. These are special cases of duality in mathematics. * The electric field (E) is the dual of the magnetic field (H). * The electric displacement field (D) is the dual of the magnetic flux density (B). * Faraday's law of induction is the dual of Ampère's circuital law. * Gauss's law for electric field is the dual of Gauss's law for magnetism. * The electric potential is the dual of the magnetic potential. * Permittivity is the dual of permeability. * Electrostriction is the dual of magnetostriction. * Piezoelectricity is the dual of piezomagnetism. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extreme Light Infrastructure
The Extreme Light Infrastructure (ELI) is an international series of physics laboratories for generating and studying intense laser light. It is part of the European ESFRI Roadmap. ELI hosts the most intense beamline system worldwide, develop new interdisciplinary research opportunities with light from these lasers and secondary radiation derived from them, and make them available to the international scientific user community. ELI aims to be the world's biggest and first international user facility in beamline and laser research. The facility will be based on four sites. Three of them are presently being implemented in the Czech Republic, Hungary and Romania, with an investment volume exceeding €850 million, mostly stemming from the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF). In Dolní Břežany, near Prague, Czech Republic, the ELI Beamlines facility is developing short-pulse secondary sources of radiation and particles. The ELI Attosecond Light Pulse Source (ELI-ALPS) in Szeged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |